Not all stellar flares are the same. They are usually a brief brightening of a star – but for FU Orionis (FU Ori), located 1,200 light-years from Earth, the brightening has turned into an 85-year-long emission that is a trillion times more powerful than the largest Solar flares ever detected, and there is no sign of stopping. The cause for this incredible event seems to finally be clear: the extreme evaporation of a planet.
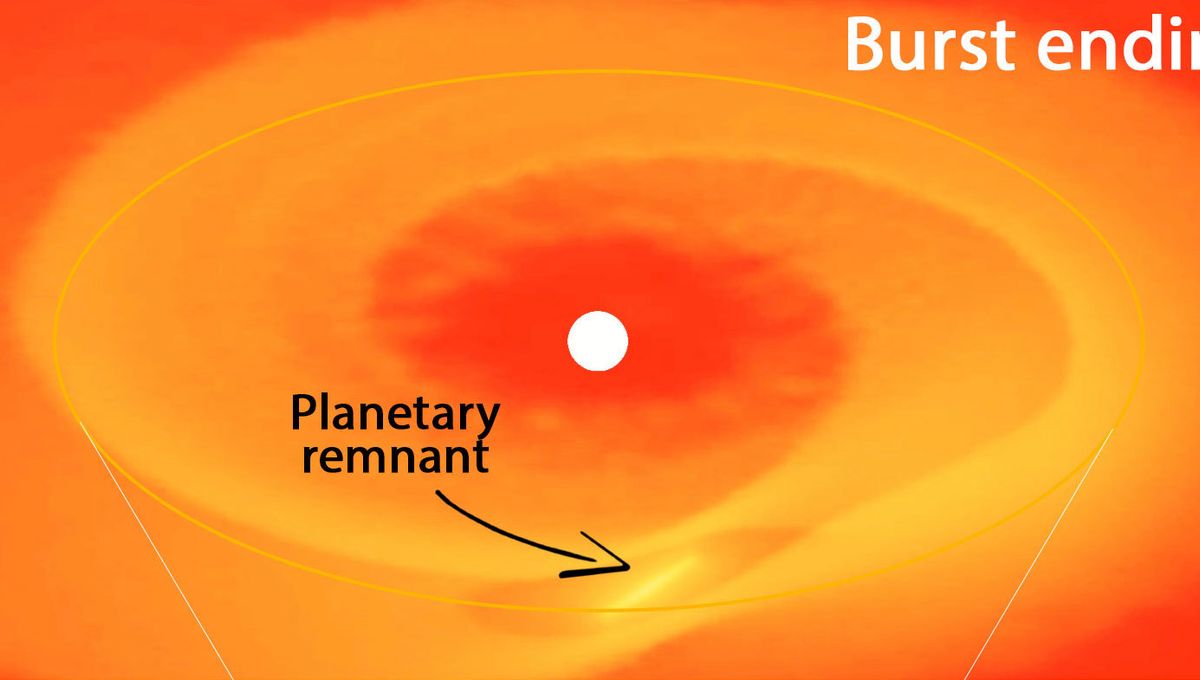
Researchers believe that a planet about 10 times larger than Jupiter had the misfortune to get too close to its fledgling star. The young star is boiling the planet apart, and the material lost in this literal inferno is being flung onto the star, producing this continuous and extreme flare.
Protostars, the initial stages of stellar life, feed on the protoplanetary discs that surround them. However, the details were not clear on how, from these discs, you could get something as extreme as FU Ori.
“These discs feed growing stars with more material but also nurture planets. Previous observations provided tantalizing hints of a young massive planet orbiting this star very close. Several ideas were put forward on how the planet may have encouraged such a flare, but the details did not work out. We discovered a new process which you might call a ‘disc inferno’ of young planets,” lead author Professor Sergei Nayakshin from the University of Leicester said in a statement.
The simulation constructed by the researchers showed a planet forming far from the star and migrating inward. Once the distance between the planet and the star is less than a tenth of the Earth-Sun distance, things go bad. The material in the disc at that distance around such a young star is so hot that it sets the whole planet alight, burning through its atmosphere. The planet itself becomes food for the star.
“This was the first star that that was observed to undergo this kind of flare. We now have a couple dozen examples of such flares from other young stars forming in our corner of the Galaxy. While FU Ori events are extreme compared to normal young stars, from the duration and observability of such events, observers concluded that most emerging solar systems flare up like this a dozen or so times while the protoplanetary disc is around,” study co-author Dr Vardan Elbakyan, also Leicester-based, added.
The team believes that if the model is correct, it might change how we think of young star systems. They are no longer places of placid growth, with planets slowly getting bigger. They would be violent and chaotic, with many young planets burning for their stars.
The work was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Source Link: Mystery Of Flare A Trillion Times More Powerful Than The Largest Solar Flares Solved