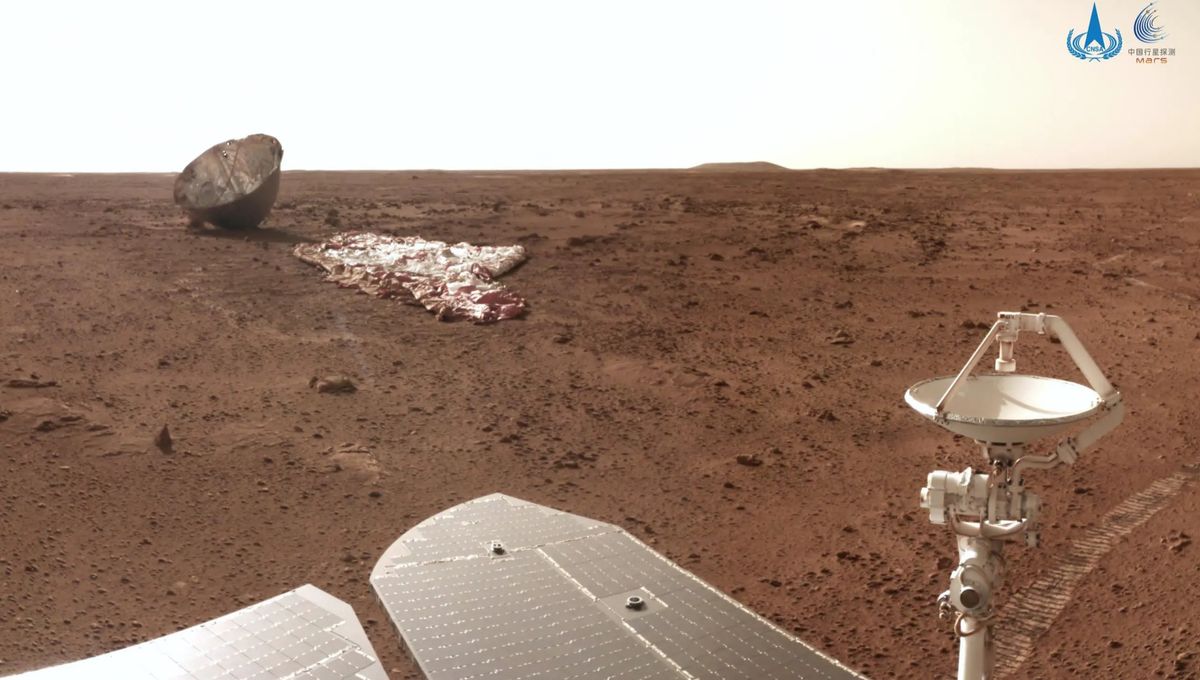
Liquid water may have been widespread on Mars as recently as 400,000 years ago, perhaps in the form of snowmelt in the planet’s iconic sandy dunes, according to new data from China’s Zhurong rover.
Zhurong has already transformed our understanding of Mars since the rover landed on the Red Planet back in early 2021. While we’ve known about the existence of ancient rivers and floods on Mars for decades now, it was long thought that the last of the liquid dried up some three billion years ago – to put that into some context, that’s around the same time as the very first single-celled organisms were figuring out photosynthesis down here on Earth.
Just last year, though, that estimate was blown out of the water – so to speak – when Zhurong discovered tentative evidence that liquid water may have been present on the planet as recently as 700 million years ago.
Even that revision, however, is nothing compared to how much the potential timeline of liquid water on Mars has now been moved up. Zhurong has spent the last couple of years investigating Utopia Planitia – a vast plain on the Martian surface which, at 3,300 kilometers across, forms the largest impact basin in the solar system – collecting data on the composition of the windswept dunes that litter the landscape.
What it has found “provides critical clues to future exploration missions searching for signs of extant life,” according to the Chinese Academy of Sciences team working on the mission. These dunes, it turns out, are coated with thin, cracked crusts and clumps of particles – features which can only be explained by the recent presence of liquid water, the scientists say.
“Sand dunes are a more modern landform,” Xiaoguang Qin, a scientist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and one of the authors of a new paper published Friday on the findings, told New Scientist. “These crusts on the dunes’ surfaces have solidified the sand dunes and stopped them moving.”
Rather than billions or hundreds of millions of years without liquid water, this new evidence suggests that the Red Planet may have been home to pockets of frost or snow between 1.4 million and 400,000 years ago – a strikingly recent time period, corresponding to a time at which archaic humans had already started roaming Europe.
It’s the presence of certain mineral deposits in the dunes which hint at the wintery origin of the water: analysis of the particles revealed substances such as sulfates, silica, iron oxide and chlorides. The most likely model for the creation of the cracks and crusts in the dunes, the team suggests in their paper, is, therefore, one in which “water vapor condensed as frost/snow on the dune surfaces when the temperature dropped below the frost point. Then, the frost/snow on salts in between the sand grains would thaw to eventually form saline water.”
After that, they explain, “the saline water would vaporize, and salts precipitate… thus agglomerating particles and forming crust. Then, continued drying or freezing would develop cracks within the crust.”
This was only possible due to Mars’s changing axial tilt, Qin explained: a few million years ago, the planet’s poles were pointed more directly at the sun, causing the ice caps to release high amounts of water vapor which condensed as snow closer to the equator. While “no water ice was detected by any instrument on the Zhurong rover,” Qin told Space.com, this model nevertheless “offers a replenishing mechanism for vapor in the atmosphere to form frost or snow at low latitudes where the Zhurong rover has landed,” he said.
While there’s still the possibility that these dunes were created by some other, unknown geological processes, other researchers have found the team’s arguments convincing. If correct, it means not just a massive rethink of the Martian geological timeline, but also its geography – as, since sand dunes are so ubiquitous across the planet, there may be far more evidence of modern water on Mars than previously known.
“The phenomenon was documented at one site,” Manasvi Lingam, an assistant professor of astrobiology at the Florida Institute of Technology who was not involved in the research, told Space.com. “But it should be applicable to a fairly large fraction of Mars’ surface at similar latitudes.”
The discovery is detailed in the journal Science Advances.
Source Link: Mars May Have Seen Snow As Recently As 400,000 Years Ago, Zhurong Rover Suggests