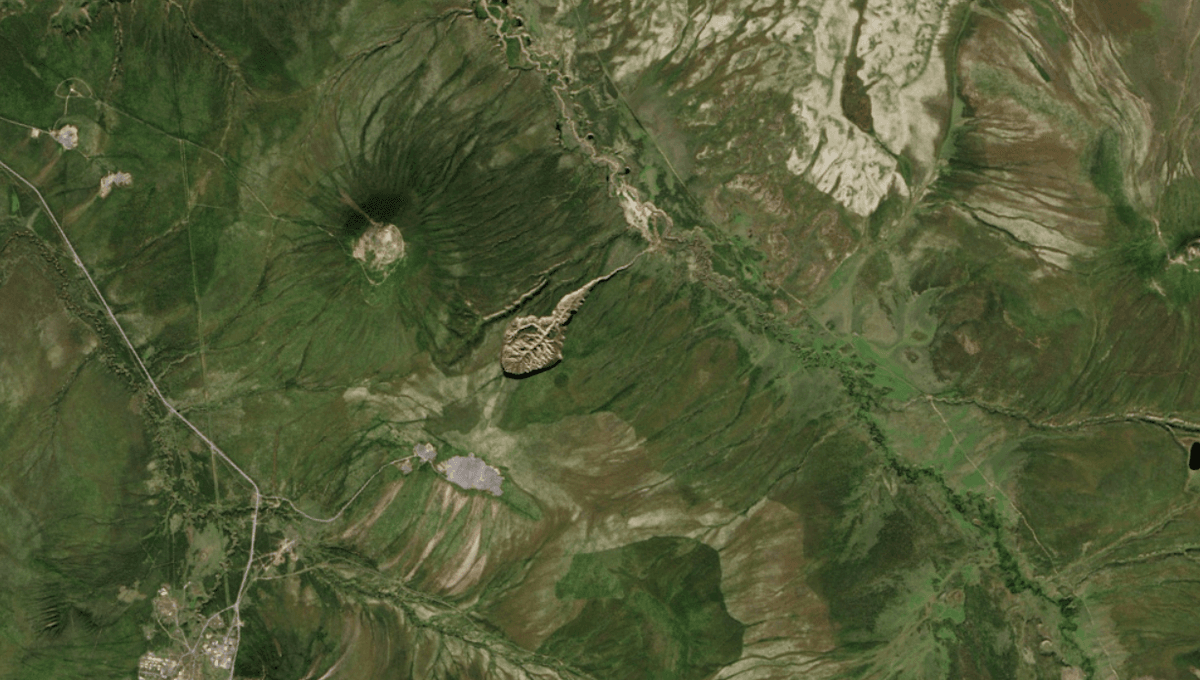
The Batagaika Megaslump is the biggest geological feature of its kind (at least that scientists know about). It sticks out of the Siberian wilderness like a tadpole-shaped slash in the land, surrounded by the green boreal forests of rural Russia. While this so-called “Gateway to Hell” is exceptional in its size and stature, it’s not the only climate-triggered slump that has scarred the planet’s surface in recent decades.
The term “megaslump” is not widely used by geologists and doesn’t have any strict scientific definition. However, it derives from the well-known term “slump,” which denotes a loosely consolidated mass of material or rock that’s stumbled down a hillside, cliff, or shoreline.
They’re typically the result of land being disturbed by earthquake shocks, melting or thawing, or undercutting from a river. When these tumbling landslides occur in Arctic areas as a result of ice-rich sections of the land melting, they’re called retrogressive thaw slumps.
The Batagaika crater – by far the largest known example of a retrogressive thaw slump – is often nicknamed a megaslump simply because of its sheer size. The trail of debris currently runs 100 meters (328 feet) deep and stretches for around 1 kilometer (0.6 miles), covering an area of 77 hectares (190 acres).
It’s found in Russia’s Sakha Republic between the settlements of Batagay and Ese-Khayya among the Chersky Range of mountains, an area that’s rich in permafrost.
It looks like a wound from a cataclysmic event in the distant past, but the slump only emerged a few decades ago due to warming temperatures – and it’s continuing to grow even to this day.
Permafrost in the soil was neatly holding the land together, but warming temperatures turned this icy cement into water. The land loosened and gave way, causing a deluge of debris to lead downhill toward the floodplain of the Batagay River.
As the land continues to slump, more frozen soil is exposed to the warmth, causing the size of the slump to grow. Some research suggests it could be expanding at a rate of 10 to 30 meters (33 to 98 feet) per year.
Beyond Batagaika, there are other retrogressive thaw slumps that are sometimes called megaslumps. According to the Northwest Territories Geological Survey, some of the largest megaslumps ever have been reported on the Peel Plateau, east of the Richardson Mountains in northern Yukon, Canada.
Russia, however, is considered to be a hotspot, as permafrost occupies nearly 65 percent of its territory.
Climate change is rapidly driving the emergence of new permafrost thaw slumps. One study found thousands of climate-triggered landslide slumps in a High Arctic environment over recent decades. Their findings suggest there was a 60-fold increase in numbers between 1984 and 2015, primarily following four especially warm summers.
Given the mounting impact of the climate crisis, especially in the Arctic, these slumps are unlikely to be the last. Whether or not we’ll see anything on the scale of the Batagaika megaslump isn’t possible to predict, but it’s safe to bet we could see the emergence of climate-triggered slumps that join its ranks in the years ahead.
All “explainer” articles are confirmed by fact checkers to be correct at time of publishing. Text, images, and links may be edited, removed, or added to at a later date to keep information current.
Source Link: Megaslumps Explained: Their Impact And Threat To Earth's Future