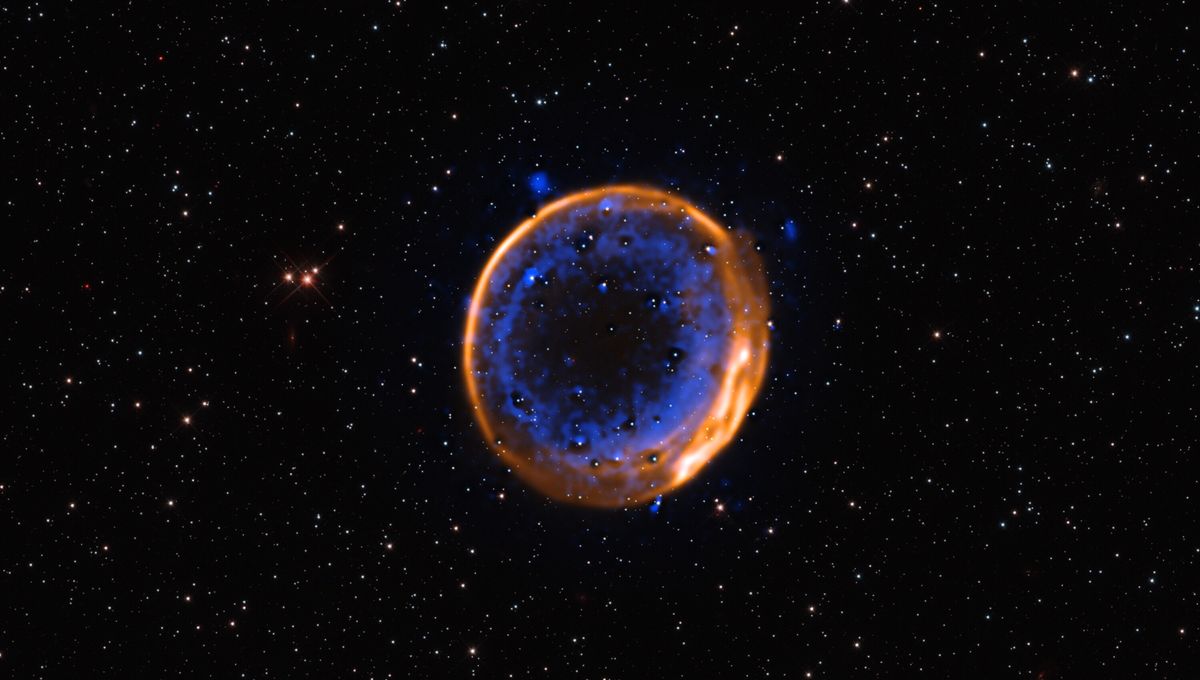
Astronomers have finally found evidence for a proposed mechanism for a special kind of supernova, known as a Type Ia supernova. It was proposed that at least some of them experience a double detonation, and now they have found evidence that this is indeed the case.
The Sun will never go supernova; it’s not massive enough. It will run out of hydrogen to fuse and then become a red giant, fusing helium. Once the helium runs out, its core will contract and it will shed its outer layers. That core will become a white dwarf. Other white dwarfs have companions, and if they have a chance to steal material from a companion, they can go supernova.
This is a Type Ia supernova. Once a white dwarf gets to 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, beyond what is known as the Chandrasekhar mass limit, it goes supernova. Given that the mass is roughly always the same, it produces a supernova with a standard luminosity. This is why they are so important. Knowing how intrinsically bright this event is, astronomers use them as a cosmic milestone to work out cosmic distances.
The idea is that some white dwarfs get covered in a blanket of stolen helium, which becomes unstable and detonates, creating shockwaves across the white dwarf. This triggers a second and fatal explosion as the whole white dwarf explodes into a supernova. Recent predictions suggested that both detonations produce calcium, which would be arranged into two shells as the material is thrown out from the expanding explosions.
This is what the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) has found around the centuries-old supernova remnant SNR 0509-67.5.
“This tangible evidence of a double-detonation not only contributes towards solving a long-standing mystery, but also offers a visual spectacle,” lead author Priyam Das, a PhD student at the University of New South Wales Canberra, said in a statement.
“[The findings show] a clear indication that white dwarfs can explode well before they reach the famous Chandrasekhar mass limit, and that the ‘double-detonation’ mechanism does indeed occur in nature,” added co-author Ivo Seitenzahl, from Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies, who led the observations.
Given the importance of the Type Ia supernova in measuring cosmic distances, which play a role in establishing how the universe expands, understanding these events better improves the rest of the field. These observations are very important.
A paper describing them is published in Nature Astronomy.
Source Link: Incredible Supernova Finding Shows That “Double-Detonation Mechanism” Happens In Nature