La Niña reared its head in the tropical Pacific in December 2024 and it’s likely to linger for a few more months. What does that mean? In short, colossal climatic forces are set to drive lower average temperatures, as well as noticeable changes to rainfall.
The NOAA Climate Prediction Center recently announced the emergence of La Niña conditions after detecting signs of temperatures cooling in the tropical Pacific Ocean late last year.
Their findings suggest that the central Pacific (Niño-3.4 region) is 0.7°C (1.26°F) cooler than normal, the western Pacific (Niño-4 region) is 0.6°C (1.08°F) cooler, and the eastern Pacific (Niño-1+2 and Niño-3 regions) is about average. These cooler-than-normal temperatures in the tropical Pacific Ocean are signs of La Niña.
However, it looks like it will be a weak one – and it won’t stay around for too long. There’s a 59 percent chance La Niña will continue to linger through February–April, followed by a 60 percent chance of neutral conditions in March–May.
The NOAA also described it as an “unusual La Niña”. They predicted that La Niña conditions were on their way back in October 2024, although it developed pretty slowly. For over a year, the world’s oceans have been significantly warmer than usual, potentially playing a role in postponing the arrival of La Niña.
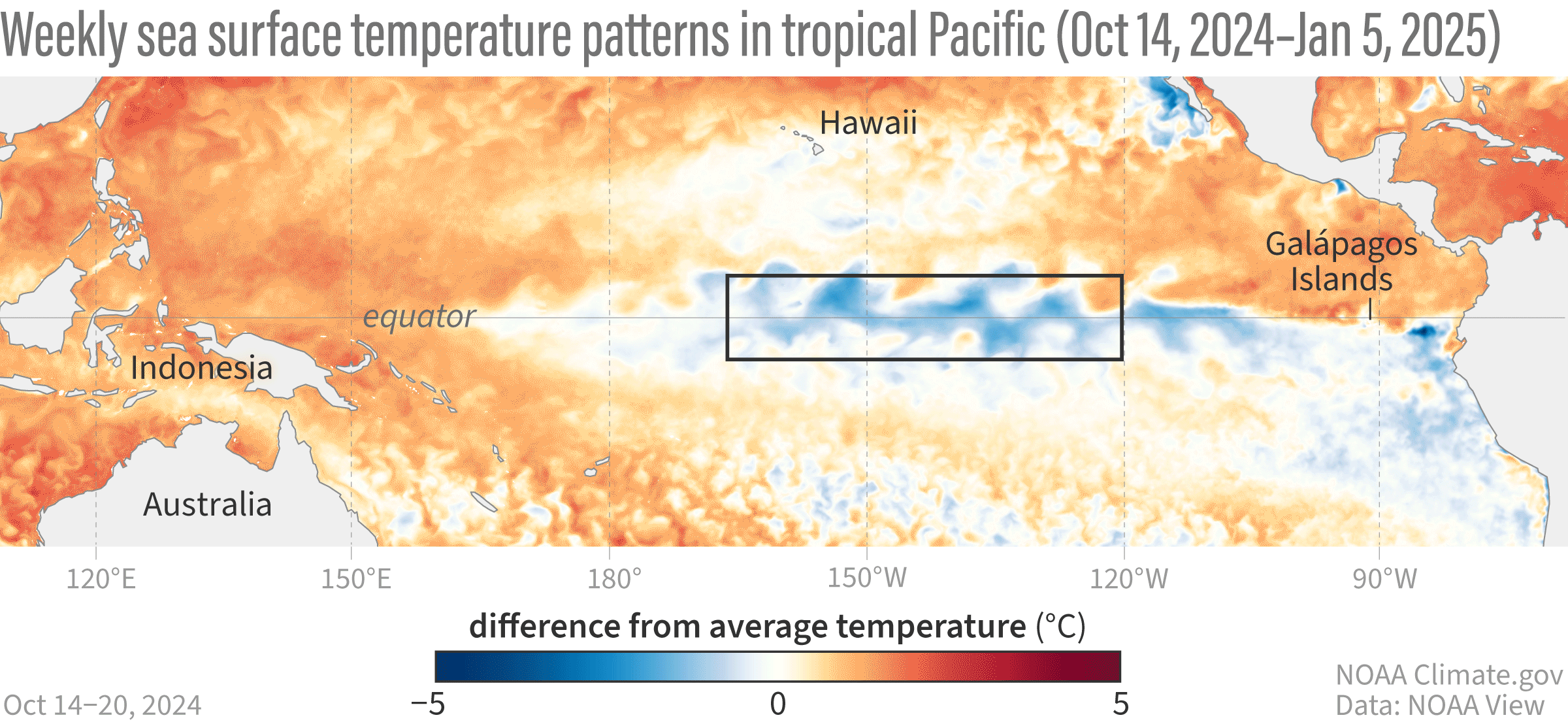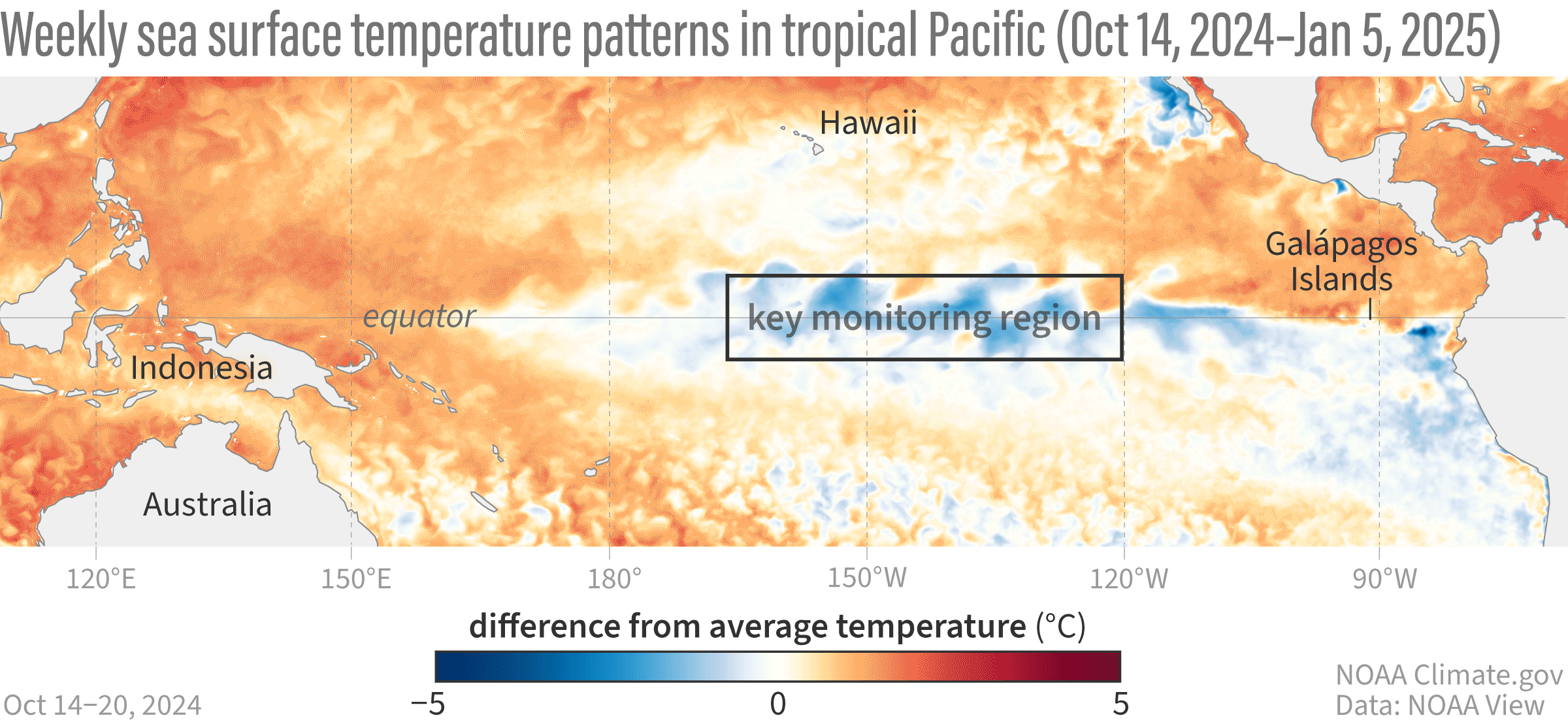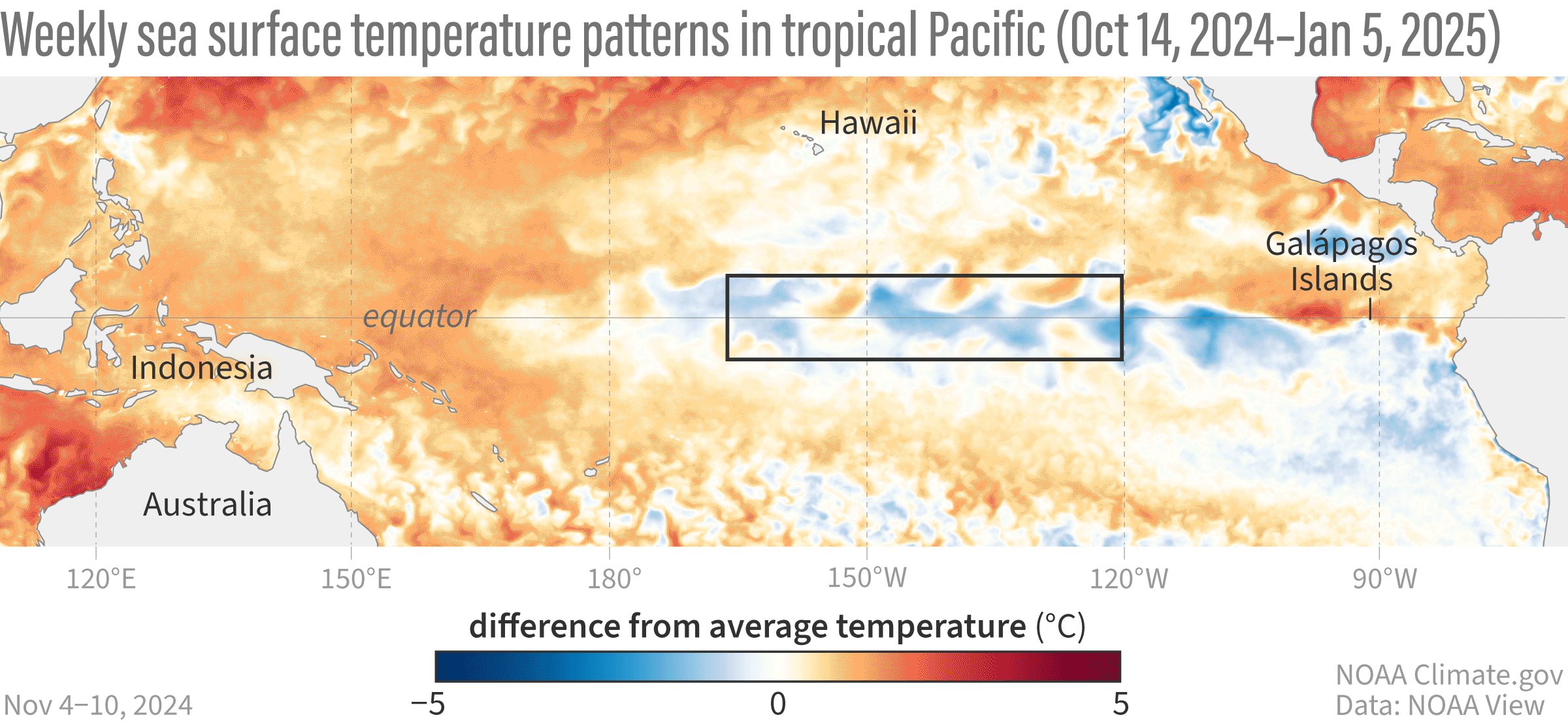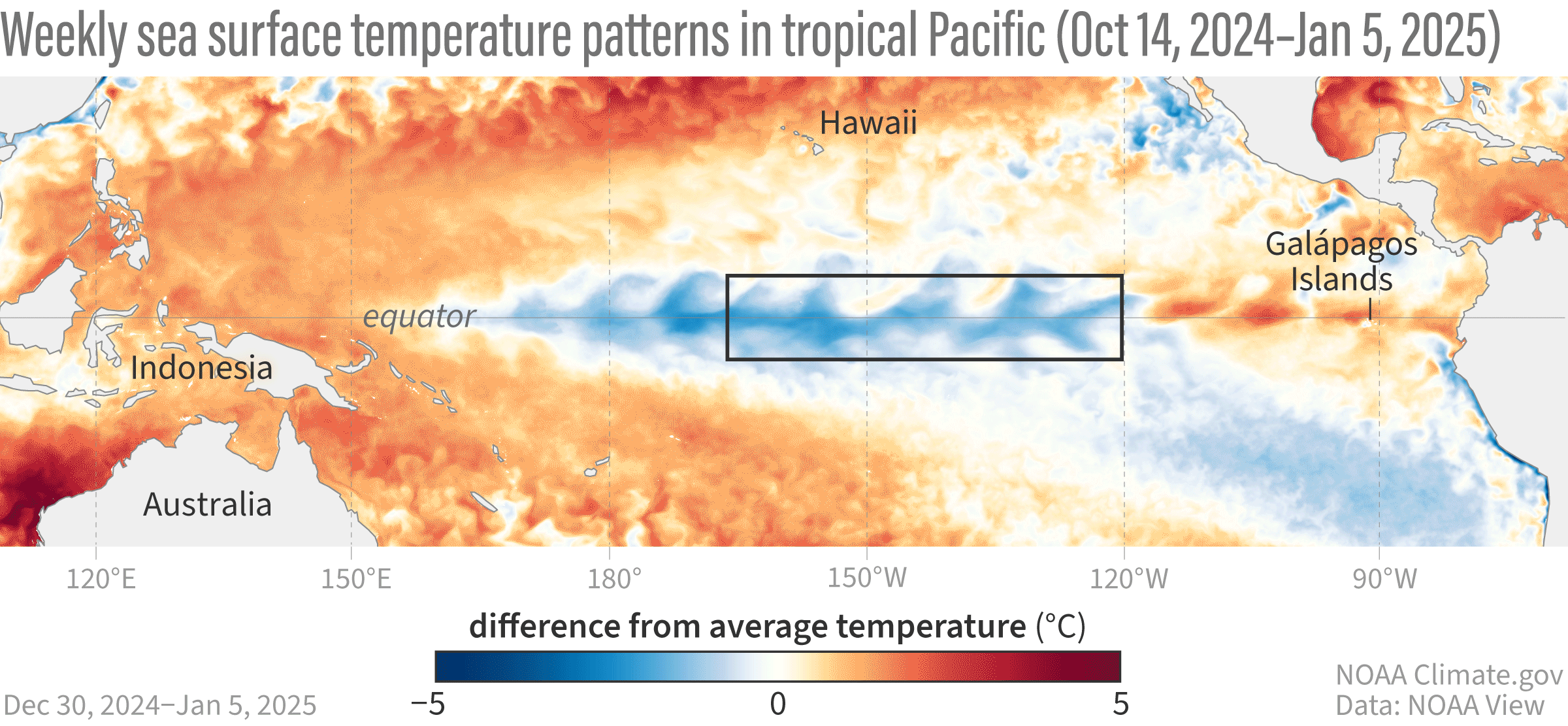
A GIF map showing weekly sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean compared to average from October 14, 2024–January 5, 2025.
Image credit: NOAA
