Scientists have found a strange warm liquid spewing out from the seabed “like a firehose” near Oregon, which they suspect could provide some hints about earthquake activity in the Pacific Northwest.
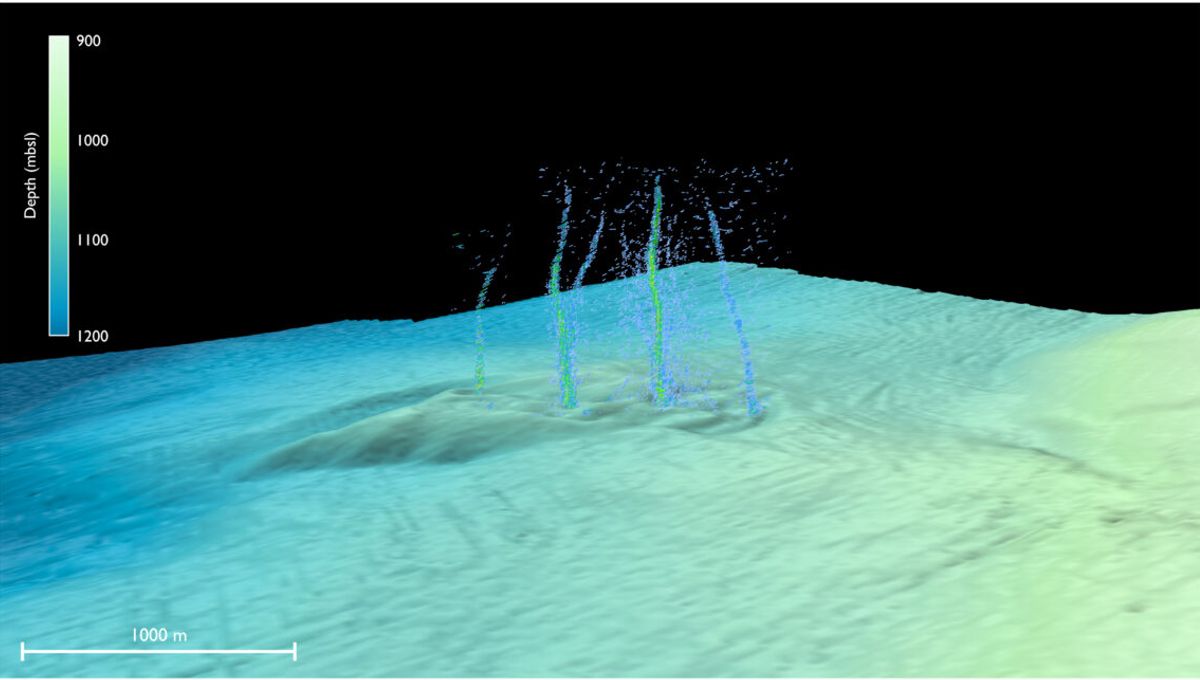
Researchers led by the University of Washington named the first-of-its-kind discovery Pythia’s Oasis. Located around 80 kilometers (50 miles) off the coast of Newport, the team used ship sonar to identify unexpected plumes of bubbles appearing from the seafloor, around 1.2 kilometers (three-quarters of a mile) beneath the ocean’s surface.
Upon further investigation, it was revealed that the liquid flowing out of the seabed was chemically distinct from the water around it, containing “extreme” amounts of boron and lithium, but notably less chloride, potassium, and magnesium.
“They explored in that direction and what they saw was not just methane bubbles, but water coming out of the seafloor like a firehose. That’s something that I’ve never seen, and to my knowledge has not been observed before,” Evan Solomon, study co-author and an associate professor of oceanography at the University of Washington, said in a statement.
Stranger still, the liquid was around 9°C (16.2°F) warmer than the background temperature. The stark temperature difference suggests that the liquid originated from the Cascadia megathrust deep beneath Earth’s surface, where temperatures are an estimated 150 to 250°C (300 to 500°F).
The massive Cascadia Subduction Zone is on a fault line between two giant tectonic plates. Given the deep subterranean origins of this warm liquid, the team suspects this liquid plays a role in the ever-shifting tectonic activity of Earth.
Solomon suggests that the fluid oozing from the fault zone is a bit like a lubricant, reducing friction between the plates and allowing them to glide gently against one another. As such, leaking lubricant could be a concerning sign that tension between the plates is increasing, upping the potential for an earthquake to occur.
“The megathrust fault zone is like an air hockey table,” Solomon explained. “If the fluid pressure is high, it’s like the air is turned on, meaning there’s less friction and the two plates can slip. If the fluid pressure is lower, the two plates will lock – that’s when stress can build up.
While these strange springs seem to be hard to detect, the researchers suspect that others may exist nearby. If they are a common feature, then perhaps they could over scientists with some insights into tectonic activity and even earthquake hazards.
“Pythia’s Oasis provides a rare window into processes acting deep in the seafloor, and its chemistry suggests this fluid comes from near the plate boundary,” added co-author Deborah Kelley, a University of Washington professor of oceanography. “This suggests that the nearby faults regulate fluid pressure and megathrust slip behavior along the central Cascadia Subduction Zone.”
The study is published in the journal Science Advances.
Source Link: Lubricant Is Leaking From The Seabed, And It May Be Raising Earthquake Risk