![]() Temperatures around the world are soaring. Both California’s Death Valley and China’s Xinjiang region have seen temperatures climb above the 50°C mark. A blistering heatwave is also sweeping across the Mediterranean, causing temperatures in parts of Italy, Spain, France, and Greece to exceed 40°C.
Temperatures around the world are soaring. Both California’s Death Valley and China’s Xinjiang region have seen temperatures climb above the 50°C mark. A blistering heatwave is also sweeping across the Mediterranean, causing temperatures in parts of Italy, Spain, France, and Greece to exceed 40°C.
In the future, the impact of scorching temperatures will extend beyond traditionally warm regions. In fact, our new research indicates that, if global temperature rise increases from 1.5°C to 2°C, countries at northern latitudes like the UK, Norway, Finland and Switzerland will face the greatest relative increase in uncomfortably hot days.
During uncomfortably hot weather, people seek ways to cool down their homes. Air conditioners often become the default solution when temperatures rise as they provide fast and effective relief from scorching heat.
But air conditioners consume a lot of energy. Many also use refrigerants called fluorinated gases that have high global warming potential when they leak.
Unrestrained usage of air conditioners in the future will result in increased emissions and further global warming. So it’s important to know the recommended steps to keep your home cool in the face of rising temperatures, without causing the climate more harm.
Block the sun
Buildings can be protected from too much heat by creating a barrier between them and the sun’s rays. There are different ways to achieve this, ranging from reflective and ventilated roofs to external window shutters and awnings. Research one of us worked on in Spain found that using external window shutters can reduce cooling needs (the thermal energy required to keep people comfortable) by up to 14 percent.
Even something as simple as painting your roof a light colour can reduce indoor temperatures. Research in very hot cities in Pakistan found that, by reflecting the sun’s energy, this approach can reduce cooling needs by more than 7 percent.
Another effective technique is to make use of the shade provided by tree canopies. Research in Melbourne, Australia, has shown that trees covering buildings in shade can lower the surface temperature of walls by up to 9°C.
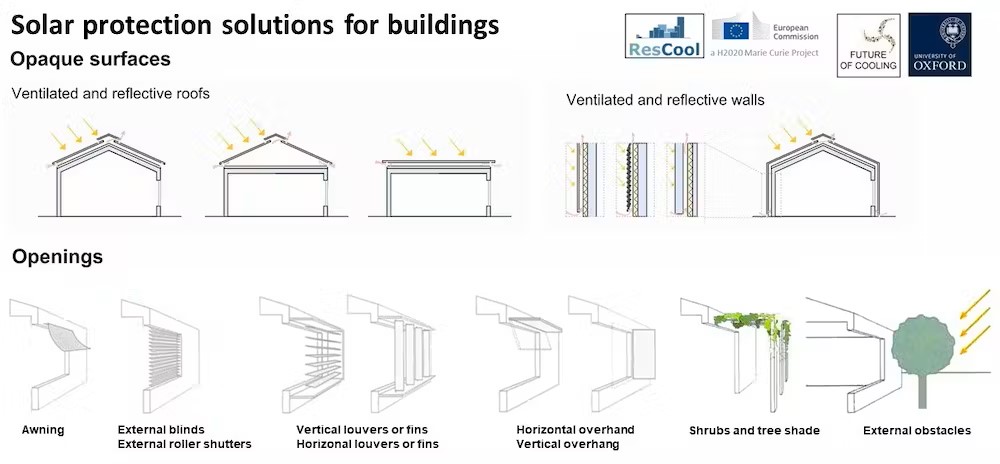
How to protect a building from the sun.
Image credit: Jesus Lizana, Author provided
Use natural ventilation
One effective way to cool down a poorly ventilated building, is to open windows when the outside temperature drops. This lets warm air escape and invites cooler air in.
But additional features, such as ventilation chimneys and roof vents, can be incorporated into building design to further assist airflow. These features are often found in hot and arid climates, particularly in the Middle East. Historically, buildings in this region made use of tall, chimney-like structures called wind catchers that capture cool prevailing winds and redirect them into homes. Ventilating a building with cool air at night can also keep it cool for longer during the day.
Buildings can also be “cross ventilated”, where a fresh breeze enters through an opening and exits through another on the opposite side. If necessary, this can be promoted by incorporating inner courtyards – a design that has been used for centuries in warmer climates to keep buildings cool.
Our previous research found that inner courtyards can reduce the total amount of time in which we need to take measures to cool down (known as indoor discomfort hours) by 26 percent.
