A path has been sketched for how molecules needed for life could have formed on Mars in the days when it was wet. We don’t know if this happened, or that it led to life, let alone whether any survived. Nevertheless, the work suggests that anyone thinking of giving up on the prospects of a living neighbor should hold onto hope a little longer.
The presence of liquid water is considered the single most important condition for life to exist, and we know Mars had that for at least 200 million years. Organic compounds that can serve as the building blocks for RNA or something similar are also essential. Some of these have been found in meteorites, which hit Mars even more frequently than Earth, but we don’t currently know if this source could supply all that were needed, and if not whether Mars itself could have supplied them.
This is where new work by Shungo Koyama of Tohoku University and colleagues on the role of formaldehyde comes in. Best known as chemical used to preserve dead specimens, the molecule H2CO is so important as a precursor molecule we produce millions of tons a year of it. According to this work, formaldehyde should have formed, after a few intermediary stages, out of carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Formaldehyde is both soluble in water and reactive. Once absorbed by the Martian ocean, back when there was one, the molecule would have undergone reactions with ammonia and other simple molecules to form amino acids, sugars and other molecules considered “bio-important”. These include ribose, essential to RNA formation.
The capacity of formaldehyde to transform into more complex molecules under water is already established, and particularly through the formose reaction. What is new in this work is the likelihood of its presence in useful quantities.
Koyama and co-authors propose the Martian atmosphere at the time was rich in carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide. The presence of atmospheric hydrogen is inferred from how warm Mars was relative to the amount of sunlight, while the CO and CO2 are anticipated to have come from volcanoes, whose remains can still be seen. Allowing for the effects of sunlight, the team predict this sort of atmosphere would lead to formaldehyde production, which would have then rained out, including into the ocean.
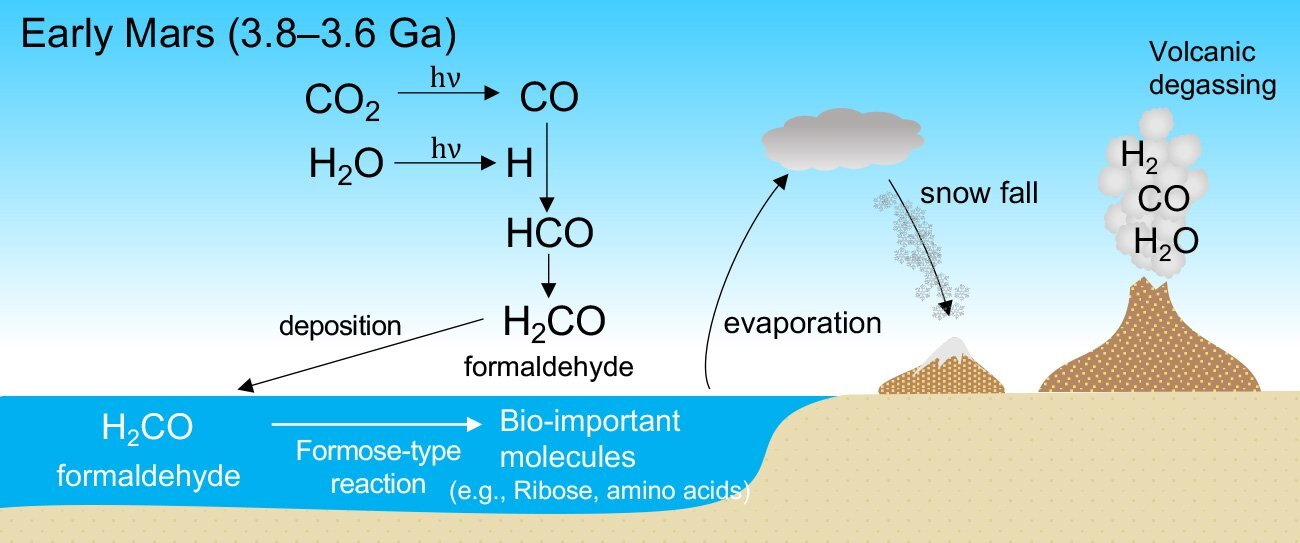
How formaldehyde could have formed in the Martian atmosphere and then turned into molecules essential for life in the ocean.
Image credit: ©Shungo Koyama
The oceans would have experienced evaporation that then fell as snow. This would have concentrated other molecules in the water left behind, making it easier for bio-important chemicals to find each other.
“Our research provides crucial insights into the chemical processes that may have occurred on ancient Mars, offering valuable clues to the possibility of past life on the planet,” Koyama said in a statement. Quite how much formaldehyde would have formed depends on the ratio of gases in the atmosphere, but it is likely at times it would have been substantial.
The theory is all well and good, but more important is to find out if this happened. With decades of data from Martian landers and rovers, the team plan to search through records for the isotopic ratios of carbon in surviving organic molecules. These could indicate the likelihood the molecules formed via this route rather than non-atmospheric alternatives.
The study is published open access in Scientific Reports.
Source Link: Instead Of Preserving The Dead, Formaldehyde On Mars Could Have Started Life