Human embryo models capable of synthesizing their own blood have been developed, in an advance that could lead to new treatments for blood disorders as well as the production of stem cells for transplants.
The 3D structures, named “hematoids”, are similar to embryos but differ in several important ways. They don’t have the capacity to continue to develop into a fetus – they lack essential tissues and would also require a yolk sac and placenta. However, what the study demonstrates is that they can effectively simulate processes that happen during the early stages of embryo growth.
The hematoids self-assemble from human pluripotent stem cells, which can be nudged down any development pathway to become any type of human tissue. On only the second day of development, the team observed that the hematoids had arranged themselves into the three layers that lay the foundation for the human body plan: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
On the eighth day, some of the hematoid cells were beating – the precursors to a heart.
And after around two weeks of development in the lab, the scientists observed the first tell-tale signs that they’d begun producing blood.
“It was an exciting moment when the blood red colour appeared in the dish – it was visible even to the naked eye,” said co-first author Dr Jitesh Neupane, of the University of Cambridge’s Gurdon Institute, in a statement.
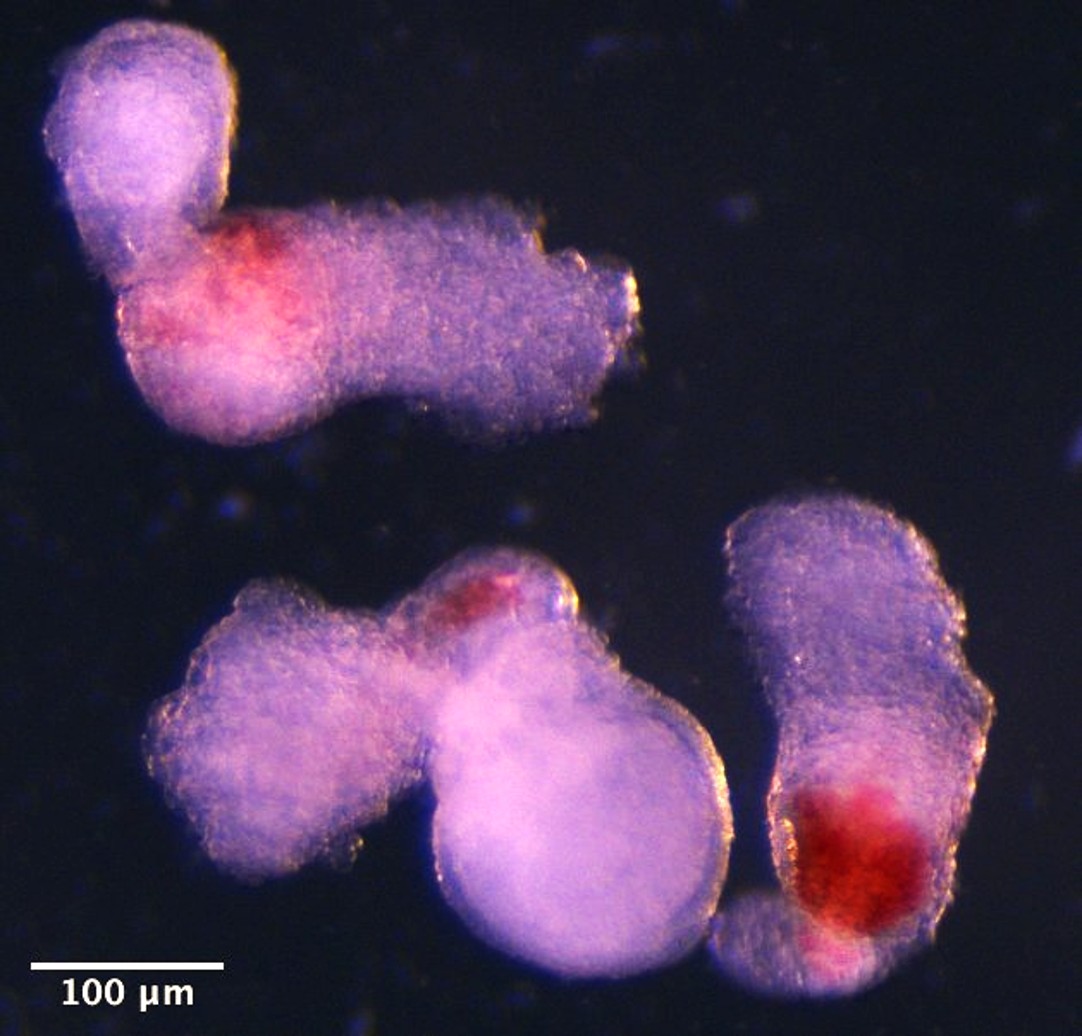
The embryo models on day 14, complete with blood.
Image credit: Jitesh Neupane, University of Cambridge
In normal embryogenesis, this stage corresponds to around four or five weeks of development. It’s not possible to observe this directly in a living human because the embryo would have implanted into the uterus wall by then, so these models are our only chance to study these processes in detail.
“Our new model mimics human foetal blood development in the lab. This sheds light on how blood cells naturally form during human embryogenesis, offering potential medical advances to screen drugs, study early blood and immune development, and model blood disorders like leukaemia,” said Neupane.
Co-first author Dr Geraldine Jowett added, “Hematoids capture the second wave of blood development that can give rise to specialised immune cells or adaptive lymphoid cells, like T cells, opening up exciting avenues for their use in modelling healthy and cancerous blood development.”
There are other ways of producing blood cells in a lab, but these typically need supplementing with a host of extra proteins to help them along the way. The hematoids don’t need this, and so more closely mimic the natural processes that happen when an embryo develops.
In the future, we could even see a scenario where a patient can donate their own pluripotent stem cells to be used to create hematoids that produce blood that is perfectly matched to their body, for truly personalized medicine.
“Although it is still in the early stages,” said senior author Professor Azim Surani, “the ability to produce human blood cells in the lab marks a significant step towards future regenerative therapies – which use a patient’s own cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues.”
The study is published in the journal Cell Reports.
Source Link: Lab-Grown 3D Embryo Models Make Their Own Blood In Regenerative Medicine Breakthrough