A team of researchers in California may have achieved something many of us could only dream of. According to a new preprint study, which has been approved for publication, the researchers claim to have created the first two-way control of a virtual object through lucid dreaming.
It is probably safe to say that, for as long as there have been dreamers, there have been efforts to understand dreams. Throughout recorded history, philosophers, theologists, and scientists from diverse cultures have all tried to interpret dreams and make sense of their broader and subjective meaning.
But today, there has been a shift in our approach to dreams. While many neuroscientists and psychologists continue to tackle how dreaming – and sleep more generally – actually works, there are others who are trying to understand how we can control them.
One way to achieve this may be through lucid dreaming. This is the state where a dreamer is aware they are dreaming and can exercise some level of control over the dream’s progression and content. Lucid dreaming was once regarded as a myth, but a meta-analysis of 34 studies conducted over 50 years has shown that not only is it very real, it is also more common than previously thought. According to this work, around 55 percent of people have experienced at least one incidence of lucid dreaming during their lifetime.
Research into lucid dreaming has become so advanced that scientists have even identified techniques that can help to induce it and gain greater control. This may sound like the stuff of sci-fi movies like Inception, but our understanding of how lucid dreaming works continues to develop at a fast pace. And now researchers believe they have found a way to put lucid dreaming to work in the waking world.
A research team with REMspace, a California-based startup, has been exploring the potential benefits of manipulating the power of lucid dreaming. Existing research has suggested that lucid dreaming could be used to help with various things, such as improving mood and decreasing depression, to addressing phobias, improving motor skills, and preventing nightmares. The researchers at REMspace even posit that mastery of lucid dreaming could be harnessed to “solve work or personal tasks while sleeping.”
Although there is a question here about work/life balance and the potential encroachment of working responsibilities into the very private realm of sleeping and dreaming, the team has nevertheless tested their hypothesis – with interesting outcomes.
In a laboratory study, the team wanted to know whether it was possible for a lucid dreamer to control real-life objects from their dream state.
“Since 1978, it has been known that people can send signals from [lucid dreams]”, the team wrote in their study, which is currently awaiting publication. “All that remains is to utilize these signals in scenarios to control virtual avatars, gadgets, programs, or real objects.”
But this is much harder than it sounds. “Sending signals from [a lucid dream] is not sufficient for full-fledged object control from [lucid dreamers] because two-way communication is required for this task.” To date, technology has not been a limiting factor here and despite some progress, researchers have not been able to demonstrate two-way object control. That is, until now.
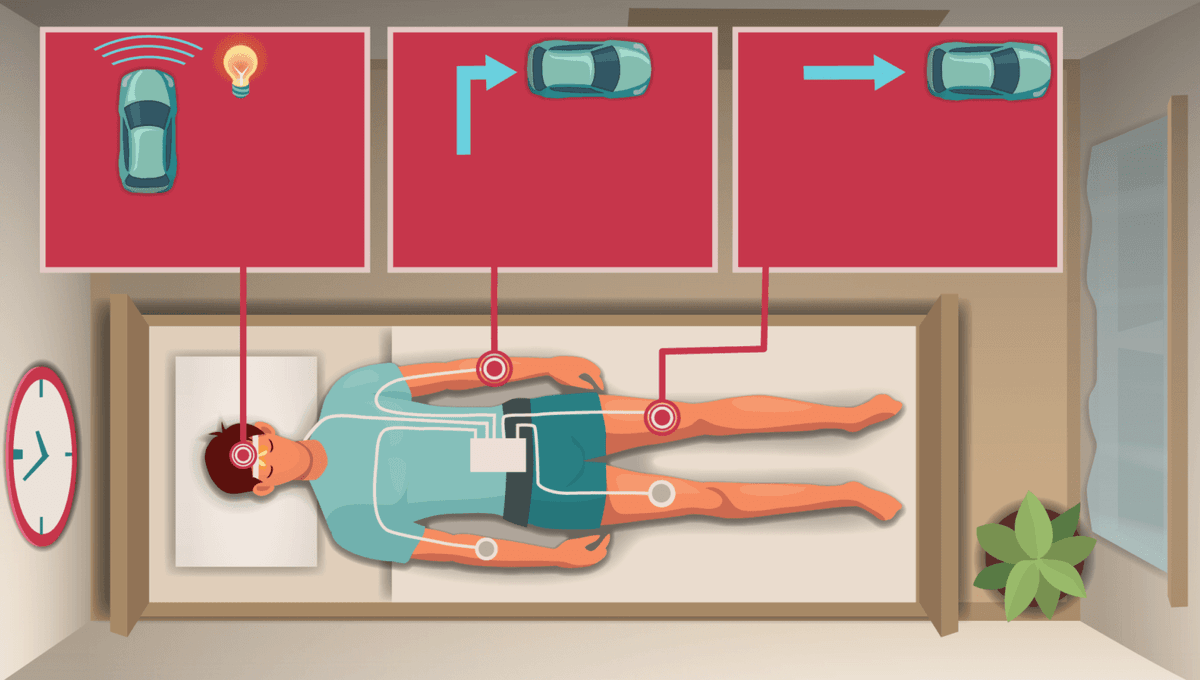
The REMspace team worked with five experienced lucid dreamers in a laboratory experiment where each individual was connected to specialized electromyography (EMG) sensors, which measure muscle and nerve responses.
Through this equipment, participants were able to move their legs while dreaming, which served as a signal to move a virtual avatar (a Cybertruck in this instance) on a computer screen. The dreamers could also move their hands to turn the car in order to avoid oncoming obstacles, which were communicated to them by sending light through the participant’s eyes.
All five of the participants were able to consciously control the virtual Tesla vehicle while asleep when their brains were in the REM sleep phase (which was confirmed by polysomnography).
During the experiment, the dreamers were able to control the virtual avatar for periods of time ranging from several seconds to several minutes. This is believed to be the first time two-way control has been established through an experiment.
“Two-way interaction with a computer from dreams opens up a whole area of new technologies,” Michael Raduga, the leader of the experiment, explained in a statement. “Now, these developments are crude, but soon they will change the idea of human capabilities.”
Back in 2023, REMspace researchers demonstrated the transmission of music and speech from dreamers. This latest study builds on this work and it is hoped that it will pave the way for more exploration to come. Towards the end of 2024, the company plans to launch the first device that gives people the ability to connect to the internet while they lucid dream.
The preprint study, which has been approved for publication, has been posted to PsyArXiv.
Source Link: Lucid Dreamers Able To Control Virtual Car While Asleep, Researchers Claim