New observations of the Great Red Spot (GRS), Jupiter’s enormous storm, have revealed that it is less stable than previously thought. Regular observations over the course of 90 days have revealed that its elliptical shape can change dimension, becoming squished in different directions.
The fact that it changes shape is not exactly unexpected. It has certainly diminished in size over the last several years – but the observations between December 2023 and March 2024, have revealed that is also sloshing about, appearing like it’s being pushed and squeezed like a stress ball.
“While we knew its motion varies slightly in its longitude, we didn’t expect to see the size oscillate as well. As far as we know, it’s not been identified before,” lead author Amy Simon, of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said in a statement. “This is really the first time we’ve had the proper imaging cadence of the GRS. With Hubble’s high resolution we can say that the GRS is definitively squeezing in and out at the same time as it moves faster and slower. That was very unexpected, and at present there are no hydrodynamic explanations.”
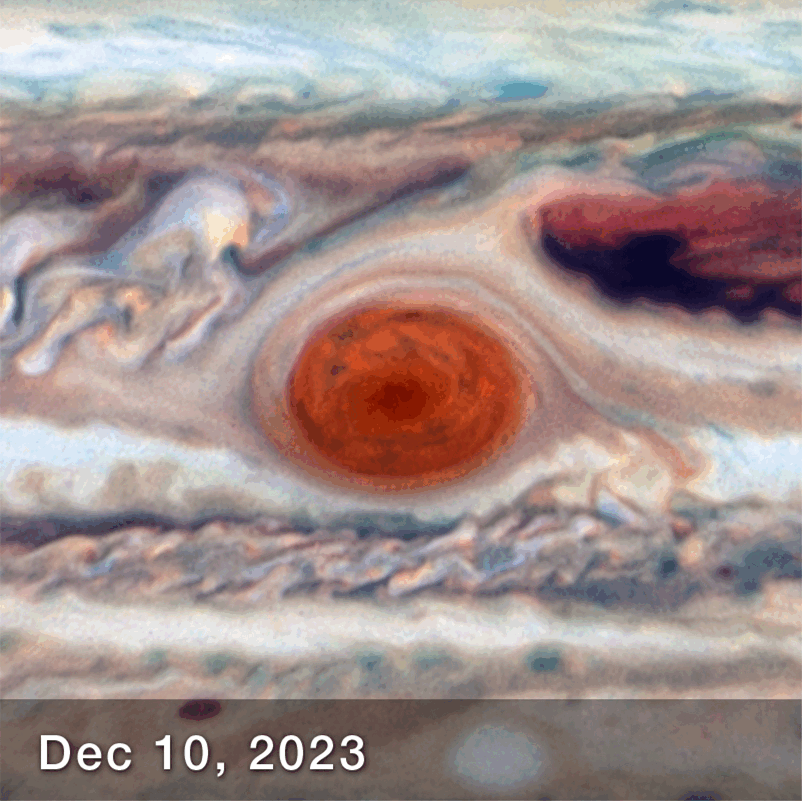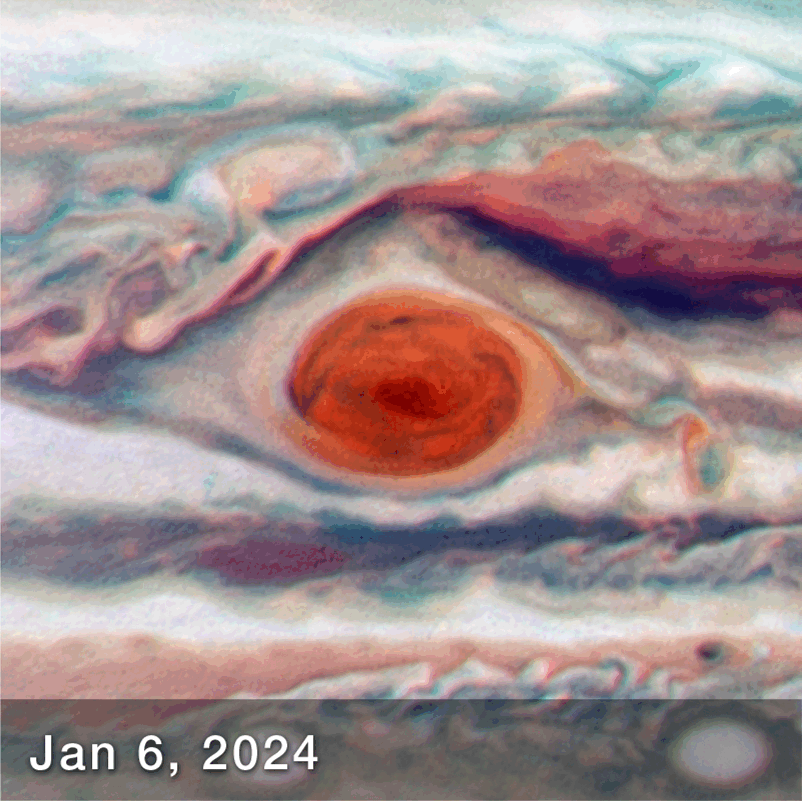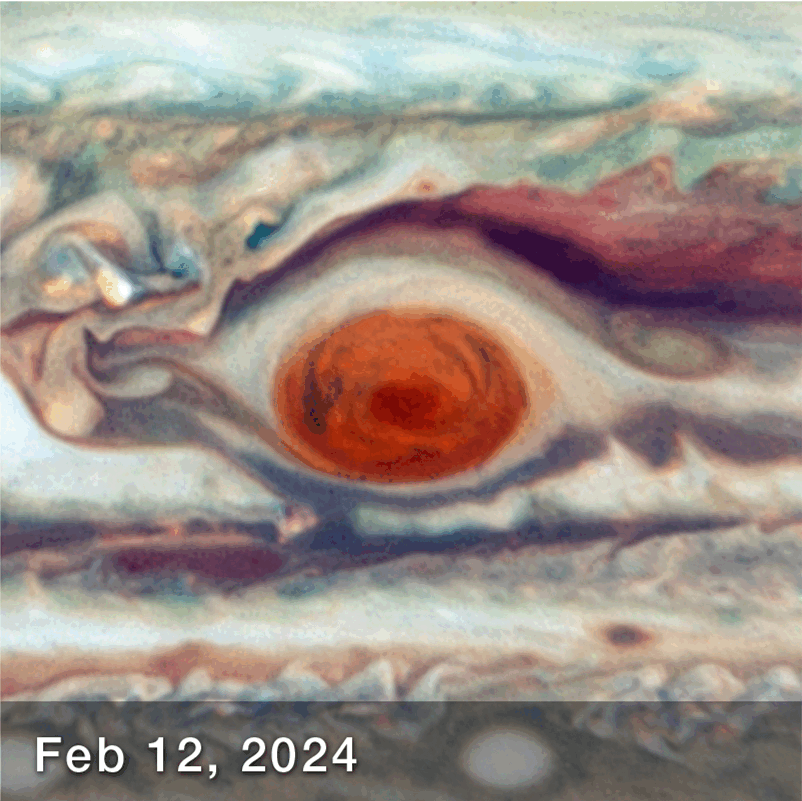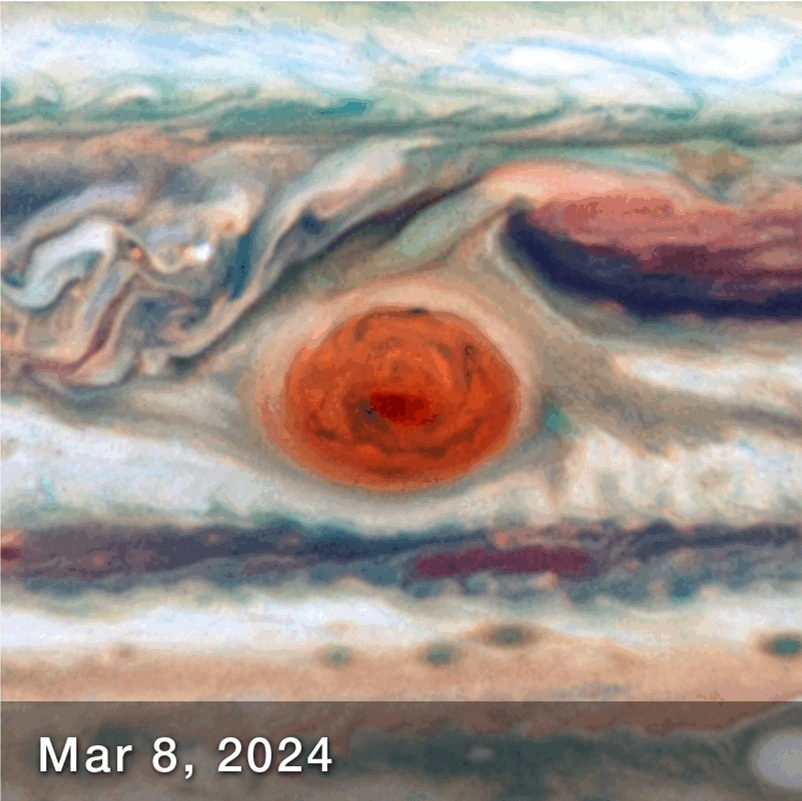
How the Great Red Spot Changed over 90 days.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC)Joseph DePasquale (STScI) – Animated by IFLScience
There are a lot of changes happening day to day – and a lot is going on. Hubble observations in ultraviolet showed that the spot’s core gets the brightest during the moments when the storm is at its largest. This implies that there is less haze. JWST has also looked at the Great Red Spot recently, but there have not been enough continuous observations to discuss changes in the infrared.
“As it accelerates and decelerates, the GRS is pushing against the windy jet streams to the north and south of it,” said co-investigator Mike Wong of the University of California at Berkeley. “It’s similar to a sandwich where the slices of bread are forced to bulge out when there’s too much filling in the middle.”
The GRS has been a feature on Jupiter for at least 150 years, maybe more. Observations from the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy program (OPAL) over the last ten years have highlighted how it might be getting smaller. This might not mean it is going to disappear – the winds that squeeze it might just keep it stable and the same size.
“Right now it’s over-filling its latitude band relative to the wind field. Once it shrinks inside that band the winds will really be holding it in place,” said Simon.
The results are being presented at the 56th annual meeting of the American Astronomical Society Division for Planetary Sciences, in Boise, Idaho, and are published in The Planetary Science Journal.
Source Link: Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Is Wobbling Like Jelly – And We Don't Know Why