Astronomers have announced a pretty cool discovery thanks to JWST, coming all the way from the very early universe. The space observatory has revealed that a far distant known galaxy is not a single object but two. The object is known as MACS0647-JD, and the light we can see today has been travelling since 400 million years after the Big Bang.
MACS0647 is a massive galaxy cluster. It is so big that it warps space-time, creating a gravitational lens. Objects located behind the cluster are magnified, so astronomers have been using it to see further back into the universe. That’s how they discovered MACS0647-JD with Hubble ten years ago, where it appeared as a single red object.
“Due to the gravitational lensing of the massive galaxy cluster MACS0647, it’s lensed into three images: JD1, JD2, and JD3. They’re magnified by factors of eight, five, and two, respectively,” discoverer Dan Coe, from Johns Hopkins University and the European Space Agency, said in a blog post from NASA.
JWST was able to resolve two objects. Either this is a merger between two galaxies, likely the most distant seen so far, or it is two clumps of stars within a single galaxy. Further observations from JWST might help shed light on this, but the team already has plenty to work on.
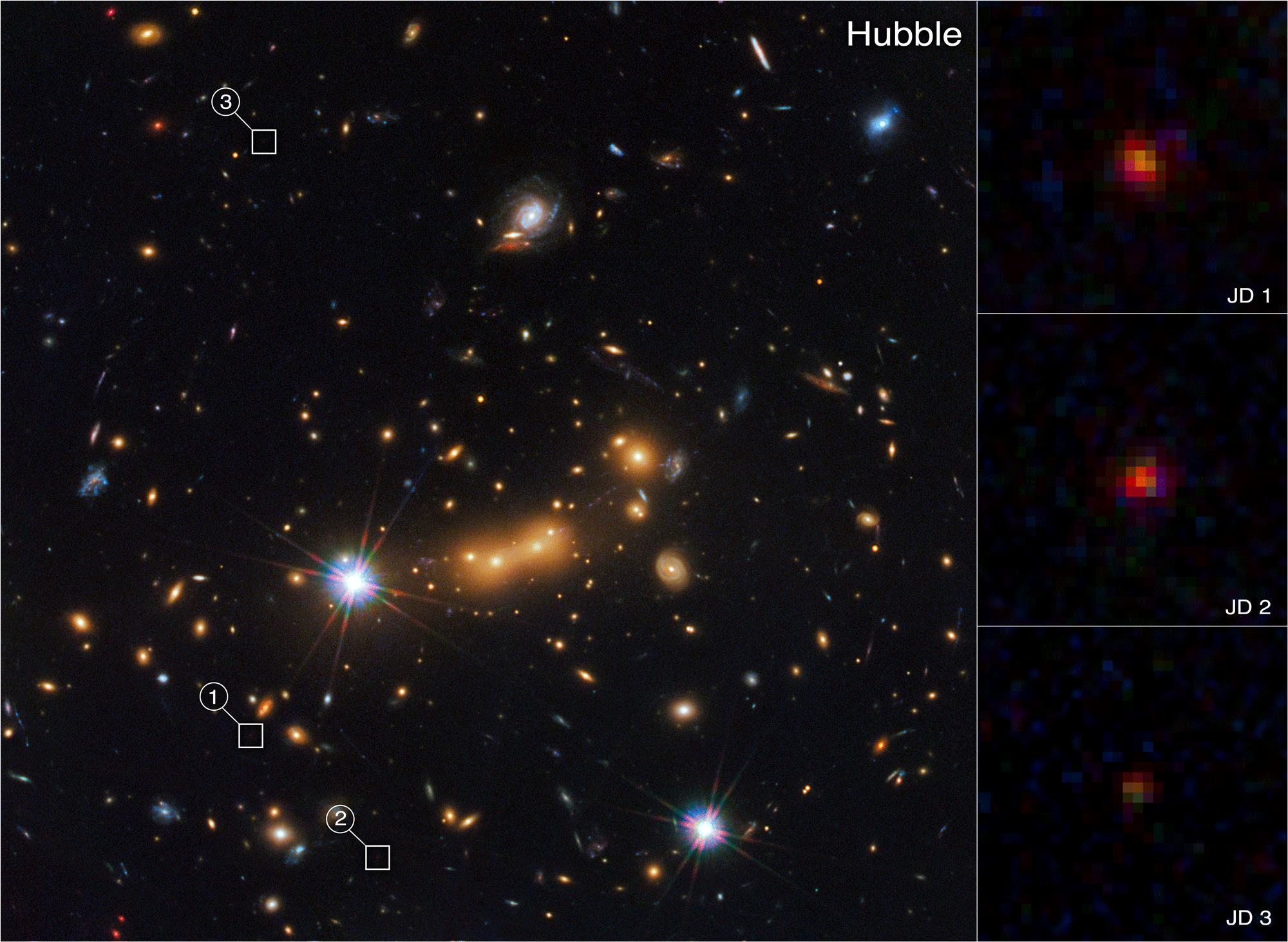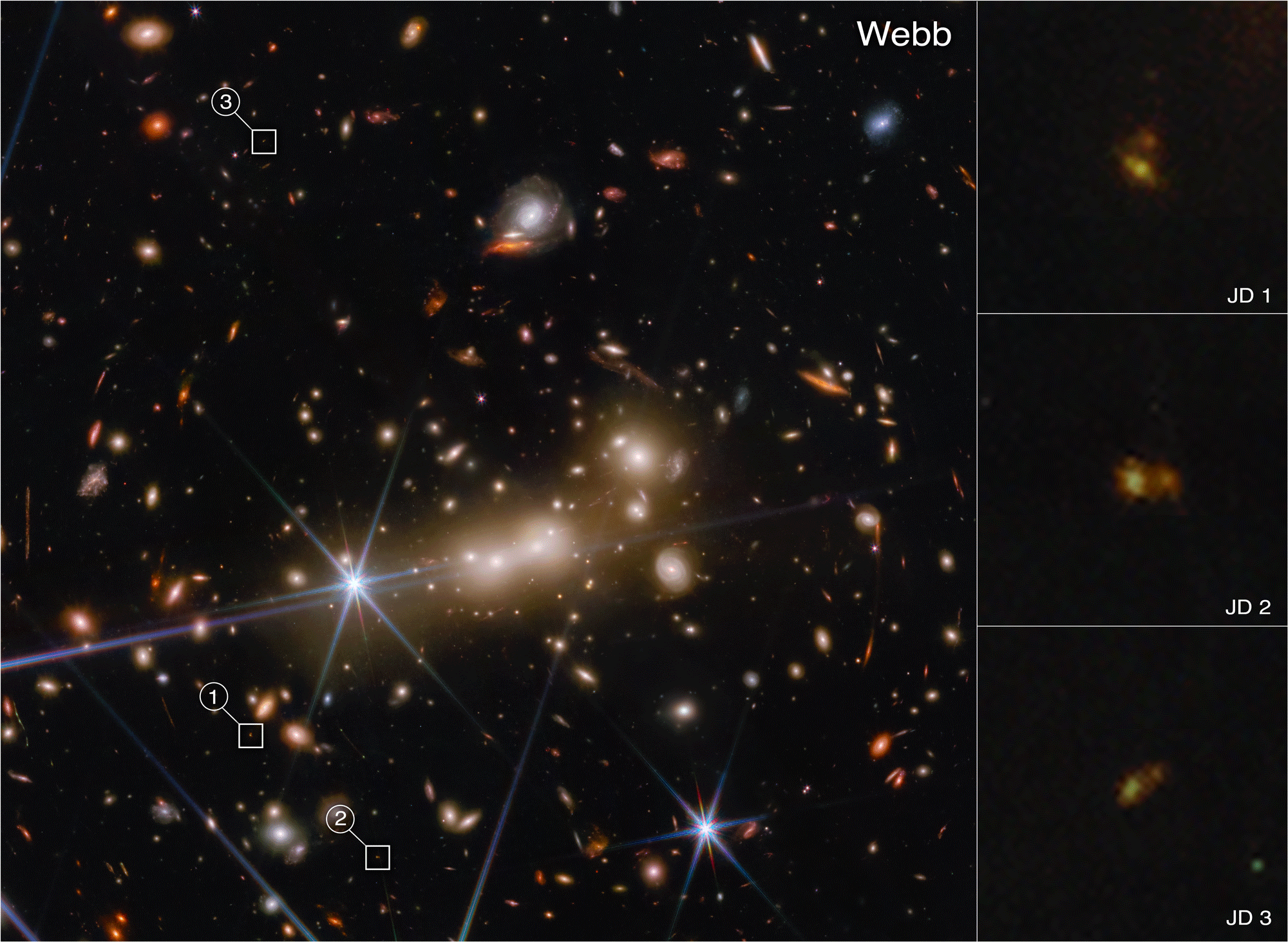
Animated comparison between Hubble and JWST. Galaxy cluster MACS0647 with the three-lensed images of the distant galaxy highlighted. Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, and Tiger Hsiao (Johns Hopkins University). Image processing: Alyssa Pagan.
“You can also see that the colors between the two objects are so different. One’s bluer; the other one is redder. The blue gas and the red gas have different characteristics. The blue one actually has very young star formation and almost no dust, but the small, red object has more dust inside, and is older. And their stellar masses are also probably different,” explained lead author Tiger Yu-Yang Hsiao, also from Johns Hopkins University.
JWST is a revolutionary observatory. It’s studying the universe in infrared light, seeing further and in more detail compared to its predecessors such as Spitzer. Astronomers have been using it to study many different objects, and it’s living up to its potential.
“Up to this point, we haven’t really been able to study galaxies in the early universe in great detail,” co-author Rebecca Larson, from the University of Texas at Austin, added. “Studying them can help us understand how they evolved into the ones like the galaxy we live in today. And also, how the universe evolved throughout time.”
The current work is submitted to Nature and available to read on the online repository arXiv.
Source Link: JWST Spots Structures From The Early Universe Never Seen Before