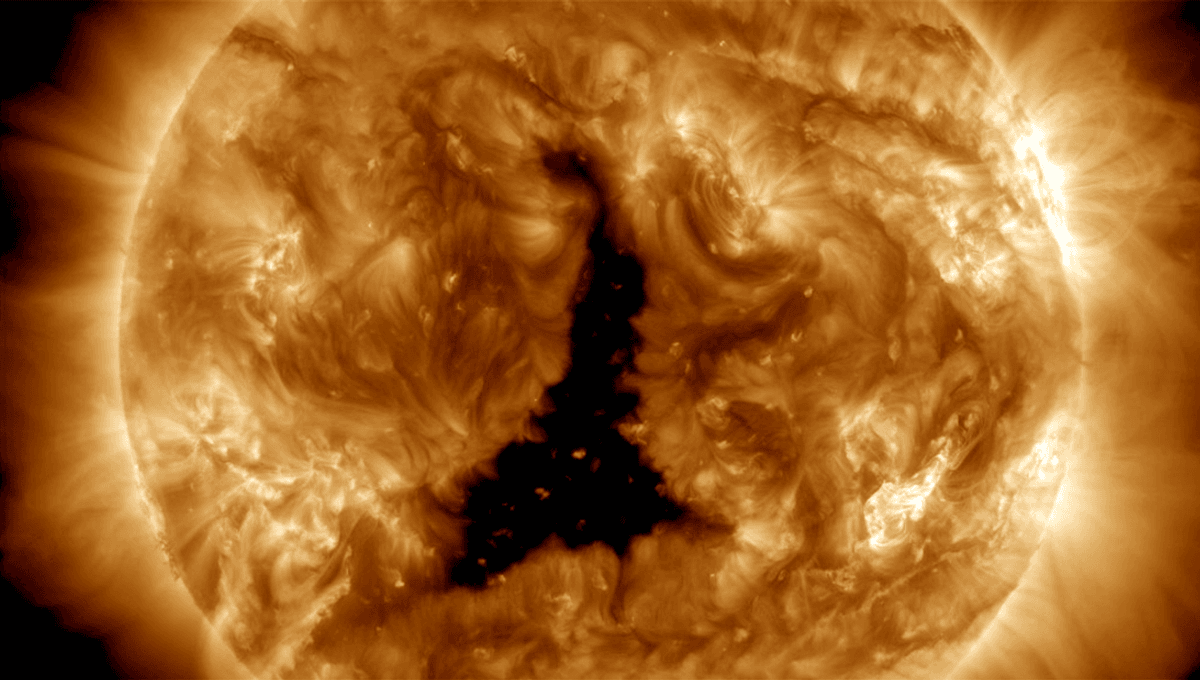
A high-speed stream of solar wind from a large coronal hole is expected to cause moderate geomagnetic storms over the next few days.
The sunspot, captured in a video by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) between December 2-4, 2023, is large, but of no major concern. Though a little unsettling in appearance, sunspots look like this in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) and soft X-ray images as they are cooler in temperature and less dense than the surrounding regions.
“Sunspots are areas where the magnetic field is about 2,500 times stronger than Earth’s, much higher than anywhere else on the Sun,” the National Weather Service explains. “Because of the strong magnetic field, the magnetic pressure increases while the surrounding atmospheric pressure decreases. This in turn lowers the temperature relative to its surroundings because the concentrated magnetic field inhibits the flow of hot, new gas from the Sun’s interior to the surface.”
The sunspot should not pose too much of a problem for Earth, with the Space Weather Prediction Center of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration predicting a minor-moderate geomagnetic storm arriving from midday (UTC) on December 4.
Sun activity increases and decreases in an 11-year cycle known as the Schwabe cycle. From 1826 to 1843, German amateur astronomer Heinrich Schwabe observed the Sun, discovering that it rotates on its axis once every 27 days. He noticed the Sun goes from quiet periods, where no sunspots can be seen, to the maximum phase where 20 or more groups of sunspots can be seen.
Solar activity is increasing at the moment. The next solar maximum – when the Sun’s activity peaks along this cycle – had been predicted by NASA to occur in 2025. However, NASA revised this prediction to between January and October 2024.
“We expect that our new experimental forecast will be much more accurate than the 2019 panel prediction and, unlike previous solar cycle predictions, it will be continuously updated on a monthly basis as new sunspot observations become available,” Mark Miesch, the solar cycle lead at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center, said in a statement at the time. “It’s a pretty significant change.”
This forecast tracks with another team’s prediction of mid-2024. This team looked at magnetic donuts which form at 55 degrees of latitude on both hemispheres of the Sun. These formations migrate towards the equator where they meet and cancel each other out, which the team dubbed a Hale cycle (two solar cycles) terminator.
This terminator event tends to happen up to two years after the minimum, and by focusing on these events, the team believed they could make better predictions about the solar cycles.
“If you measure how long a cycle is, not the minimum to minimum, but from terminator to terminator, you see that there is a strong linear relationship between how long one cycle is and how strong the next one is going to be,” NASA research scientist Robert Leamon told Space.com.
Expect more big sunspots like this one as activity moves towards its peak.
Source Link: Large Hole In The Sun's Atmosphere Sends High-Speed Solar Wind Toward Earth