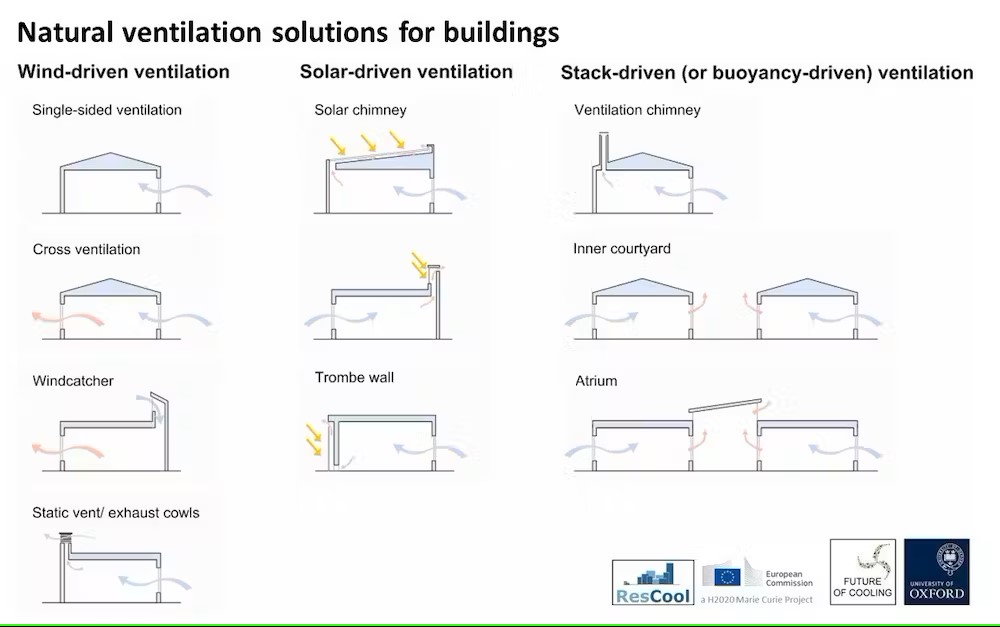
Natural ventilation techniques for buildings.
Cooling beyond temperature control
Our perception of coolness is not solely determined by temperature. Factors like humidity and air speed also play a role in how comfortable we feel.
That’s where fans come in handy, whether they’re on the ceiling or standing on their own. By combining fans with air conditioning, it’s possible to raise the thermostat setting from 24°C to 27°C and still feel cool. This simple adjustment can reduce household energy consumption for cooling by more than 20 percent.
Centralised air conditioning systems also often end up cooling us down more than necessary or even waste energy by cooling empty rooms. But we can tackle this by combining more relaxed cooling settings, like raising the thermostat, with personal cooling devices such as desk fans, cooled seats or wearable thermoelectric coolers. These devices allow people to have more control of their immediate cooling needs without having to cool down an entire space.
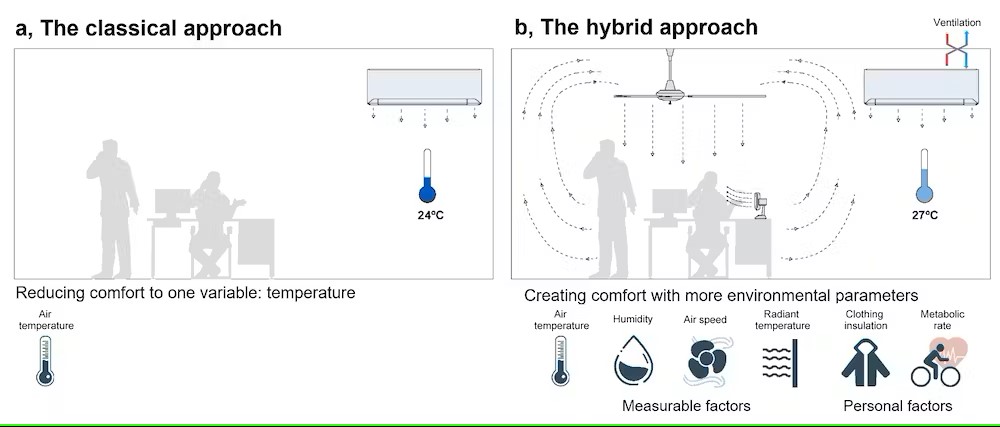
(a) Keeping cool only by temperature control; (b) using all thermal comfort variables.
When air conditioning still remains necessary, choose units with a high efficiency rating using refrigerants with low global-warming potential. To figure out how efficient they are, there’s an indicator called the energy efficiency ratio (ERR) – you’ll want to pick a unit with an ERR that’s close to or above four.
When designing or adapting buildings, it’s essential to consider the overall heating and cooling demands. For example, maximising ventilation can prevent overheating during summer, but minimising ventilation can help reduce the need for heating during winter.
The key is to find solutions that work well together and can be adapted easily so that the cost of installing energy-intensive air-conditioning systems can be avoided or reduced. This approach will allow people to stay comfortable during hotter temperatures, without compromising the climate further for future generations.
Jesus Lizana, Marie-Curie Research Fellow, Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford; Nicole Miranda, Senior Researcher and College Lecturer in Engineering, University of Oxford, and Radhika Khosla, Associate Professor, Smith School of Enterprise and Environment, University of Oxford
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source Link: How To Make Homes Cooler Without Cranking Up The Air Conditioning