A man browsing Google Maps whilst planning a camping trip in Quebec’s Côte-Nord region has potentially discovered the site of an ancient asteroid impact.
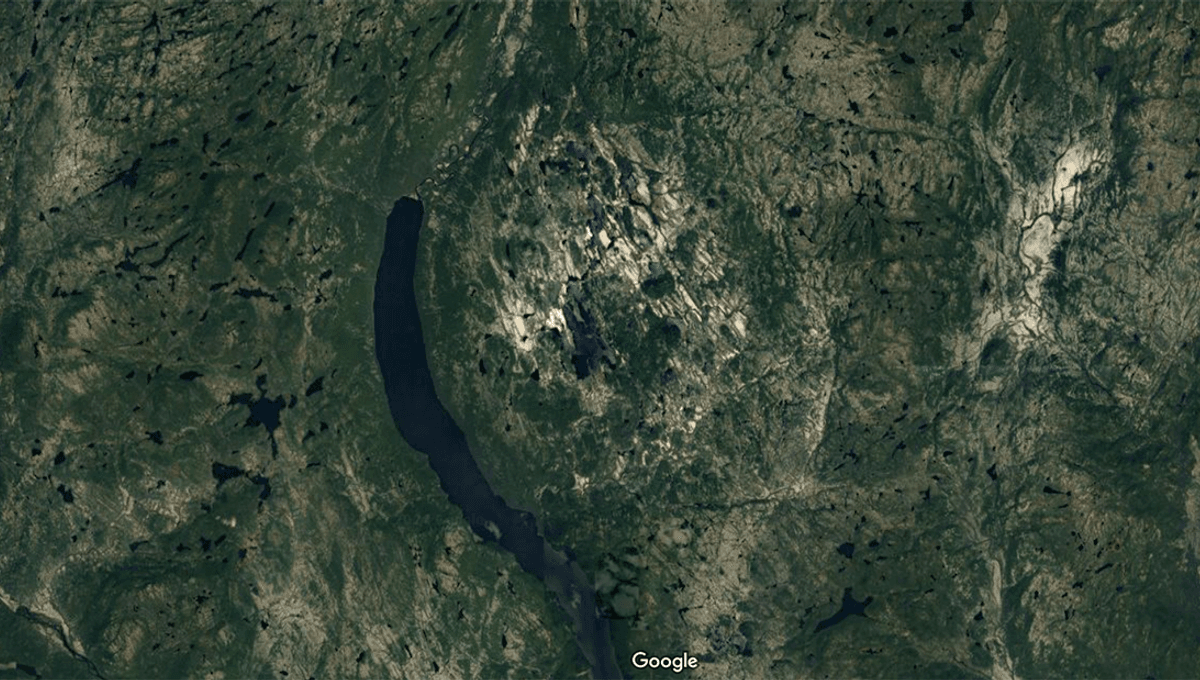
People have discovered all sorts of oddities while browsing through Google Maps, from “aliens” and camera-hogging cats to the answer to decades old cold cases. In the latest find, Joël Lapointe stumbled across an unusual, roughly spherical structure about 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) across surrounding Marsal Lake in Quebec.
Lapointe contacted geophysicist Pierre Rochette of the Centre de recherche en géosciences de l’environnement (CEREGE) in France for help identifying the strange feature.
While generally structures found on Google Maps can turn out to be nothing, the team has determined an ancient impact event could have caused it.
“Looking at the topography, it’s very suggestive of impact,” Rochette told Canadian news outlet CBC.
Intrigued, Rochette and colleagues took a closer look at the area, and now believe the ring of small mountains surrounding the lake may have previously been miscategorized.
“This formation, interpreted as a volcanoclastic diatreme formation named Marsal breccia, in an area devoid of post Grenvillian magmatism […] is in fact more in agreement with a crater floor clast-poor melt rock, quite similar to the Mistastin and Janisjarvi cases,” the team wrote in a new paper.
The area shows no sign of a gravity anomaly, where gravity is stronger or weaker than the expected value based on the amount of mass we believe to be in the area (think slightly denser or lighter rock). However, the team believes that the data isn’t fine-grained enough to distinguish an anomaly smaller than 10-15 kilometers (6.2-9.3 miles) in diameter, requiring further fieldwork.
While not confirmed, signs do look promising that Lapointe stumbled across an ancient impact event while idly browsing Google Maps. Looking at samples taken from the site, the team identified silicates, abundant magnetite, sulfides, and zircons, all promising indications of impact melt rock. Based on levels of erosion, the team estimates that the impact could have taken place between 450 and 38 million years ago.
“Based on the already available preliminary evidence, Lake Marsal seems to be a serious candidate to become the 11th confirmed impact structure from Quebec,” the team wrote, adding “confirmation of impact origin may be gained from the available sampling or else may wait for a future dedicated expedition.”
The team hopes to visit the site soon, to assess it for further evidence of an impact event.
The findings were presented in a paper at the 86th Annual Meeting of the Meteoritical Society 2024.
Source Link: Man Finds Unusual Spherical Structure While Browsing Google Maps. It Could Be A Huge Discovery