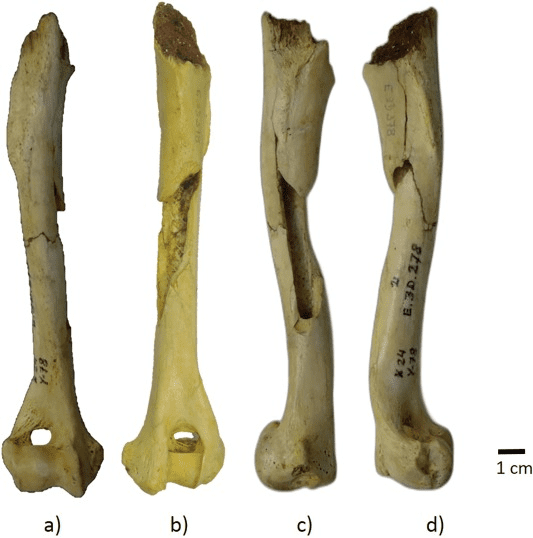
An ancient humerus recovered from Erralla Cave in the Basque Country, Spain, is thought to be the earliest domesticated dog remains ever found in Europe. Dating back to around 17,410 and 17,096 years ago, it topples the previous title holder remains that were found in Germany, and estimated to be nearer 15,114 to 14,237 years old.
The Erralla Cave remains were retrieved from the Lower Magdalenian level of the dig site, a time in which the Magdalenian cultures of the Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic were kicking about in western Europe. Their stretch is thought to have sat between 17,000 and 12,000 years ago, showing the newly reported bones are some of the oldest remains from the period.
Researchers investigating the humerus used several approaches to assess the bones and work out what species it belonged to. One technique was radiocarbon dating which uses carbon-14, a naturally occurring and radioactive form of carbon. It decays over time, meaning scientists can date objects by testing how much the ratio of carbon-14 to nonradioactive carbon has changed.
They were then able to look at the genetic and morphological characteristics of the humerus to try and work out if it were dog or wolf, something that’s easier said than done as the domestication of dogs saw a transitionary period between the two. Fortunately, they were able to arrive at an answer.
“Our results confirm the identification of this specimen as Canis lupus familiaris,” wrote the study authors, who say the data indicates “that the Erralla specimen represents one of the earliest domesticated dogs in Europe”.
The mitochondrial lineage of the specimen points to an emergence for the species of around 22,000 years ago, during a period of cold climate that lined up with the Last Glacial Maximum. It raises interesting questions about exactly when humans and canines teamed up, at least in Europe, as they point to an earlier time for the emergence of domesticated dogs here than previously thought.
“These results raise the possibility that wolf domestication occurred earlier than proposed until now, at least in western Europe, where the interaction of Palaeolithic hunter-gatherers with wild species, such as the wolf, may have been boosted in areas of glacial refuge (such as the Franco-Cantabrian) during this period of climate crisis,” concluded study co-author Conchi de la Rúa, head of the Human Evolutionary Biology group at the University of the Basque Country, in a statement.
The study was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
Source Link: Humerus Bone Reveals Oldest Known Remains Of Domesticated Dogs In Europe