The supernova 1987a left behind a neutron star, and the JWST has finally found it, offering astronomers their best chance to examine the early days of this astronomical phenomenon. Although older supernova remnants within our own galaxy provide much closer opportunities to study matter in its most extreme form, this helps build a picture of the explosion on which we have the most detailed data.
Supernovae formed by the deaths of giant stars produce either neutron stars or black holes, depending on the mass and composition of their progenitor. In 1987, for the first time, we had archival images of the progenitor star before the explosion, and its estimated mass indicated a neutron star was more likely. The length of the neutrino burst that accompanied the explosion – and transformed our knowledge of these cryptic particles – also favored a neutron star.
Astronomers have sought this legacy object ever since, but have found only indirect evidence in the form of a pulsar wind nebula, which some neutron stars create. The JWST has changed that, according to newly published research.
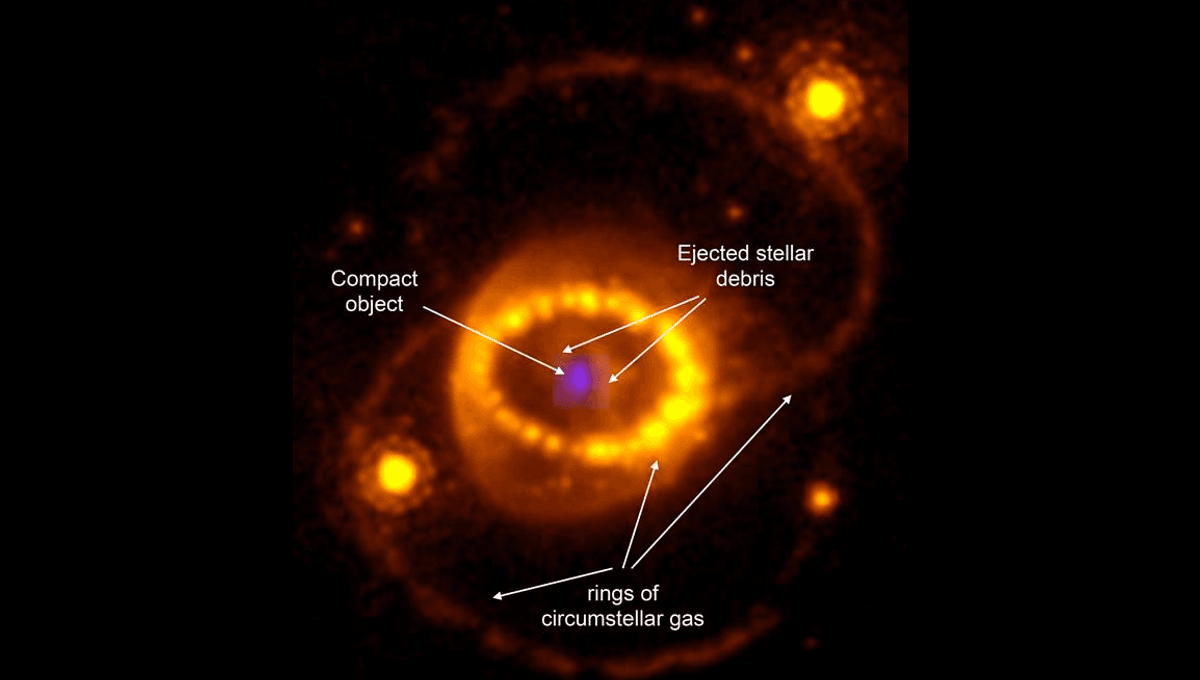
The clouds of gas and dust thrown off by SN 1987a have been a popular target for telescopes that can see the southern skies since the event. JWST joined in soon after its operations began, revealing the keyhole and rings at infrared wavelengths. It also found crescent structures that had not been seen before, and hints that raised hopes of spotting the neutron star itself.
Now, a team including Professor Mike Barlow of University College London has detected emission lines from highly ionized argon and sulfur in those observations. Although not coming from the object itself, the radiation from these gases indicates they are being lit up by a source of X-rays and ultraviolet light. Neutron stars have two processes by which they can produce this sort of high-energy radiation, but black holes have none.
“This radiation can be emitted from the million degree surface of the hot neutron star, as well as by a pulsar wind nebula that could have been created if the neutron star is rapidly spinning and dragging charged particles around it,” Barlow said in a statement. Settling which is responsible will be a priority in the future.
Finding the neutron stars within supernova remnants can be a challenge; before they die, the stars that become supernova often throw off enormous amounts of material which can hide what is occurring at the core. In the case of 1987a, this is complicated further by an equatorial ring, thought to be made up of material thrown off 20,000 years ago when the star that became 1987a swallowed a companion.
Some of the ejecta thrown off by 1987a’s progenitor has collided with the equatorial ring at such high speed it has produced X-rays. Previous observations had picked up radiation from argon illuminated by X-rays, but had not been able to tell if these were from the suspected neutron star or equatorial ring collisions.
The JWST’s superb resolution has changed this, revealing a component whose distribution and blueshift show it to be coming from the remnant’s center. The fact that only argon and sulfur were detected in this way is also telling. Both are produced by the fusion of oxygen and silicon and therefore are found towards the inner core of supernova ejecta, being produced very late in the pre-supernova process. For these gases to be lit up by something behind them, from our perspective, the source must be at the very heart of the remnant.
The amount of blueshift in the emission lines indicates the neutron star experienced a “natal kick”. This is a common phenomenon for black holes and neutron stars, leaving them moving compared to the average of the surrounding material.
The study has been published in the journal Science.
Source Link: JWST Finds A Neutron Star In Remnant Of SN1987a, The Last Naked-Eye Supernova