Across July 14-15, 1965 (depending on your time zone), the Mariner 4 mission was doing something incredible. This early NASA mission performed the first flyby of Mars and took the first close-up photograph of another planet. Space exploration was changed for good 60 years ago.
If we consider Mars alone, there are now multiple missions from multiple space agencies looking at the planet from orbit and from the ground. We have spacecraft around Jupiter, or crossing interplanetary space to reach Mercury or asteroids. There are cameras pointed at the Sun and the Moon, and much more. But it all started with Mariner 4.
The early exploration of the Solar System by humans is pretty fascinating stuff. There are fewer than eight years between Sputnik and Mariner 4, but so much happened in between that made the two approaches possible. On October 4, 1957, Sputnik became the first ever Earth Orbiter. The first lunar flyby is also another soviet success, Luna 1 in January 1959. The first image from space was taken by Luna 3, also launched on October 4, but in 1959.
At the same time, NASA is not sitting idle. Explorer 1 (1958) discovered the Van Allen radiation belts, Pioneer 4 (1959) performed a lunar flyby, and Pioneer 5 (1960) went into interplanetary space, confirming the presence of magnetic fields between the planets. The focus of the American and Soviet space programs in the 1960s was getting humans to the Moon, but when it came to science, the space agencies looked much further afield.
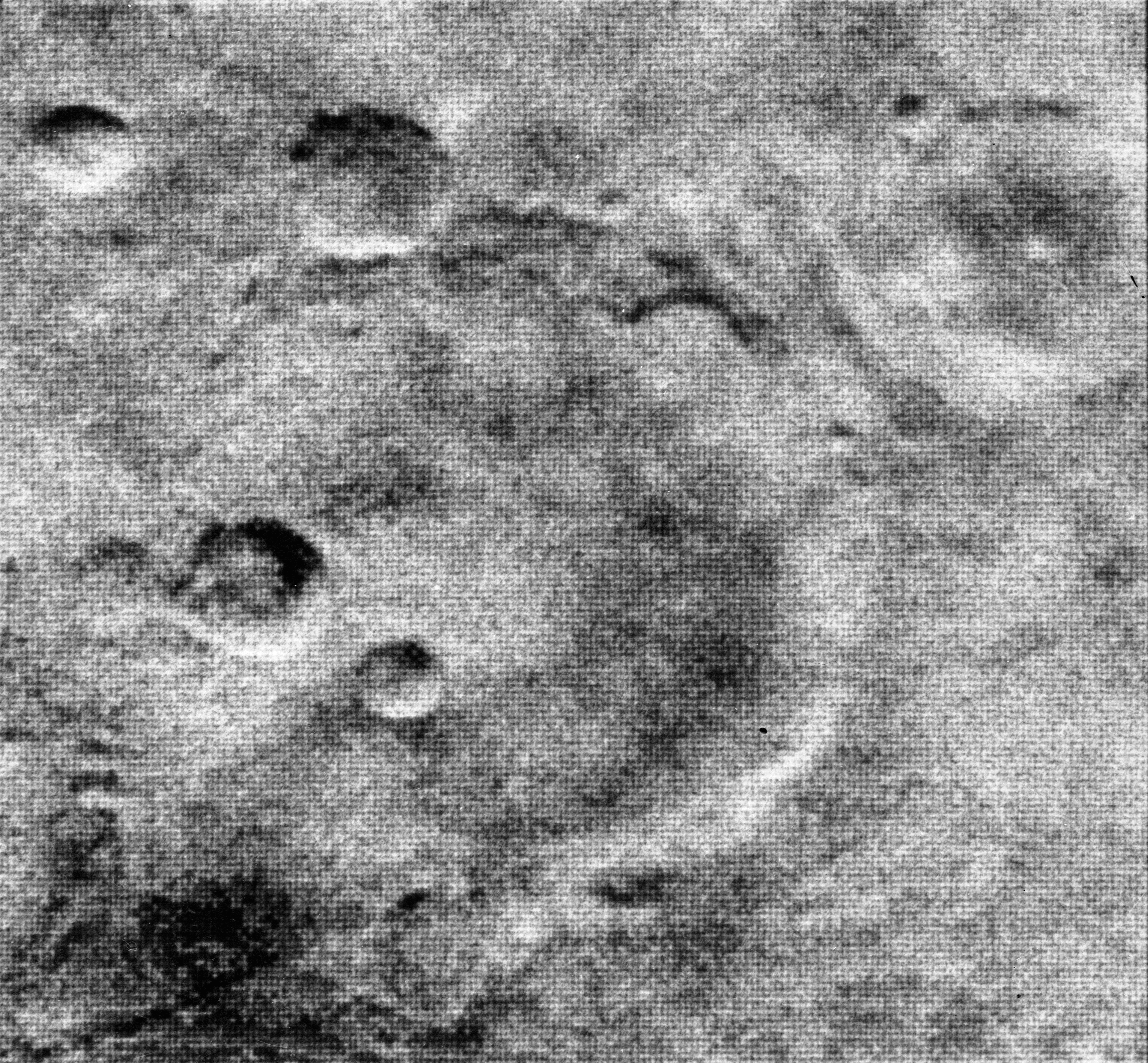
The clearest image of Mars taken by Mariner 4.
