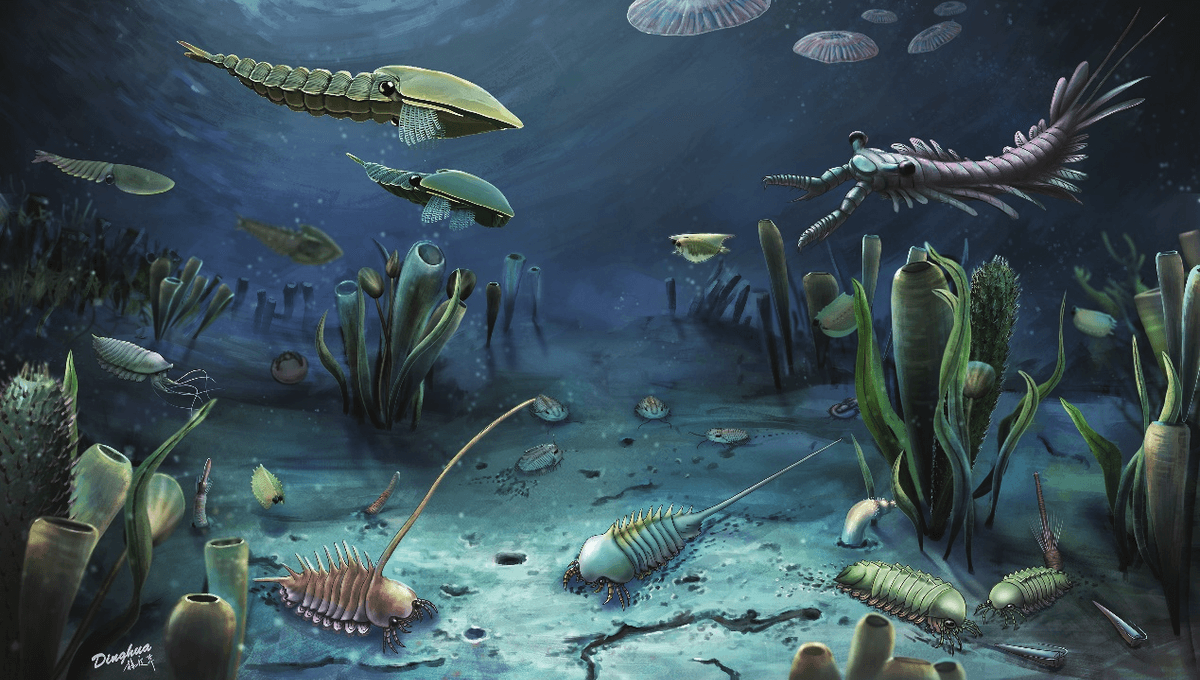
New research shows that the Cambrian explosion, one of the most important interludes in the story of life on Earth, may have been triggered by a small increase in oxygen levels. Using datasets from an international consortium of scientists, the team show that modest changes in oxygen levels may have been enough to cause the major evolutionary leap we see in the fossil record.
What was the Cambrian explosion?
The Cambrian explosion occurred around 540 million years ago and brought with it a rapid burst of evolution, which resulted in greater diversification of life on the planet. Before this, life mostly consisted of single-celled and smaller multicellular organisms. But the fossil record shows that, within 20 to 30 million years – basically a single heartbeat in geological time – we see a huge variety of complex creatures emerging. Each new species has its own strange and novel body plan, with features like mineralized shells, gripping appendages, and sensory organs like eyes.
“The specific animals that we observe as fossils from rocks of this age may look weird and wonderful to us,” Dr Richard Stockey, lead author of the new study and a paleobiologist at the University of Southampton explained to IFLScience, “but the ecological roles they were playing were very similar to marine animals that we know and love today.”
“Unravelling whether there was an environmental trigger to this (geologically) rapid shift in the habitability of Earth’s oceans is a question that is fundamental to our understanding of our biosphere, and even potentially for the habitability of other planets.”
Scientific uncertainty
For decades, scientists believed the Cambrian explosion was kicked off by a sudden surge in atmospheric oxygen that brought oceanic oxygen levels close to what they are today.
However, evidence for this has been limited, scattered, and, in some cases, contradictory.
“As a community, we have been balancing a number of different lines of evidence, based on the chemical composition of ancient sediments,” Stockey added.
“Some of these seemed to indicate a big oxygenation event around the Cambrian explosion, while others seemed to indicate that this scale of oxygenation didn’t occur until around 140 million years later.”
But by conducting a comprehensive, large-scale data analysis, Stockey and colleagues have found that only a small increase in atmospheric oxygen actually occurred at the time of the Cambrian explosion.
We have demonstrated that these changes in ocean oxygenation likely took place at a time where they could have played a key role in the major ecological and evolutionary changes we see during the so-called Cambrian explosion.
Dr Richard Stockey
They did this by analyzing data showing levels of the metals uranium and molybdenum contained in sedimentary rock that formed in low-oxygen environments at the bottom of the world’s ancient oceans. The concentration of these metals in black shale is useful for assessing oceanic oxygen levels, essentially offering a way to investigate them across 700 million years of history.
In the past, studies have found traces of metals in black shale during the Cambrian explosion, but they were based on data collected from sites where local factors can lead to increased levels of metal concentration. But statistical and machine learning techniques allowed Stockey and his team to assess data across a much larger scale and to match it with oceanographic models that give a better picture of historical oxygen levels.
They found that changes in organic carbon in black shale have led to changes in trace metals that researchers have been seeing for the last 15 to 20 years.
“It’s not until 140 million years after the Cambrian explosion, in the Devonian period, that we see trace metals increasing at a rate that would indicate whole ocean oxygenation,” Stockey explained in a statement.
Setting the oxygen record straight
The black shale data were compiled as part of the Sedimentary Geochemistry and Paleoenvironments Project. This is a first-in-its-field research consortium that unites geochemical data in a standardized dataset for collaborative and large-scale analysis.
“Our community-driven approach has been absolutely critical to making this research possible,” Stockey told IFLScience.
“We have found that the environmental conditions in which marine sediments were deposited are often very important in structuring the chemical composition of those sedimentary rocks, impacting the records that geochemists use to reconstruct the oxygenation of the oceans.”
Geologists are specialists at figuring out key environmental changes, but they have limitations.
“[G]eology has historically been quite a descriptive science and descriptive data is often difficult to integrate into state-of-the-art data science and machine learning techniques. By working with the geologists who originally described and collected the specific samples we use in this study, we are able to all use a common language and vocabulary to describe differences between the rocks we use from different geographic locations and time periods.”
With this common vocabulary, researchers can apply sophisticated data science techniques that use this “geological knowledge” to address significant questions like the one being investigated here.
“We have demonstrated that these changes in ocean oxygenation likely took place at a time where they could have played a key role in the major ecological and evolutionary changes we see during the so-called Cambrian explosion. I am really excited to keep investigating the extent to which those changes really did drive these changes,” Stockey concluded.
“I think that we have a lot to learn from researchers who work on the impacts of environmental changes in modern oceans, as well as continuing to develop techniques that translate geological and palaeontological knowledge into powerful datasets that can be rigorously tested with modern data science.”
The study is published in Nature Geoscience.
Source Link: Just A Small Rise In Earth's Oxygen Levels Led To The Cambrian Explosion And Its Evolutionary Leaps