The JWST has turned its powerful eye on the Apep Nebula, sometimes known as the Cosmic Serpent, and found it eating its tail. Or perhaps you could argue the tail, in the form of enormous shells of dust, is being consumed by its half-sibling in a tale worthy of ancient myth. The system could be the key to understanding the processes that produce much of the dust in early galactic development, shaping the formation of planets thereafter.
In a universe filled with marvels, Wolf-Rayet stars still manage to stand out. The final stage that certain giant stars undergo before becoming supernovae, Wolf-Rayet stars release staggeringly powerful stellar winds that cause them to shed the majority of their mass before exploding. When these winds collide with the stellar winds from other large stars, the impact can cause carbon atoms to clump together into dust particles.
Massive stars tend to form together, Macquarie University student Ryan White, author of a new preprint paper, told IFLScience. Nevertheless, even the most giant stars never reach a Wolf-Rayet stage, and for those that do, it is short by astronomical standards. Consequently, in the entire galaxy, we know of only one system where two Wolf-Rayet stars orbit each other so that their winds collide. Now the JWST has allowed us to see the inner workings of this cosmic wonder.
The Wolf-Rayet pair and their surrounds are known as Apep after the Egyptian snake god, and they are unusual in other ways as well. The colliding wind binary we see usually involves a Wolf-Rayet and a supergiant star orbiting relatively close to each other, contributing to the winds’ interactions. Apep’s primary components, however, are about 100 astronomical units (the Earth-Sun distance) apart, which White says is about 10 times the distance of stars in other colliding-wind nebulae, and take 193 years to circle each other.
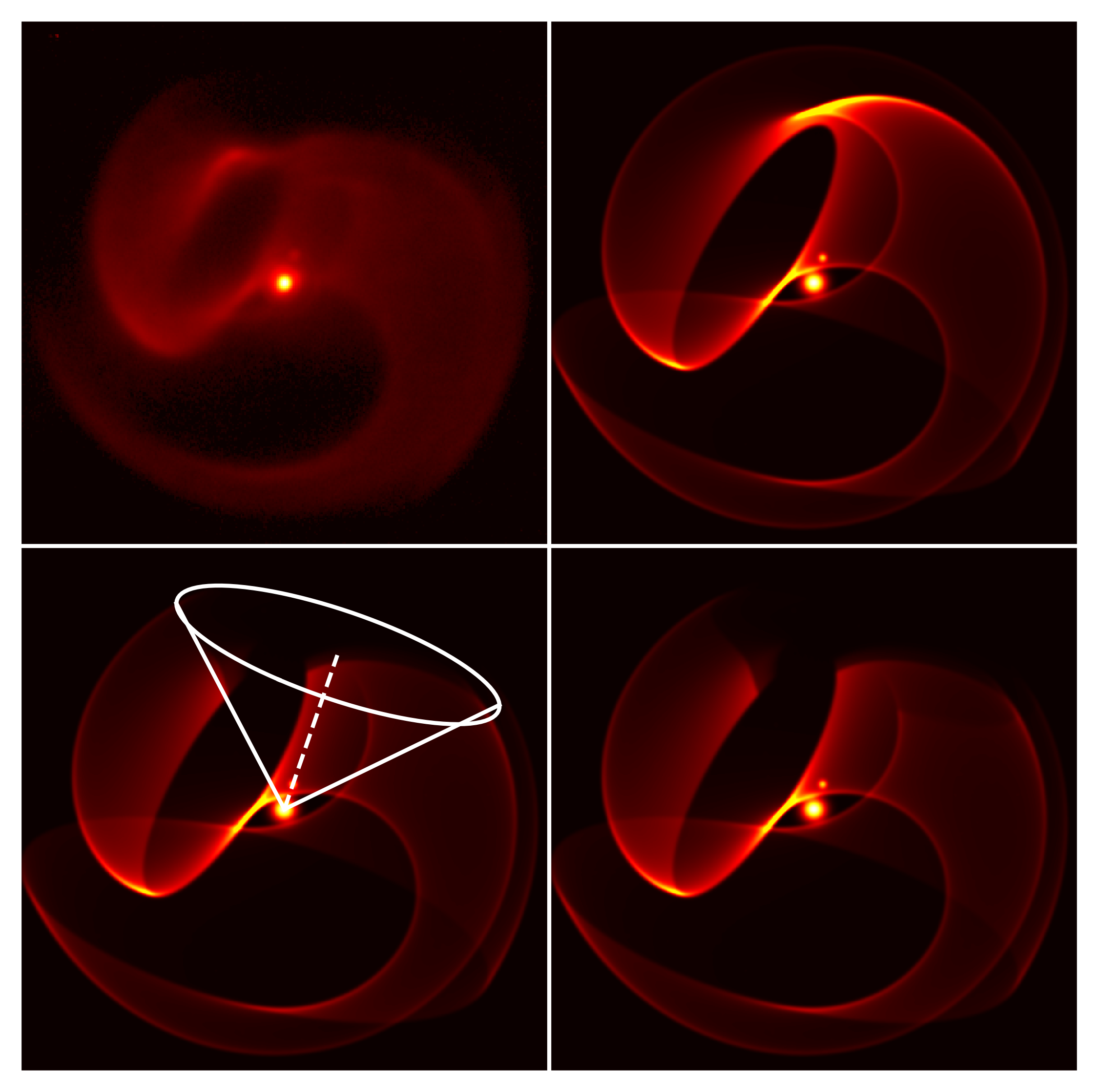
For most of this time, the two stars are too far apart for even their mighty winds to make dust, but their orbits are quite eccentric. For a few decades around closest approach, immense clouds of dust are produced that White compares to puffs of smoke. These puffs form shells that slowly expand outwards. The Very Large Telescope has been used to image the innermost shell in the past, but lacks the resolution to see those made more recently. The JWST has gone where other telescopes cannot, revealing the three innermost shells.
Its observations reveal winds from one star racing outwards at 2,100 kilometers per second (1,300 miles/s) and an even more astonishing 3,500 km/s from the other.

Simulation showing Apep’s evolution, where phi is the proportion of an orbit passed from closest approach
