Indo-European languages are spoken by almost half of the world’s population, and while dialects as diverse as French and Bengali might seem completely unrelated, it is widely believed that they all share a common ancestor. For centuries, linguists have been arguing over the origins of this group of mother tongues, and researchers have now traced the roots of all Indo-European languages back to over 8,000 years ago.
Until now, two main theories had dominated the debate. The first of these is known as the Steppe hypothesis and holds that the ancestral language first appeared on the Pontic-Caspian Steppe no earlier than 6,500 years ago, before spreading across Eurasia with horse-based pastoralism.
The second theory – known as the farming hypothesis – suggests an earlier origin around 9,500 years ago in a part of the Fertile Crescent that now comprises Turkey and Iran. According to this thesis, the emergence of Indo-European languages from the region was facilitated by the spread of agriculture across the Eurasian landmass.
To try and settle the debate, the authors of a new study constructed a dataset of 170 core words in 161 different Indo-European languages, including 52 historical languages such as Ancient Greek, Classical Latin, and Old English. By analyzing patterns and similarities between these various languages, the researchers were able to create a “language tree”, showing how new dialects emerged as older languages split.
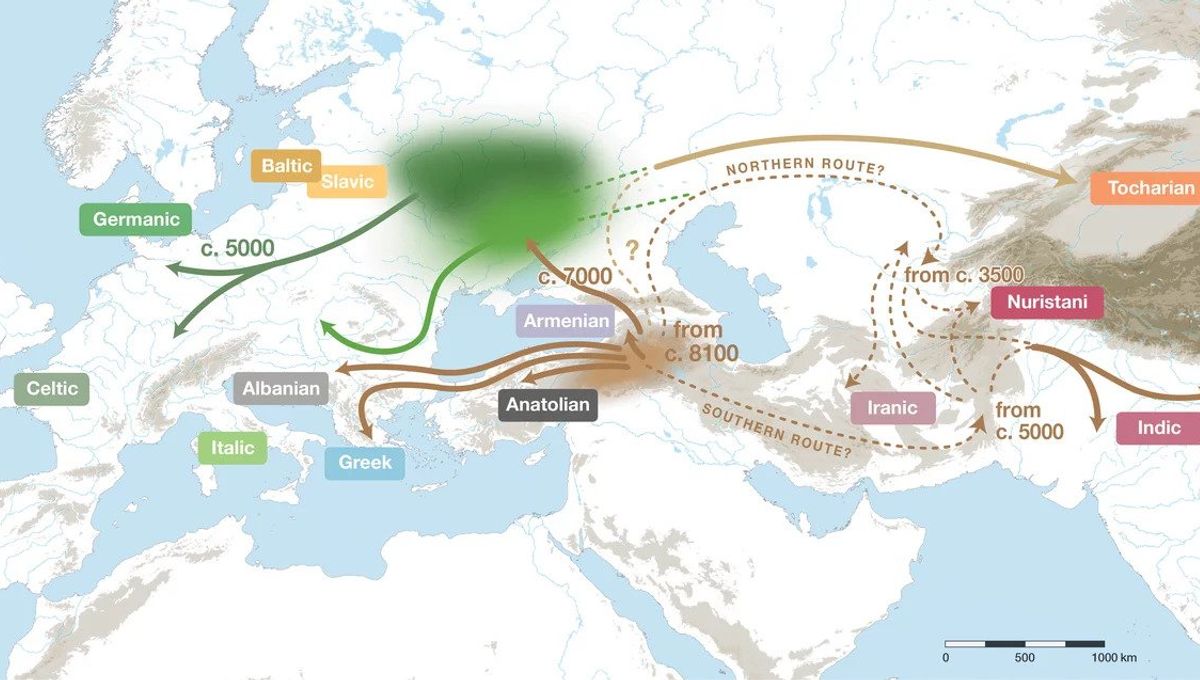
Working their way backward, the study authors traced the origins of Indo-European languages to 8,120 years ago and suggest that the ancestral tongue did indeed arise in the Fertile Crescent. However, the researchers’ model indicates that the language didn’t spread across Europe and Asia in a single wave – as proposed by the farming hypothesis – but split into several branches, some of which are considerably older than others.
For instance, they found that the Albanian, Greek, Armenian, and Anatolian branches of the tree had all split from the ancestral language by around 7,000 years ago. It wasn’t until about 2,000 years later, however, that a second wave of expansion occurred as Indo-European languages spread across the Steppe with cultures such as the Yamnaya and the Corded Ware.
This is backed up by genetic studies which have shown that a major migration across the Steppe and into Europe occurred around 5,000 years ago.
“Germanic and Celtic are estimated to have diverged from each other [about 4,890 years before present], and Italic from them somewhat earlier, [roughly 5,560 years before present],” write the study authors. “Balto-Slavic is less closely associated with these three, splitting earlier, [around 6,460 years before present].”
Overall, then, the language tree supports neither the Steppe nor the farming hypotheses, but offers an alternative “hybrid” model, whereby Indo-European languages originated in Anatolia before spreading in multiple directions. One of these branches exploded out of the Pontic-Caspian Steppe, giving rise to many of the languages that have dominated Western Europe for the past five millennia.
“Ancient DNA and linguistic phylogenetics thus combine to suggest that the resolution to the 200-year-old Indo-European enigma lies in a hybrid of both the farming and Steppe hypotheses,” conclude the researchers.
The study is published in the journal Science.
Source Link: Language Tree Traces Origin Of Indo-European Languages To 8,100 Years Ago