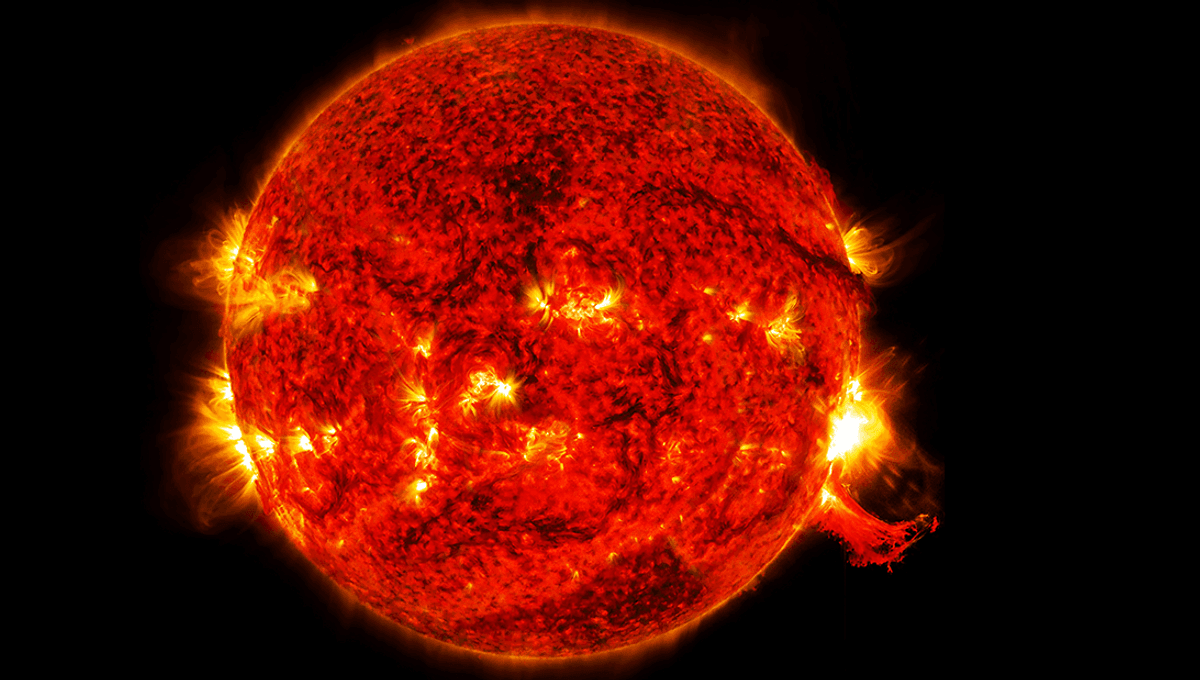
An eruption that appeared to cover “over half the Sun” has been captured in videos produced by NASA and solar physicist Keith Strong.
The eruption, which took place on Saturday, saw a large filament released from the Sun’s surface. Known as a coronal mass ejection (CME), electrically charged plasma was sent out from the Sun, some of it heading right at Earth.
NASA captured its own footage of the eruption.
The large filament eruption had been forecast by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), which issued a geomagnetic storm watch in anticipation of the plasma reaching Earth. Such storms can cause havoc with Earth’s communication systems.
“The main source of space weather is the Sun,” Dr Nigel Meredith of the British Antarctic Survey explained to IFLScience in a recent episode of our podcast The Big Questions.
“We have explosions on the surface of the Sun, they send out bursts of charged particles and magnetic field into space and when they reach the Earth, they can tear open the geomagnetic field, giving rise to a geomagnetic storm and this can cause disruption to satellites, to communication and navigation signals, to aviation, and also to power supplies. The nature of this risk is such that severe space weather was added to the UK national risk register back in 2012.”
The storm, which hit Earth 12 hours earlier than anticipated, was moderate as predicted.
Sun activity increases and decreases in an 11-year cycle known as the Schwabe cycle. From 1826 to 1843, German amateur astronomer Heinrich Schwabe observed the Sun, discovering that it rotates on its axis once every 27 days. He noticed the Sun goes from quiet periods, where no sunspots can be seen, to the maximum phase where 20 or more groups of sunspots can be seen.
The Sun’s activity, including coronal mass ejections and sunspots, is increasing at the moment, with the next solar maximum predicted to be around July 2025. Another team that looked at the activity of magnetic “donuts” during this cycle, however, believes that they have a better prediction and that the solar cycle may peak a whole year early.
[H/T: Insider]
Source Link: Massive Eruption Covering "Half The Sun" Causes Geomagnetic Storm On Earth