Image Credit: White et al.
In studying these images, White and co-authors found an enormous cone carved out of the shells, which can be traced to a neighboring O-type supergiant star. This neighbor would have been born with somewhat less mass than the two Wolf-Rayets, White told IFLScience. However, he added, “The pair has thrown off so much material that the O-type star is now the largest mass in the system.”
The supergiant is so powerful that even at a distance of around 1,700 astronomical units (10 times further than Voyager I is from the Sun), it is somehow managing to destroy a slice of the dust the Wolf-Rayets are busy making. White told IFLScience the team has yet to satisfactorily explain this dust-busting capacity. “Probably many things are happening in parallel,” White said. “Literally, it’s wind colliding with the dust, but this star is so bright it is emitting enormous amounts of X-rays and UV light, which may be destroying the dust.”
The O-type supergiant is so far away that there was previously some uncertainty as to whether it was even associated with Apep, or if it happened to be at a different distance in the same direction. Identifying the void it is carving in the nebula settled that question.
The Apep nebula and the cone carved in the dust by the power of the neighboring O-type supergiant star.
Image Credit: White et al.
White told IFLScience it is likely but not confirmed that the three stars formed together and their greater initial mass has seen the inner pair evolve faster, reaching the Wolf-Rayet stage first. “They would be no older than 5 million years at most,” White added.
A star’s Wolf-Rayet stage lasts less than 100,000 years, but we don’t know how far through it this pair is, and therefore whether we can expect fireworks any time soon. “People have tried to look at stars in other galaxies to work out what happens with Wolf-Rayet stars before they go supernova,” White said. However, results have been inconclusive, so we don’t know the signs to look out for. “We have a better idea for red supergiants,” he added.
Although Wolf-Rayet stars are rare today, and a pair apparently unique in the galaxy, giant stars were much more common in the early universe, so when the Milky Way was forming, systems like this were probably much more common. It is thought that a lot of the dust we now see in giant clouds and streamers surrounding the inner galaxy formed under conditions like this.
Two papers on the Apep system have been submitted to The Astrophysical Journal, with preprints on Arxiv.
Source Link: JWST Reveals Dust Being Destroyed In The Galaxy’s Most Extreme Colliding-Wind Binary