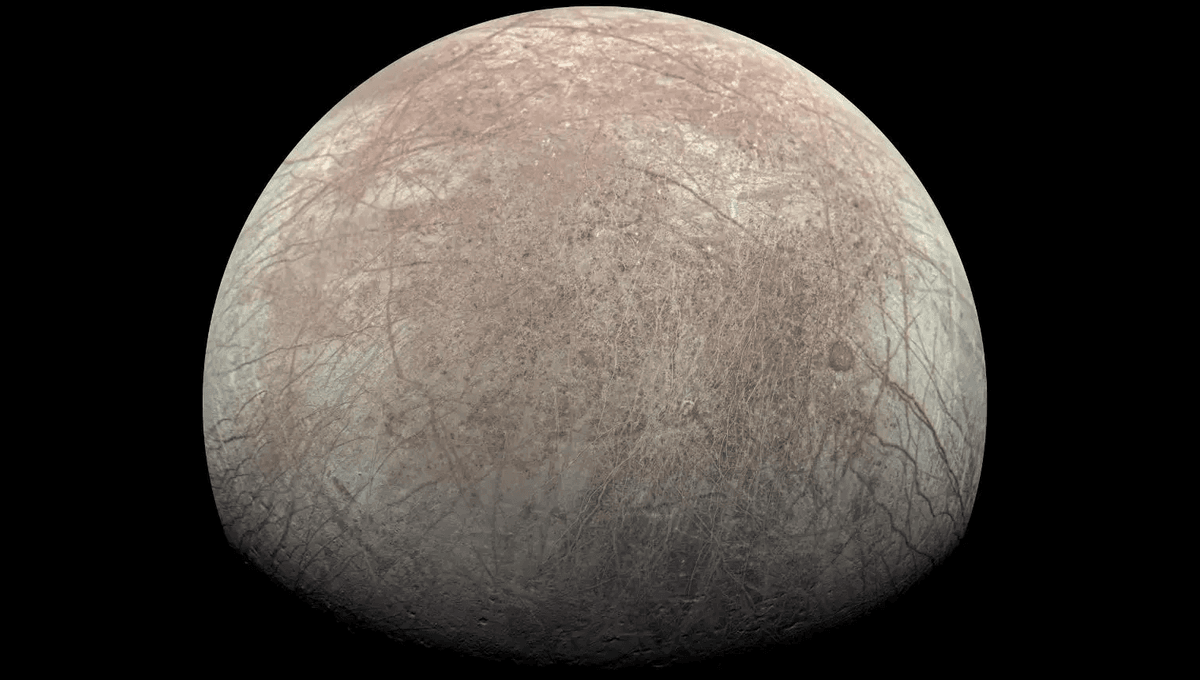
The icy moons of gas giant planets are considered a possible place for the formation of life beyond Earth. Enceladus and Europa have deep oceans with intriguing chemistry buried below an outer shell of ice many kilometers thick. We can’t simply go drilling through such an icy shell. But we might not need to dig deeply to find evidence of life.
New research looks at how these biosignatures might survive in ice under the radiation exposure that exists around both Jupiter’s Europa and Saturn’s Enceladus. They found that while amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, degrade over time in such conditions, being trapped in ice allows them to survive for eons, especially from within biological sources.
“Based on our experiments, the ‘safe’ sampling depth for amino acids on Europa is almost 8 inches (around 20 centimeters) at high latitudes of the trailing hemisphere (hemisphere opposite to the direction of Europa’s motion around Jupiter) in the area where the surface hasn’t been disturbed much by meteorite impacts,” lead author Alexander Pavlov of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, said in a statement.
“Subsurface sampling is not required for the detection of amino acids on Enceladus – these molecules will survive radiolysis (breakdown by radiation) at any location on the Enceladus surface less than a tenth of an inch (under a few millimeters) from the surface.”
The experiment focuses on the breakdown of amino acids through radiolysis. It measured this breakdown in amino acids (on their own) in ice or in a mixture of ice and dust, as well as within dead bacteria (in this case E. Coli). They found that the one in dead bacteria had a slower decline in degradation.
“Slow rates of amino acid destruction in biological samples under Europa and Enceladus-like surface conditions bolster the case for future life-detection measurements by Europa and Enceladus lander missions,” said Pavlov. “Our results indicate that the rates of potential organic biomolecules’ degradation in silica-rich regions on both Europa and Enceladus are higher than in pure ice and, thus, possible future missions to Europa and Enceladus should be cautious in sampling silica-rich locations on both icy moons.”
A paper discussing this research is published in the journal Astrobiology.
Source Link: If There's Life On Icy Moons, We Don’t Need To Dig Deep To Find It