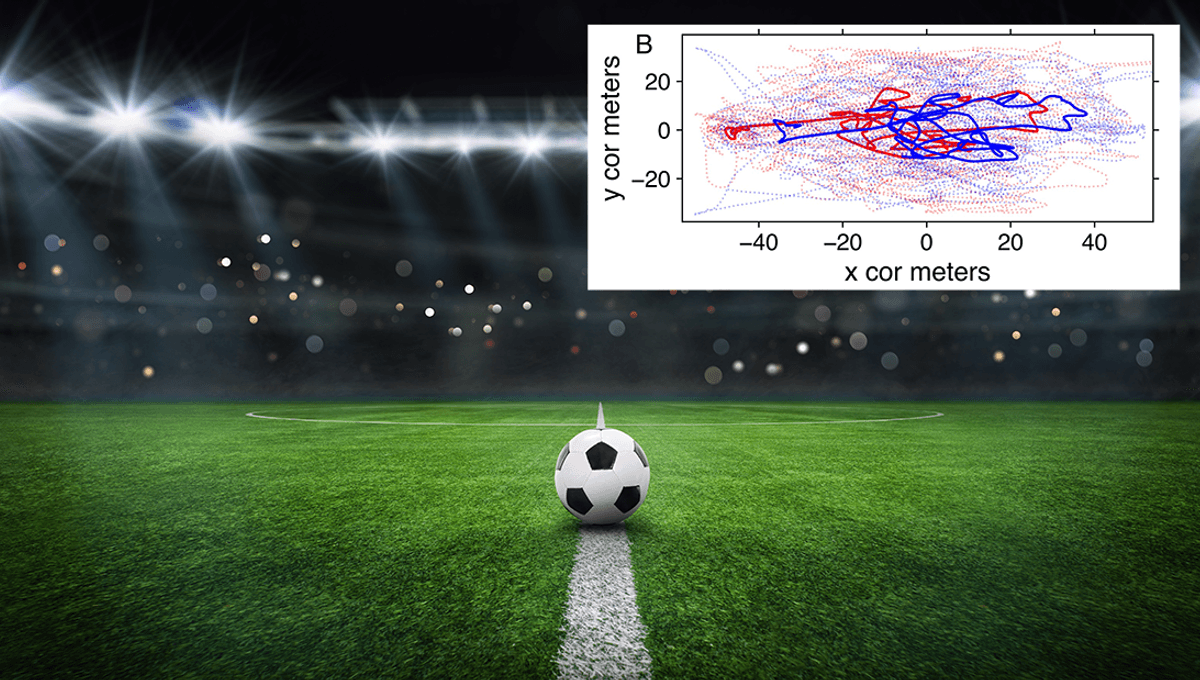
A new study on soccer teams (or, to use the correct term, “football teams”) has found that teams appear to act as if they are one single person, and follow movement patterns similar to albatrosses searching for food, or particles in a turbulent fluid.
ADVERTISEMENT
There’s a lot to unpack here. The team, from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) in Japan, were interested in Lévy walks, and whether they apply to teams playing a game of football. The Lévy walk, or Lévy flight, is a mathematical description of the path of objects (or in this case, football players) characterized by a cluster of short steps, with sudden longer steps in-between.
“Lévy walk is a type of random walk, with its key characteristic being that the distribution of step lengths is drawn from a scale-free (power law) distribution,” the team explain in their paper. “Particles exhibiting Lévy walk dynamics manifest superdiffusive behavior, spreading faster than Brownian walkers. The resultant trajectory possesses fractal properties, with clusters of short steps interspersed with much longer sprints.”
The walks are seen in a bizarre number of systems, from the microscopic to that of animals seeking prey.
“They have been seen in the molecular machinery operating within cells during intracellular trafficking, in the movement patterns of T cells within the brain, in DNA, in some molluscs, insects, fish, birds and mammals, in the airborne flights of spores and seeds, and in the collective movements of some animal groups,” a review on the topic explains. “Lévy walks are also evident in trace fossils (ichnofossils) – the preserved form of tracks made by organisms that occupied ancient sea beds about 252-66 million years ago.”
While nobody is really sure what causes various systems to carry out these walks in all the areas they crop up, they do appear to be advantageous. For example, it may provide living organisms with the optimal strategy in searching for resources like food, balancing exploiting nearby resources (clusters of short steps) and exploring for potential new resources further afield (the long step).
“Football is a game about scarcity of resources: to win, a team requires possession of the ball, and there is only one ball in play,” Professor Tom Froese, senior author of the study and leader of the Embodied Cognitive Science Unit at OIST, said in a statement.
ADVERTISEMENT
“And so, it makes sense for individual players to move in a way that balances exploration and exploitation, ensuring that they do not stay in the same place too long while increasing their chances of getting the ball at each point. We found that the teams as a whole act in exactly the same way.”
The Lévy walk, of course, was seen when they were actively looking for the ball. Weirdly, further analysis showed that the team appeared to act like an individual entity.
“We found through statistical tests that the players exhibited Lévy walk when hunting for the ball – much like animals foraging for food. As soon as they got the ball, they deviated from Lévy walk, possibly due to the constraints of interacting with the ball,” Ivan Shpurov, first author and PhD student in the unit, added. “We saw the same behavior in the team’s centroid – the average position of all players – which suggests that the teams act as an individual agent when seeking possession of the ball.”
ADVERTISEMENT
Player movement tracked in an unrelated YouTube video.
The analysis looked at teams in the Japanese football league, J-League, and tracked the position of each player down to the centimeter, and how close they (and the team’s average position) was to the ball. They found that individual players who showed a more pronounced Lévy walk were closer to both the average team position and the ball itself.
“While we cannot conclude that Lévy walk is the hallmark of a good football player, it does suggest that players who strongly exhibit Lévy walk movement are more active and generally closer to the ball, and contribute better to the team dynamic,” Shpurov added.
Though the teams appeared to behave like foraging animals, or particles in a turbulent liquid, the team stresses that footballer behavior is more complicated than that. Nevertheless, it is intriguing that they appear to follow this pattern, with no conscious effort to follow this specific mathematical rule.
ADVERTISEMENT
“A football team is an entity that has a goal and can pursue it by modifying its behavior, both during the game and before it in the training process,” the team concludes. “It comes as no surprise then that the movement strategy that the ‘Team self’ adapts to optimize its performance shares statistical properties with the movement strategies adopted by individual ‘Selves’ who experience similar environmental pressures.”
The study is published in the journal Complexity.
Source Link: Lévy Flight: Football Teams Appear To Follow A Specific Mathematical Rule Without Realizing It