For beings of our size and lifespans, space is pretty big. So big, in fact, that to make it to our nearest star system you would need to factor in the fairly sizeable downside that you will die of old age before you get there.
Humanity has focused on making our spaceships more speedy, as well as the possibility of sending smaller, uncrewed lightweight ships to the system potentially within human lifespans. But if we want to send humans to the star system in the future (or go on other long-distance trips) we may have to accept that it will take several human lifespans to get there.
With the restraints placed upon them by physics, sci-fi writers have imagined “generational ships” for decades. The idea is pretty simple: creating a ship that will sustain a small society of humans for however many generations it takes to get to the intended destination. But in practical terms, such a mission would be pretty complex.
For a new competition exploring the practicalities of generational ships, dubbed Project Hyperion, scientists competed to design their own ship which could feasibly take humans to a hypothetical habitable planet at least 250 years away in terms of travel time. The winning team went one step further, designing a spaceship named “Chrysalis” which they propose could deliver thousands of people to Alpha Centauri, a trip taking over four centuries.
From the outside, the ship has a very simple design, looking like a giant tube. While other entries were more elaborate, the team chose this design to ensure safety for the occupants during acceleration at speeds up to 0.01 percent of the speed of light (c).
“A long cylindrical shape and geometry minimises the frontal section and MMOD shielding and reduces structural stresses during the linear acceleration and deceleration phases,” the team explains in their submission. “The majority of the spaceship mass is the liquid propellant for the [acceleration phase] and, to a lesser extent, the [deceleration phase], contained in the spaceships’ cylindrical tanks (mass sizing is presented in the next slide). The habitat module is contained in the inner core of the front module structure.”
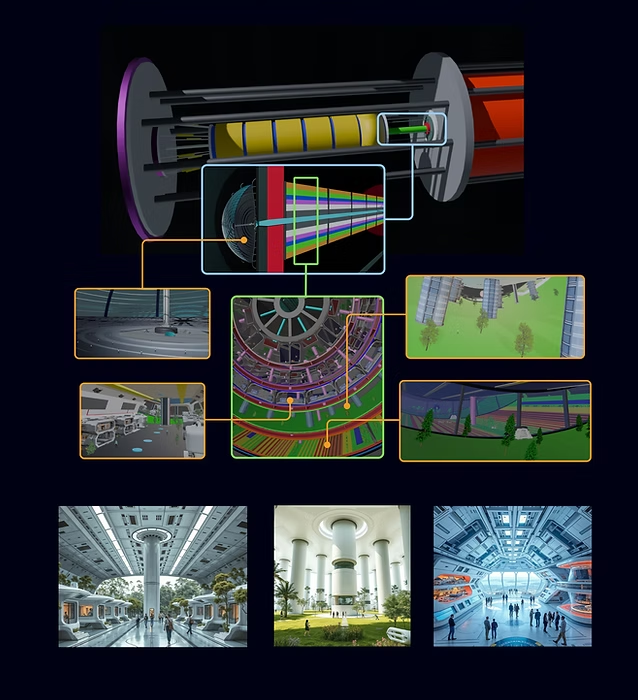
The ship’s interior would rotate to produce artificial gravity.
Image credit: Giacomo Infelise, Veronica Magli, Guido Sbrogio’, Nevenka Martinello, Federica Chiara Serpe, Project Hyperion
To counteract the issues humans may experience when missing gravity for a large chunk/entirety of their lifetime, the ship would use rotating interior shells to create artificial gravity using the centrifugal force. This is only possible with a large ship, as with smaller ships it could create a lot of discomfort and potentially health problems for the crew (voluntary, and later involuntary).
“The smaller the space craft is, the faster it has to rotate, so if you’re going to generate gravity, it’s got to be done with a very large spacecraft that spins very slowly. The bigger the disk, the slower you can rotate it,” John Page, a senior lecturer in the School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering at the University of New South Wales, explained to ABC Science.
“This would avoid having a large gravitational difference between your head and your feet, which would result in blood accumulating at your feet and making you feel light headed.”
Building a structure that will initially hold over 1,000 humans (and later more as they produce more humans) would be quite some effort. In total, the ship would have a mass of around 2,400,000,000 tons, and measure over 58 kilometers (36 miles) from end to end. As such, they proposed that it be built in Lagrange point 1 between the Earth and the Moon.
“Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system like the Sun and Earth produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion,” NASA explains. “These can be used by spacecraft as ‘parking spots’ in space to remain in a fixed position with minimal fuel consumption.”
The team estimates that construction would take 20-25 years, which is a fair amount of time but peanuts when you know that it won’t be you who completes the mission, but your descendants. In fact, the team suggests that before launch the initial generations of inhabitants should spend 70-80 years living into the Antarctic to adapt the society to life in an isolated environment. This, they believe, will be the key challenge of such a mission.
“The personal decision to volunteer for an interstellar mission should be of paramount importance to its inhabitants. Abandoning Earth could have dramatic psychological consequences in the long term. When designing the starship, we considered these issues with the clear understanding that, for the future inhabitants of Chrysalis, feeling part of an epic and sacred journey for humanity will be crucial,” the team explains, questioning what it would be like to arrive at a new exoplanet, a journey started by the crew’s ancestors.
“Perhaps future generations will be so accustomed to life in deep space that the prospect of landing on a new planet will seem irrelevant, and they will instead feel as though they are unique beings with their own spaceship home,” they add. “They will be creatures of the cosmos – a new line of evolutionary development in deep space, formed through the symbiosis of humans, advanced technologies, artificial intelligences, and cyberspace in a confined biosphere.”
The team put some thought into how these societies should operate.
“Chrysalis is not only a physical environment but also a cognitive space for the inhabitants: the phenomenological aspect of living and dwelling in the deep space, what is experienced, the psychological meaning of being a creature of the Cosmos is central in the design of the spaceship,” they wrote in a statement. “Chrysalis is a living spaceship where humans, robots and artificial intelligent agents (AI-agents) share information, experiences and decision-making processes.”
The design won the competition, with the jury praising how the team’s design copes with radiation, as well as the thought they put into the spacecraft’s construction.
“The presentation is rich and visually engaging, drawing comparisons to iconic works like Rama, and showcasing a clear passion for both design and storytelling,” the jury wrote. “Its overall spacecraft design seems to take inspiration from the gigantic world ship concepts of the 1980s.”
While very much a concept design and not something humanity is planning on doing – we haven’t even got to Mars yet – it’s good to know that if we ever have to leave our Solar System, at least we have options.
Source Link: Meet Chrysalis, The Generational Ship Designed To Take Humans On A 400-Year Trip To Alpha Centauri