Two weeks of observations of the Didymos/Dimorphos system have confirmed NASA’s DART mission has substantially changed Dimorphos’s orbit, the first time humans have changed the motion of a natural object in space and altered its orbit forever.
The finding demonstrates that under the right circumstances, smashing a spacecraft into a space rock can be all that is required to deflect a threat. Further investigations continue to improve estimates of what is possible for future cases.
When NASA established the DART mission, the asteroid Dimorphos took 11 hours and 55 minutes to orbit its larger partner. Reducing that by 73 seconds was considered the minimum for the DART mission to be considered a success. Anything less would have indicated either a failure in the mission, such as partially missing the target or some more fundamental obstacle to moving asteroids.
Those worries have been blown apart like the asteroids in Hollywood’s imagining of such missions because post-impact Dimorphos now orbits Didymos in 11 hours and 23 minutes. Not only can we change an asteroid’s orbit, but the force required to do it is a practical one, at least in this case. A 32-minute shift is 25 times that minimum goal.
For the first time ever, humans changed the motion of a celestial object. More details: https://t.co/aQj8N7fnuV pic.twitter.com/NLR6AqEcaO
“This result is one important step toward understanding the full effect of DART’s impact with its target asteroid,” said NASA’s Dr Lori Glaze in a statement. “As new data come in each day, astronomers will be able to better assess whether, and how, a mission like DART could be used in the future to help protect Earth from a collision with an asteroid if we ever discover one headed our way.”
“We conducted humanity’s first planetary defense test, and we showed the world NASA is serious as a defender of this planet,” NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said at a news conference.
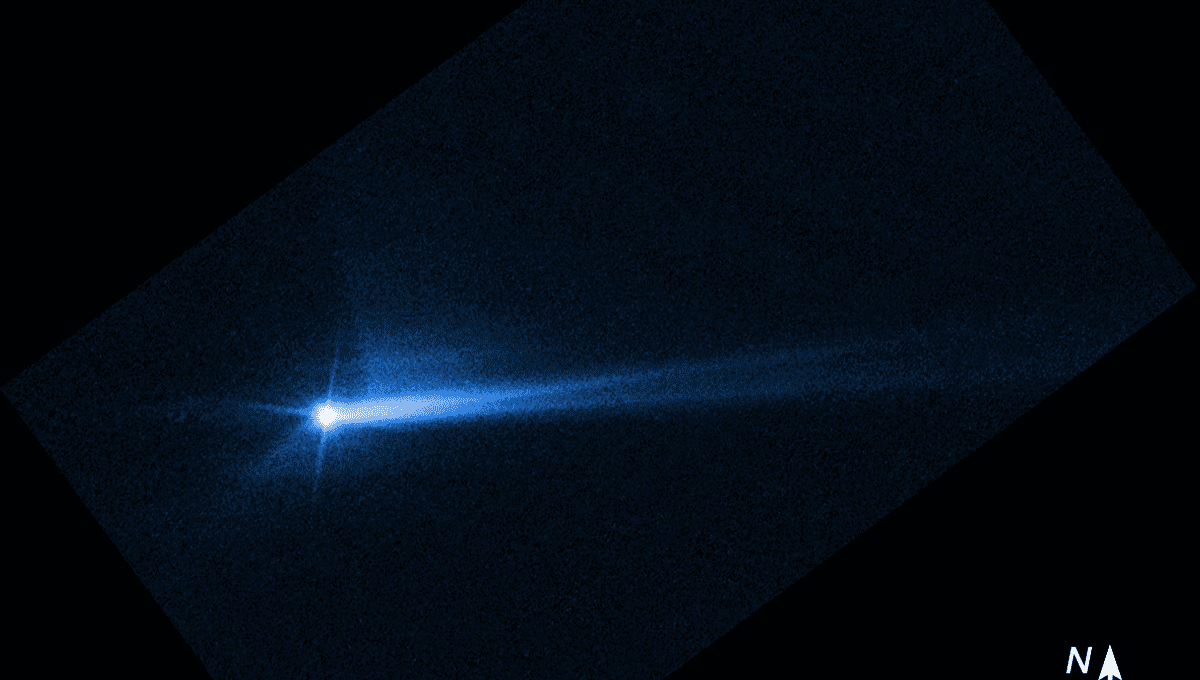
The success of the mission does not make asteroid threats a solved problem. Dimorphos is a small asteroid, just 170 meters (560 feet) across. The “dinokiller” was an estimated 60 times that width, and therefore perhaps 200,000 times as massive. A dinosaur DART would have been a mere fleabite to it, and not one carrying plague.
Moreover, we know from meteorites that asteroids have highly varied compositions, while comets are something different again. What works on one may not succeed for others. We don’t, for example, know how a “rubble pile” asteroid would have responded to an impact like this.
Perhaps we will only settle this question by slamming a lot of spacecraft into different types of asteroids, but for the moment astronomers plan to mine the data from this mission for everything they can get.
That includes working out how much of DART’s 3.5 million kgm/s momentum transferred to Dimorphos, as well as studying the ejecta thrown off in the impact. Newton’s laws say the many tons of rock observed escaping in one direction must have caused the remainder of Dimorphos to recoil, enhancing the orbital change.
In 2026 the European Space Agency’s Hera mission will visit the Didymos/Dimorphos system to examine the aftermath and add some precision to our estimate of the effects.
Neither asteroid represents an imminent threat to Earth. Dimorphos was chosen because its orbit around Didymos made it easy to measure the success or failure of the mission in just this way.
Medieval astronomers thought angels pushed the planets around. Today, we have become those angels.
Source Link: It Worked! DART Changed Asteroid’s Orbit To Shorten It By 32 Minutes