Astronomers are getting unprecedented details of supernova explosions and supermassive black holes thanks to a new space telescope. The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM)launched a year ago and researchers have now published its first scientific results – and they are very good.
XRISM – pronounced crism – is a mission led by the Japanese Space Agency (JAXA) with the support of NASA and the involvement of the European Space Agency (ESA). With the aging and defunding by NASA of Chandra (and just the aging of ESA’s XMM-Newton), there was a risk of having a gap in X-ray observations before ESA’s ATHENA was launched since that is still a decade away. XRISM was seen as a stopgap for that, but these initial results, show that is way more than that.
One of the observations is of supernova remnant N132D in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way located 160,000 light-years from Earth. From our point of view, it exploded 3,000 years ago and now XRISM was able to see some of its more salient details.
First of all, the explosion did not create a spherical shell, but rather something akin to a donut. XRISM was able to measure that the shell of plasma is expanding with an apparent speed of around 1,200 kilometers (750 miles) per second.
That’s not all: The telescope was able to measure the temperature of this plasma. XRISM showed features in the plasma in the millions of degrees, but the most extraordinary and extreme find is the presence of iron at a temperature of ten billion degrees Kelvin. The atoms were heated when the incredible shockwaves of the supernova spread inward. This had been predicted in theory, but had not been observed before. XRISM has 30 times the resolution of its predecessors.
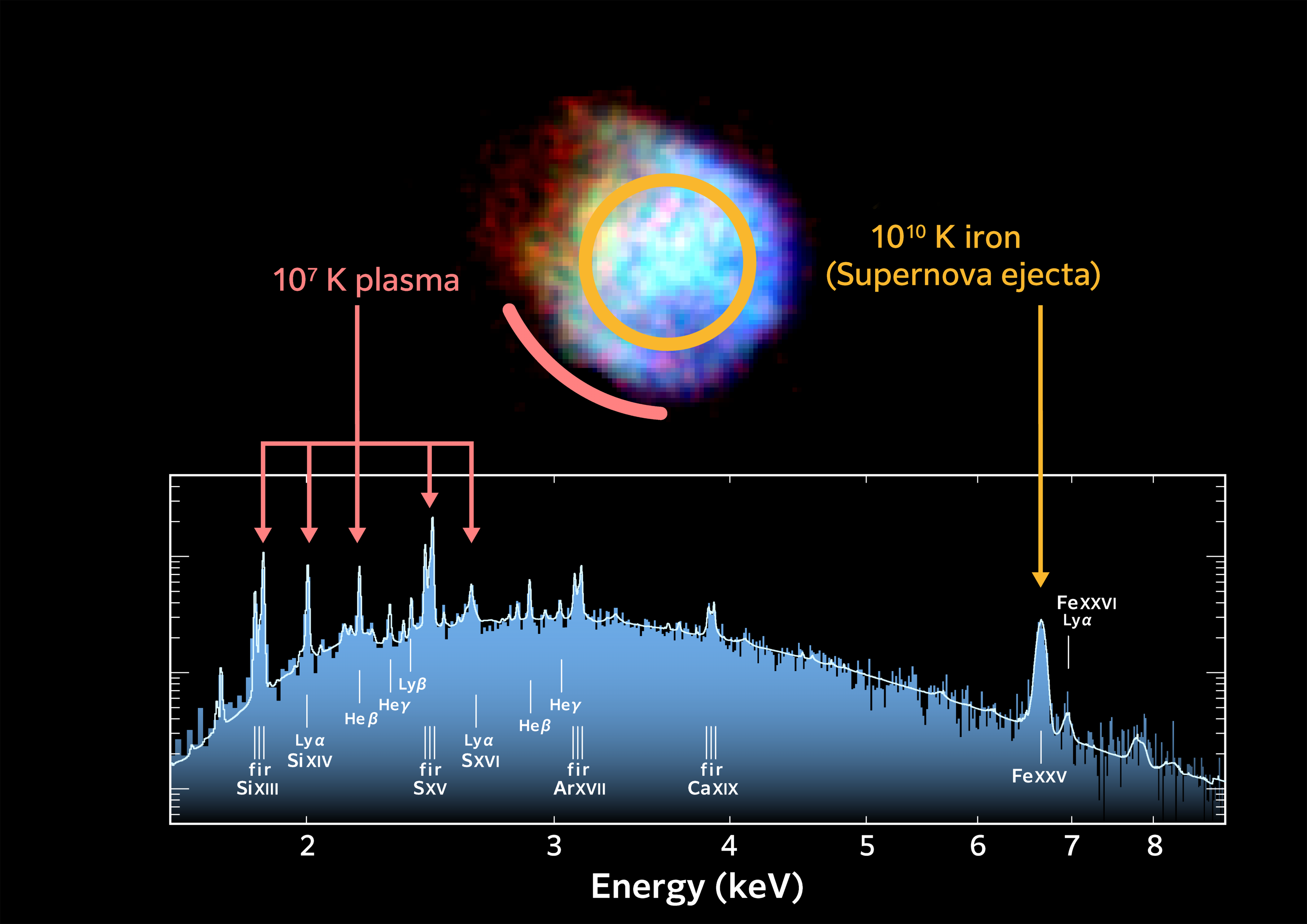
The spectrum of supernova N132D and the elements and temperature of the plasma.
Image Credit: JAXA
If zooming into a supernova is not enough, XRISM’s first results also report on another usual target for X-ray telescopes: an active supermassive black hole. At the center of galaxy NGC 4151, located 62 million light-years away, there is a supermassive black hole with a mass of 30 million suns.
XRISM could tell the distribution of matter around this black hole over a radius of about 0.001 light-years to 0.1 light-years. That’s roughly the same as the Sun-Uranus distance then up to 100 times that. Measuring the motion of this gas will allow astronomers to work out how these gargantuan objects feed and grow, and learn more about them and the galaxies in which they reside.
“These new observations provide crucial information in understanding how black holes grow by capturing surrounding matter, and offer a new insight into the life and death of massive stars. They showcase the mission’s exceptional capability in exploring the high-energy Universe,” ESA XRISM Project Scientist Matteo Guainazzi said in a statement.
These results by the XRISM Collaboration are accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Letters and Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan and are available on arXiv here and here respectively.
Source Link: Iron At 10 Billion Degrees Seen Around Supernova In New Telescope's First Discovery