Despite being a weird and weak one, it could have significant effects on the Earth’s climate and weather.
La Niña, along with El Niño, are the two main phases of the El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO), an alternating pattern of sea surface temperature and atmospheric changes in the tropical Pacific Ocean.
As opposed to El Niño, it’s often called the “cold phase” of the ENSO as it’s generally associated with lower global average temperatures.
The cooler Pacific waters shift the jet stream northward, bringing drier conditions to the southern United States while causing wetter and colder weather in the Pacific Northwest and Canada. During La Niña, winters in the southern US tend to be warmer, while northern regions experience cooler-than-average temperatures.
La Niña also tends to reduce the severity of hurricane seasons in the Pacific but intensifies hurricane activity in the Atlantic. Additionally, it often leads to drier conditions in East Africa and South America, while Australia and parts of Southeast Asia experience wetter weather.
Since La Niña conditions tend to lower global average temperatures, it could impact our view of the deepening climate crisis. However, don’t expect this quick blip of cooling conditions to save the planet.
Recent reports have found that every year from 2015 to 2024 ranks among the 10 warmest years ever recorded. Even with the influence of La Niña at the start of the year, it’s likely that 2025 will continue to follow the trend of worrying warm global temperatures.
Source Link: La Niña Has Finally Returned To The Pacific With A Weird And Weak Episode