Image Credit: NASA
Both wanted to get to the planets whose orbits are the closest to us: Venus and Mars. The soviet Venera 1 was the first probe ever launched to another planet. On February 12, 1961 – two months exactly before Yuri Gagarin went to space – it flew toward Venus. Unfortunately, contact was lost before the intended flyby. Mariner 2 was instead successful in passing by on December 14, 1962, the first mission to ever encounter another planet.
Mariner 2 did not carry a camera. Mars 1, the soviet mission to Mars, launched after Mariner 2, instead had it. The first mission to Mars was lost before it made it to the Red Planet. Mariner 3 was also going to Mars with a camera, but a launch failure meant it only lasted eight hours in space.
So we get to Mariner 4, launched just three weeks after its predecessor (November 28, 1964), traveling across interplanetary space to get 9,846 kilometers (6,118 miles) from the surface of Mars, snapping the first photos of the Red Planet. And that is not all.
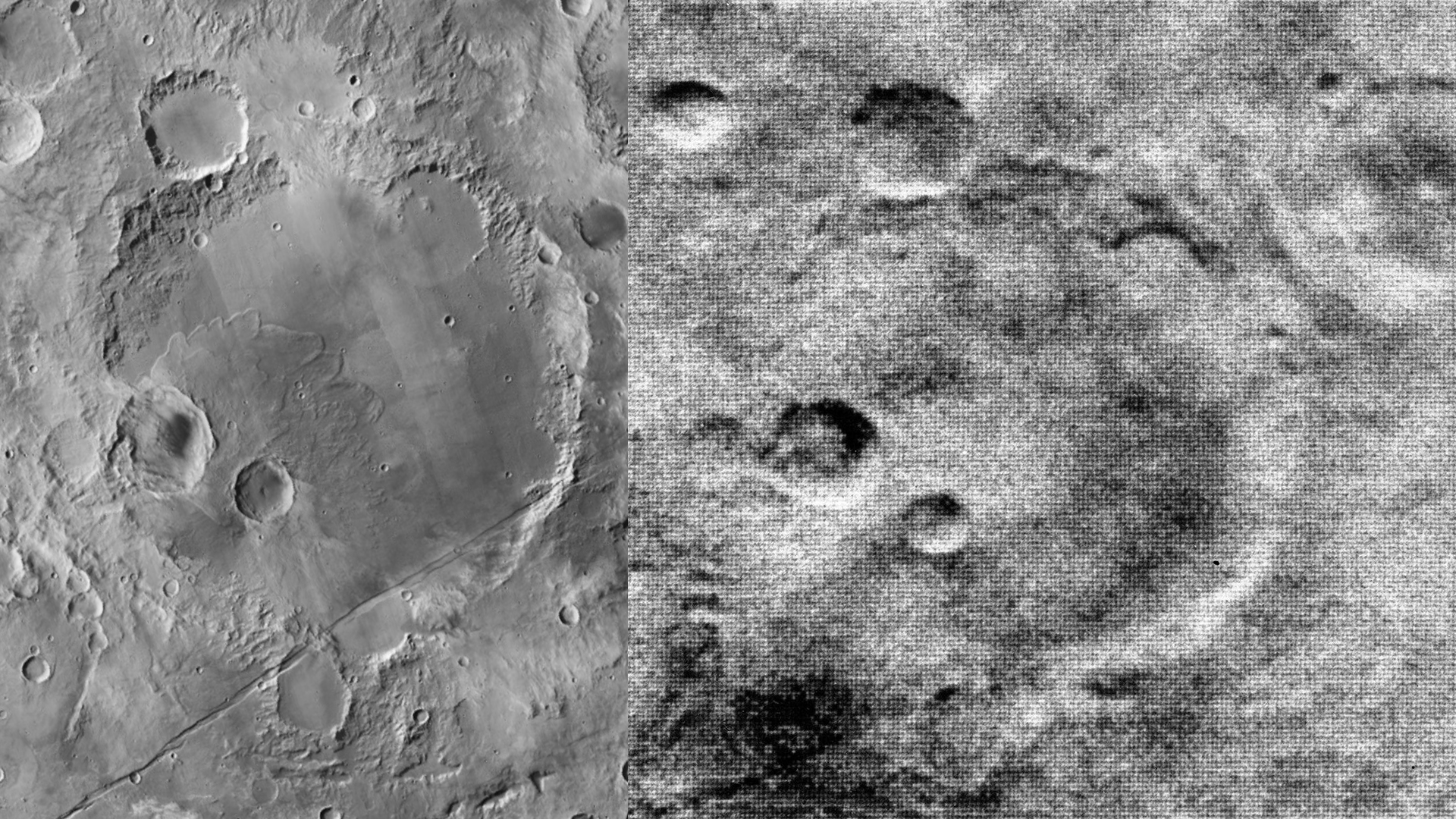

Imagery: NASA, JPL, MSSS, Caltech/Murray Lab, Esri | NASA/JPL/M2020 | NASA/JPL/MSL
Mariner 4 started the proud tradition of continuing to work long past its mission end. It was supposed to work for eight months, but the mission continued for just over three years, even conducting interplanetary measurements with Mariner 5, which met Venus in 1967. These missions seem almost too simple after decades of incredible investigations of other celestial bodies, but it is this work that made all the rest possible!
Source Link: Mariner 4: 60 Years Ago Today, NASA Changed How We Study The Solar System