Antarctica, the icy continent, is experiencing a surprising transformation as its fringes turn green with plant life in the wake of warming temperatures. This remarkable change is vividly captured in a new map created by NASA’s Earth Observatory using data from archives of satellite imagery.
The amount of green vegetation on the Antarctic Peninsula has increased more than tenfold in less than 40 years. Between 1986 and 2021, the area of vegetated land on the Antarctic Peninsula increased from 0.86 to 11.95 square kilometers (0.33 to 4.61 square miles), according to a study published earlier this year.
The researchers arrived at these figures by trawling through data collected by the Landsat program, which has continuously acquired images of the Earth’s land surface since 1972.
In a new post, the team at NASA Earth Observatory has published a revamped version of the study’s data visualization.
Each hexagon represents 5,000 square kilometers (1,931 square miles) and is shaded according to levels of plant greenness and density. The observations were gathered in March each year, towards the end of summer in Antarctica, when plant growth is most extensive.
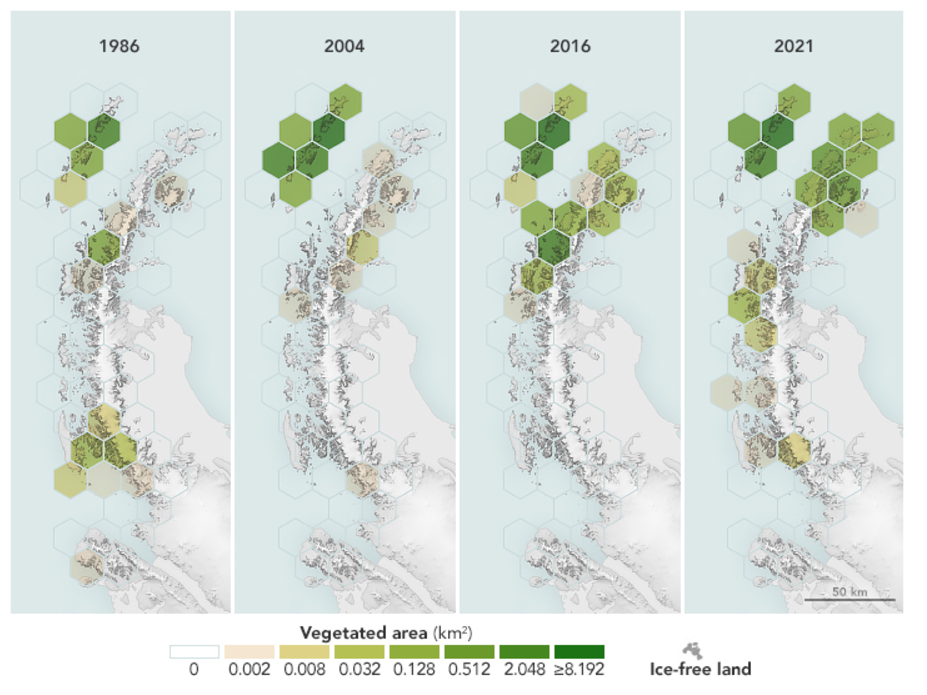
A map showing the increase in green vegetation on the Antarctic Peninsula in just 35 years.
Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory maps by Michala Garrison, based on data from Roland, T.P., et al. (2024).
“The plants we find on the Antarctic Peninsula – mostly mosses – grow in perhaps the harshest conditions on Earth,” Dr Thomas Roland, study author of the recent paper and environmental scientist from the University of Exeter, said in a statement.
“The landscape is still almost entirely dominated by snow, ice, and rock, with only a tiny fraction colonized by plant life. But that tiny fraction has grown dramatically – showing that even this vast and isolated ‘wilderness’ is being affected by anthropogenic climate change,” Roland continued.
The green revolution of Antarctica is being driven by climate change. As temperatures increase, glaciers and ice sheets are receding to reveal more land where plant life can grow. However, this isn’t exactly rich, fertile soil, so plant life tends to build up itself through several stages.
First, pioneering algae and cyanobacteria settle on the land and live between sandy grains, where they create a surface for other organisms to grow upon. Lichens and mosses use the surface to establish themselves and grow. Over time, larger plants use the damp mossy bed as a place for their seeds to germinate and grow.
Along with mosses, Antarctica has two native species of vascular plants: Antarctic hair grass and Antarctic pearlwort. While these two species were once relatively rare on the ice-dominated continent, they’ve become increasingly common in the past couple of years due to rising temperatures.
The continent has also been invaded by over 100 other plant species that are not native. This includes common lawn grass, which has rapidly spread over sub-Antarctic Islands and appears to be working its way down the Antarctic Peninsula.
Source Link: Maps Show Antarctic Is Turning Green With Plant Life – A Troubling Sign For The Planet