New observations from JWST have revealed intriguing details of the atmosphere of a relatively nearby exoplanet. The world is called VHS 1256 b and orbits not one but two stars. The system is located 40 light-years away and is an ideal target for JWST.
VHS 1256 b is the planetary-mass object with the biggest change in brightness to date. The observations from JWST suggest that silicate material is constantly being churned over the course of the planet’s 22-hour rotation, reaching a scorching 830 °C (1,500 °F) at the top of the atmosphere.
It’s not just clouds made of a sand-like material – JWST also got clear detections of water, methane, and carbon monoxide. There is also evidence for the presence of carbon dioxide. So far, this is the highest number of molecules spotted in the atmosphere of a planet beyond the solar system.
“VHS 1256 b is about four times farther from its stars than Pluto is from our Sun, which makes it a great target for the JWST,” lead author Brittany Miles of the University of Arizona, said in a statement. “That means the planet’s light is not mixed with light from its stars.”
This celestial body is truly a complicated one. With a mass around 12 or 16 times that of Jupiter, this object is around the lower end of the brown dwarf mass scale. Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that failed to become stars, never massive enough to fuse regular hydrogen. They can fuse a heavier version of hydrogen known as deuterium, but it is not clear if this is the case here.
The high temperature of the object, despite being so far from its two stars, doesn’t necessarily mean it’s fusing something at its core. VHS 1256 b is only 140 million years old. When gas giant planets form, they tend to be quite hot. The gas from the protoplanetary nebula is compressed and the gravitational potential energy is converted into heat.
Both brown dwarfs and massive planets can have weird weather phenomena, including the clouds spotted around this world. JWST was able to deliver such detailed observations that researchers could tell that there are different types of grains in the clouds.
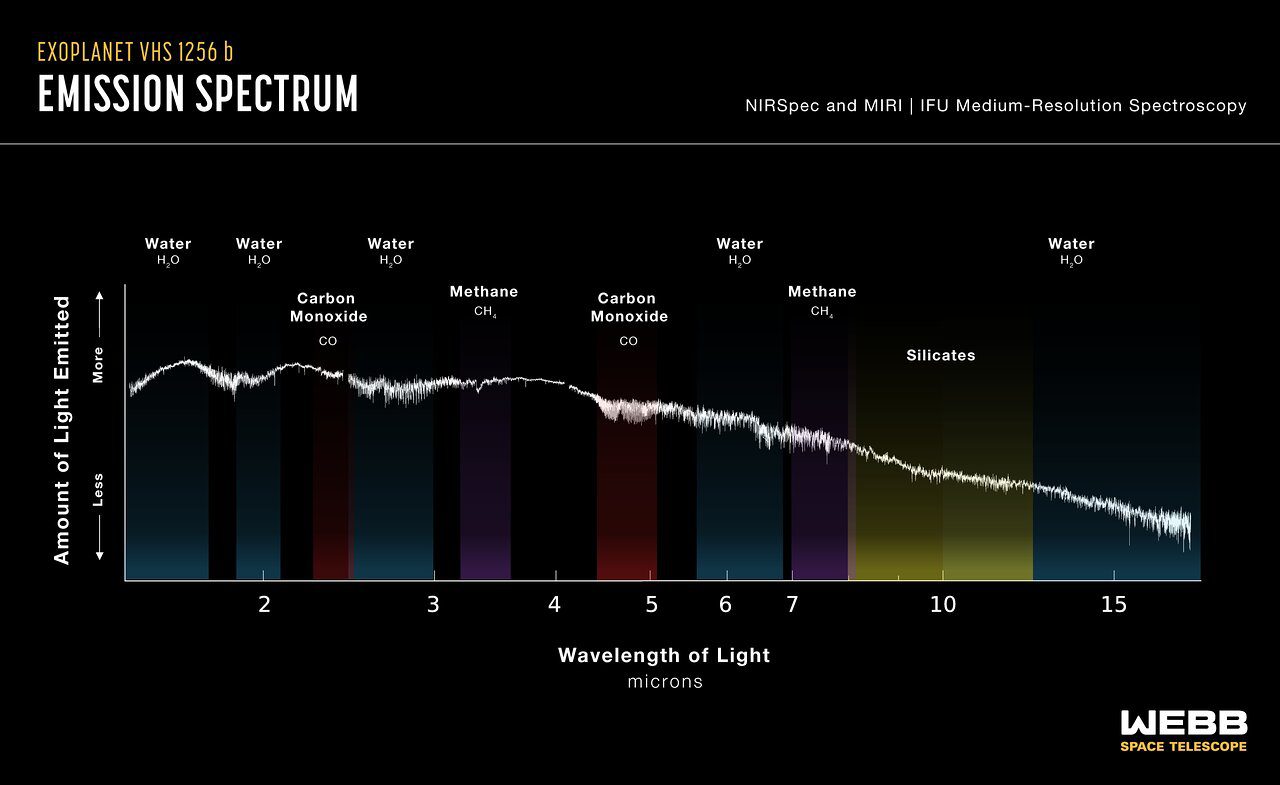
The emission spectrum of the planet allowed researchers to spot all the different molecules. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted (STScI), B. Miles (University of Arizona), S. Hinkley (University of Exeter), B. Biller (University of Edinburgh), A. Skemer (University of California, Santa Cruz)
“The smaller silicate grains in its atmosphere may be more like tiny particles as in smoke,” added co-author Beth Biller of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland. “The larger grains might be more like very hot, very small sand particles.”
These observations were part of the Early Release Science Programme, and they are just the beginning of the study of this fascinating celestial body.
“We’ve isolated silicates, but better understanding which grain sizes and shapes match specific types of clouds is going to take a lot of additional work,” co-author Elisabeth Matthews from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Heidelberg, Germany, explained. “This is not the final word on this planet – it is only the beginning of a large-scale modeling effort to understand JWST’s complex data.”
The study is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Source Link: JWST Spots Hot Gritty Silicate Clouds On Nearby Exoplanet Orbiting Two Stars