A large mass of granite that has been slowly releasing heat has been discovered buried underneath a crater on the Moon. This is not science fiction, it’s ancient volcanism. The Moon used to have lava fields and eruptions, but astronomers had never actually found a more traditional Earth-like volcano – until they looked at what was beneath the Compton and Belkovich craters on the far side of the Moon.
Granite is not very common outside of Earth so finding it on the Moon is very exciting. On our planet, it forms deep beneath the surface, usually under a volcano where magma can cool down and crystalize. To make granite, having water and plate tectonics helps a lot. The team used a combination of data from Chinese and American lunar orbiters to discover this heat-emitting mass below the surface, identifying a volcanic process never before seen on the Moon.
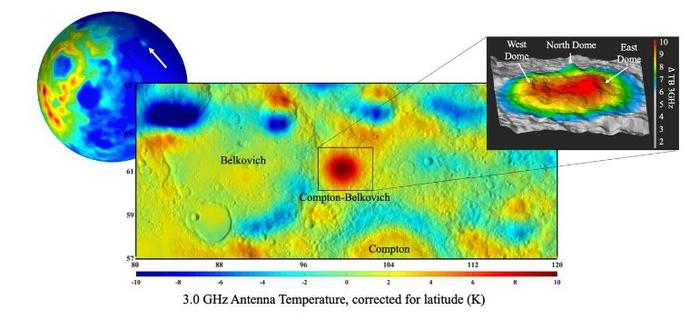
“Using an instrument looking at microwave wavelengths – longer than infrared – sent to the Moon on both the Chinese Chang’E 1 and 2 orbiters, we have been able to map temperatures below the surface. What we found was that one of these suspected volcanoes, known as Compton-Belkovich, was absolutely glowing at microwave wavelengths,” co-lead researcher Dr Matt Siegler, of the Planetary Science Institute, said in a statement.
“What this means is that it is hot, not necessarily at the surface, as you would see in infrared, but under the surface. The only way to explain this is from extra heat coming from somewhere below the feature within the deeper lunar crust. So Compton-Belkovich, thought to be a volcano, is also hiding a large heat source below it.”
Evidence of a new volcanic process on the Moon discovered.
Image Credit: Siegler at al, Nature July 2023
The data shows a 20-kilometer (12-mile) wide silicon-rich surface feature that they believe is the caldera of this ancient volcano. The temperature there is 10°C (18°F) warmer than its surroundings, but it’s not from magma under the surface – the last time, the volcano erupted was 3.5 billion years ago – it’s from radioactive elements that were stuck in the rocks.
“We interpret this heat flux as resulting from a radiogenic-rich granite body below the caldera,” Dr Siegler said. ” To tell the truth, we were a bit puzzled when we found it: fortunately, my wife, Dr Rita Economos, is the geochemist in the family, so with her guidance, we were able to piece together the probable geologic cause of the heat anomaly.”
As Dr Economos explains: “This find is a 50km wide batholith; a batholith is a type of volcanic rock that forms when lava rises into the earth’s crust but does not erupt onto the surface. El Capitan and Half Dome, in Yosemite in California, are examples of similar granite rocks which have risen to the surface.”
The presence of such a large granite deposit where you don’t expect it suggests that there could be other areas of the Moon where granite can be found. Perhaps elsewhere in the Solar System, too.
The findings were reported in the journal Nature.
Source Link: Massive Heat-Emitting Mass Discovered Buried Under The Surface Of The Moon