Just like a panting chihuahua and a hot dog, the jet stream and the Gulf Stream can be easily mixed up but are very different.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
The jet stream – or, more accurately, jet streams – are fast-moving currents of air flowing from west to east around the globe, while the Gulf Stream is a specific ocean current of drifting seawater. The two forces are driven by differences in temperature and the Earth’s spin, plus they both impact weather across a wide part of the world, yet they operate in very different ways.
To simplify massively these two highly complex processes: jet streams are the movement of air and the Gulf Stream is the movement of water.
Jet streams = air
Jet streams consist of strong wind currents in the upper levels of the atmosphere around 9,100 meters (30,000 feet) above Earth’s surface.
You’ll often hear the singular term the jet stream, referring to the northern polar jet stream that moves over the middle to northern latitudes of North America and Europe. However, Earth actually has four main jet streams: two polar jet streams near the poles and two subtropical jet streams closer to the equator.
They travel from west to east because of Earth’s spin and the action of the Coriolis force. They’re also driven by heat from the Sun’s energy: the uneven heating of Earth’s surface creates temperature differences between the equator and the poles, leading to pressure gradients that, combined with Earth’s rotation, generate these high-altitude wind currents.
How do jet streams affect airplanes?
Airplanes can fly in the jet stream and can use the band of rapidly rushing air to “hitch a ride” and use less energy. This is why an airplane journey from west to east can often take less time than traveling the same route from east to west.
How do jet streams affect weather?
This form of atmospheric circulation has a huge influence on weather systems.
The strength and position of a jet stream can impact the weather. In winter months, the temperature difference between the poles and the tropics is greater, causing the subtropical jet streams to gain further move strength. This partially explains why the UK is so rainy, especially in the winter months, compared to other parts of the world.
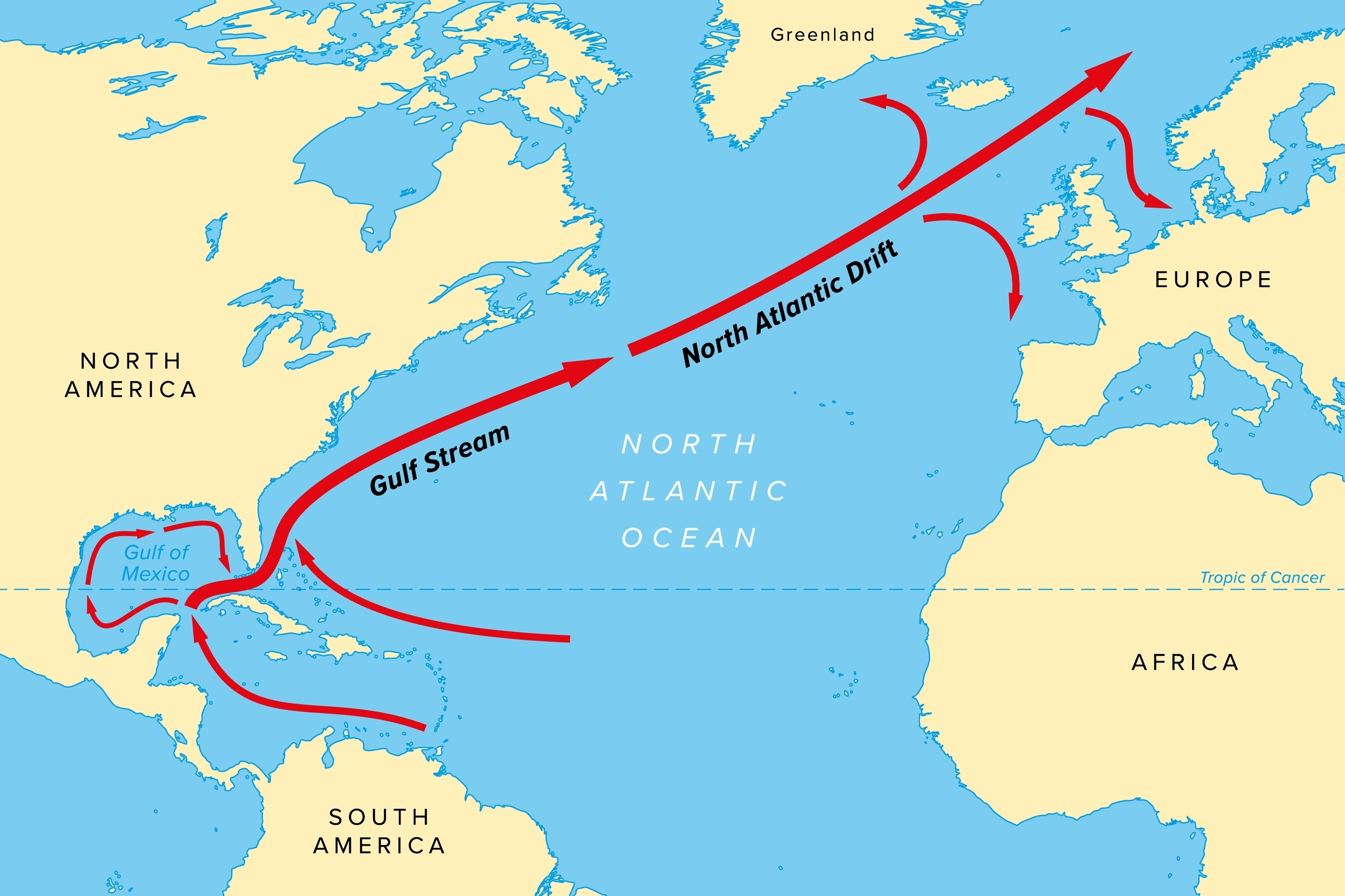
A map of the Atlantic Ocean, showing the movement of water associated with the Gulf Stream.
Image credit: Peter Hermes Furian/Shutterstock.com
Gulf Stream = water
The Gulf Stream has more to do with ocean convection, as opposed to air movement, although there are overlaps.
The Gulf Stream refers to a specific “conveyor belt” of moving water that originates amid the tropical warmth of the Gulf of Mexico (or should we say the Gulf of America now?). The water rides the east coast of North America and moves across the North Atlantic, eventually hitting northern Europe, before recirculating to other parts of the world’s oceans.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
The Gulf Stream is driven by wind patterns blowing from west to east across the Atlantic Ocean, as well as Earth’s rotation – hence why it is sometimes confused with jet streams.
It’s also under the influence of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a large-scale ocean circulation driven by differences in temperature and saltiness. As warm equatorial waters flow toward the poles, they cool and evaporate, increasing salinity. This results in denser water that sinks into the ocean depths, moving slowly until it resurfaces through a process known as “upwelling.”
By carrying warmer water northwards across the Atlantic, it helps make Western Europe’s climate milder than you’d expect for its latitude (although some believe that’s a bit of an oversimplification and argue that atmospheric wind patterns are the main culprit).
The current moves with an average speed of 6.4 kilometers per hour (4 miles per hour). That said, there is emerging evidence that the Gulf Stream has slowed down significantly over the past four decades, very likely because of climate change.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
Some scientists are speculating that the AMOC, the major force underpinning the Gulf Stream, could experience some form of collapse in the next few decades. However, the science isn’t fully settled and complex systems like this are notoriously tricky to predict with absolute certainty.
Source Link: Jet Streams Vs The Gulf Stream: What's The Big Difference?