Over 50 years after the last time it was reported, researchers have rediscovered the sailback houndshark, stumbling upon the long-lost species during a survey of fisheries in Papua New Guinea.
If you haven’t heard of this shark before, don’t be surprised; not only has it been missing for a significant amount of time, but the last time it was reported to science was also the first time. It was collected in 1970 in northern Papua New Guinea, described in 1973 – and then appeared to vanish off the face of the Earth.
Even an extensive study of the sharks and rays of the country’s waters in the 2010s didn’t fish it up. Then, in 2020, a team with the World Wildlife Fund carried out a survey of artisanal and subsistence fishers in Madang that finally came up with the goods: photographs of not just one, but five sailback houndsharks. All were deceased females.
Another fisher came up trumps in September 2022, documenting the first-ever record of a male sailback houndshark (also deceased).
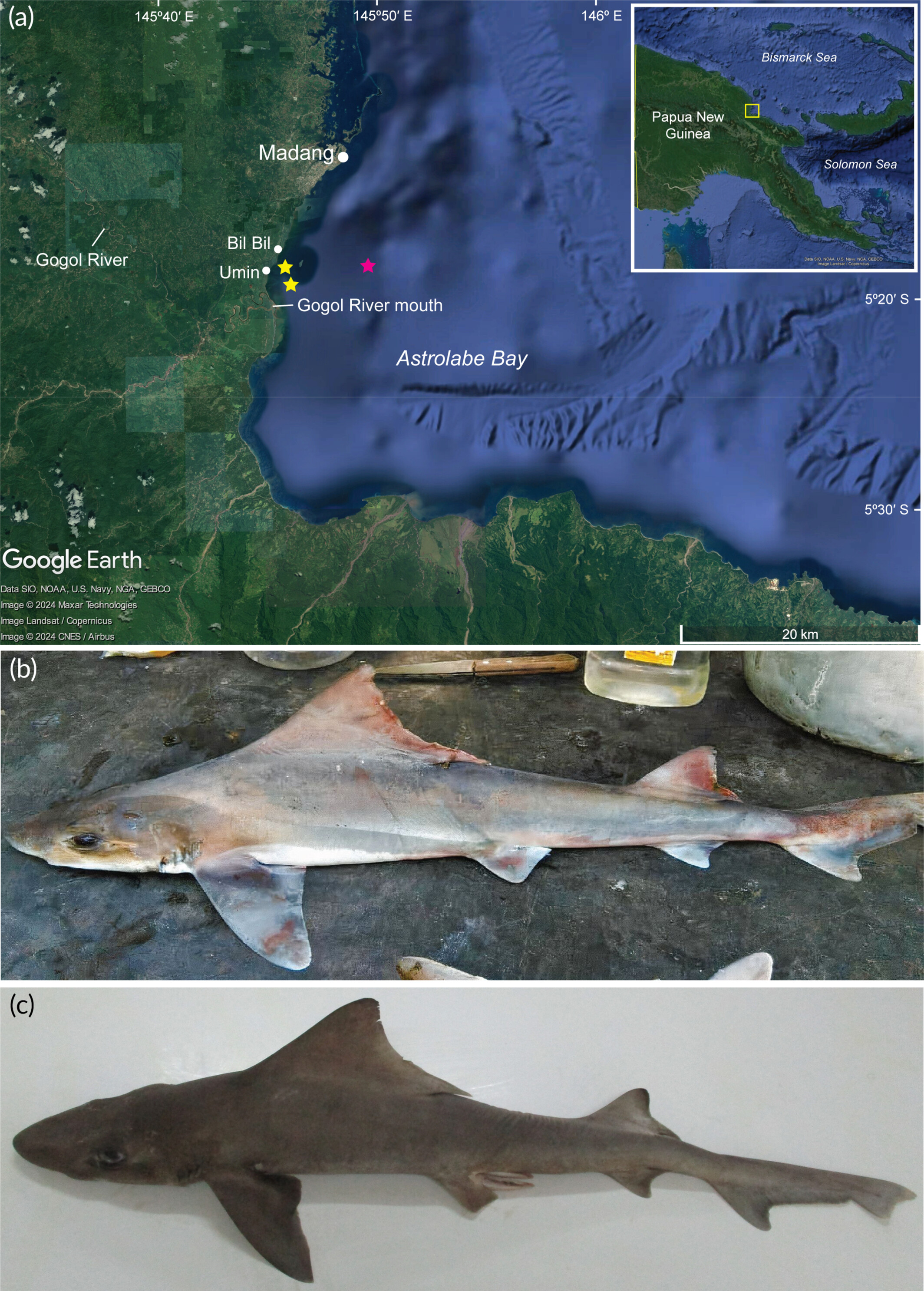
A. Map of Papua New Guinea showing the Astrolabe Bay area, where the sharks were found. B. One of the female specimens. C. The male specimen.
If informal reports are to be believed, it seems the previously “lost” species has been hiding under science’s nose all this time. “Anecdotal reports from fishers in Bilbil village and within Madang Lagoon indicate that the species is caught occasionally when fishing within Astrolabe Bay,” write the authors of the study detailing the rediscovery.
While it’s good news to know that this rare shark is still out there, the team also point to concerns about its future. They believe that the species could be restricted to a small area around Astrolabe Bay – a place that is seeing increasing interest in the trade of fish swim bladders, or fish maw. Sailback houndsharks could end up in the crossfire as bycatch.
“This possible micro-endemism could make this species susceptible to population declines from increased fishing effort in the future,” the authors explain, though they also mention that plans for monitoring and management of the sharks have already begun.
The sailback houndshark is one of many “lost” species that have been found again in recent years, but that doesn’t mean that their rediscovery is a simple process.
“It’s more of an exclusion process than anything else,” Sérgio Henriques, Indianapolis Zoo’s Invertebrate Conservation Coordinator, told IFLScience. Henriques is part of a team that rediscovered a tap-dancing spider after a 92-year disappearance.
“But in effect, [it involves] being on our hands and knees, looking at the ground. We put ourselves in a position where it’s likely, or it’s possible, that the spider is there, and then we just look really,” he continued.
“It’s just a matter of patience, perseverance, and just looking at clues in the environment over and over again. Over a course of hours, days, weeks. We just keep at it until we are lucky.”
The study is published in the Journal of Fish Biology.
Source Link: Long-Lost Sailback Houndshark Not Seen Since 1973 Rediscovered In Papua New Guinea