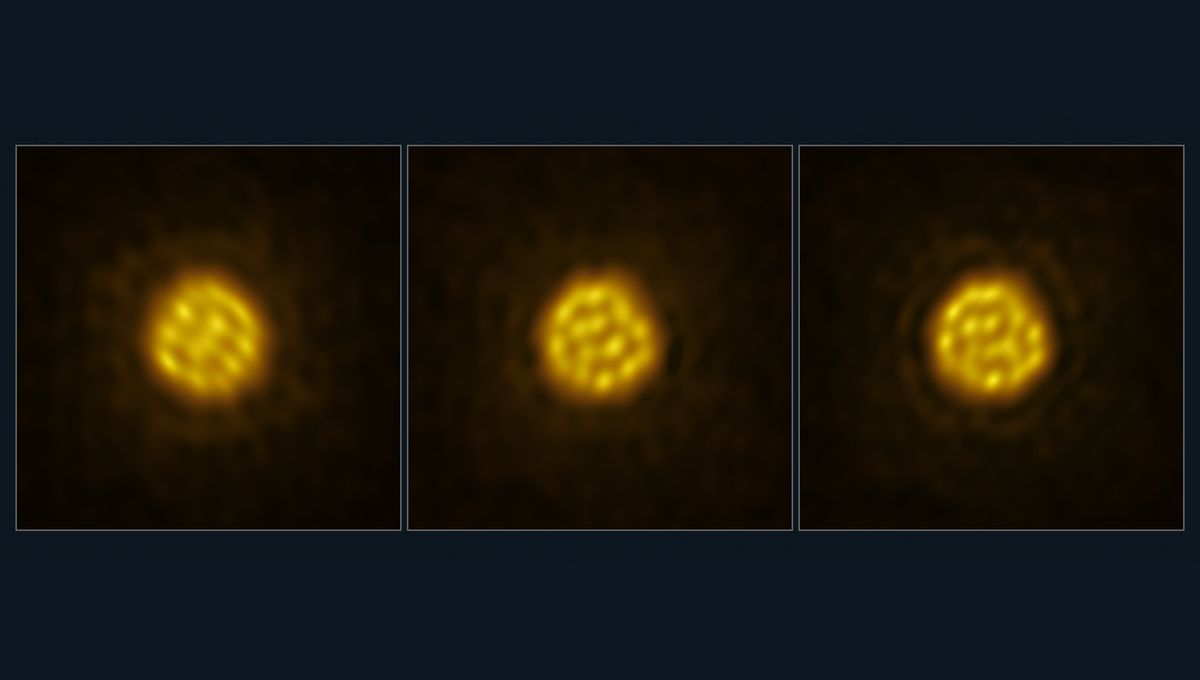
Astronomers have seen bubbles on the surface of red giant star R Doradus for the first time. This is the first time scientists have observed such incredible details on the surface of a star that is not the Sun.
R Doradus is a variable red giant star. It has a volume over 5 million times that of our Sun but has roughly the same mass. This means that its outer layers are more loosely bound to the star and the convection cells that move the plasma around – a bit like a lava lamp – change the surface more dramatically. So much so, they are visible from 180 light-years away.
“This is the first time the bubbling surface of a real star can be shown in such a way,” lead author Wouter Vlemmings, a professor at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, said in a statement. “We had never expected the data to be of such high quality that we could see so many details of the convection on the stellar surface.”
These convection cells are enormous – each is about 75 times the size of the Sun. As the stars produce energy in their cores, hot plasma rises and cool plasma falls, creating these visible structures on the surface. They can be seen on the Sun (tiny compared to R Doradus) but had never been seen on another star before.
“Convection creates the beautiful granular structure seen on the surface of our Sun, but it is hard to see on other stars,” added co-author Theo Khouri, also at Chalmers. “With ALMA, we have now been able to not only directly see convective granules – with a size 75 times the size of our Sun! – but also measure how fast they move for the first time.”
The convection granules seem to move with a month-long cycle. That’s faster than scientists expected based on the Sun. But the Sun is a main sequence star; it won’t become a red giant for many billions of years.
“We don’t yet know what is the reason for the difference. It seems that convection changes as a star gets older in ways that we don’t yet understand,” added Vlemmings.
The team studied the star in July and August 2023 using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). The ability to study the internal motions of stars beyond the Sun is key to understanding just how typical – or not – our little yellow star is. Thanks to these observations, humans are directly probing the convection processes.
“It is spectacular that we can now directly image the details on the surface of stars so far away, and observe physics that until now was mostly only observable in our Sun,” concludes Behzad Bojnodi Arbab, a graduate researcher at Chalmers who was also involved in the study.
The study is published in the journal Nature.
Source Link: Moving Bubbles On The Surface Of Another Star Seen For The First Time