There’s a dusty old rumor that duck quacks don’t echo. You might’ve heard it, you might’ve read it, you might even have watched the British comedy show Duck Quacks Don’t Echo that was named after it.
The concept is pretty simple: take a duck and put it in an echoey space, make it quack, and marvel at the quirk of nature. Only there’s one downside, it’s not true.
Duck quacks don’t echo: Myth
You may have anecdotal evidence that a duck’s quack does echo, perhaps from a walled corner of the park or after getting cornered in an alleyway by some urban-dwelling waterfowl. Just to settle the argument for sure, scientists came up with some concrete acoustic data to prove that yes, duck quacks do echo, even if they are a little hard to hear.
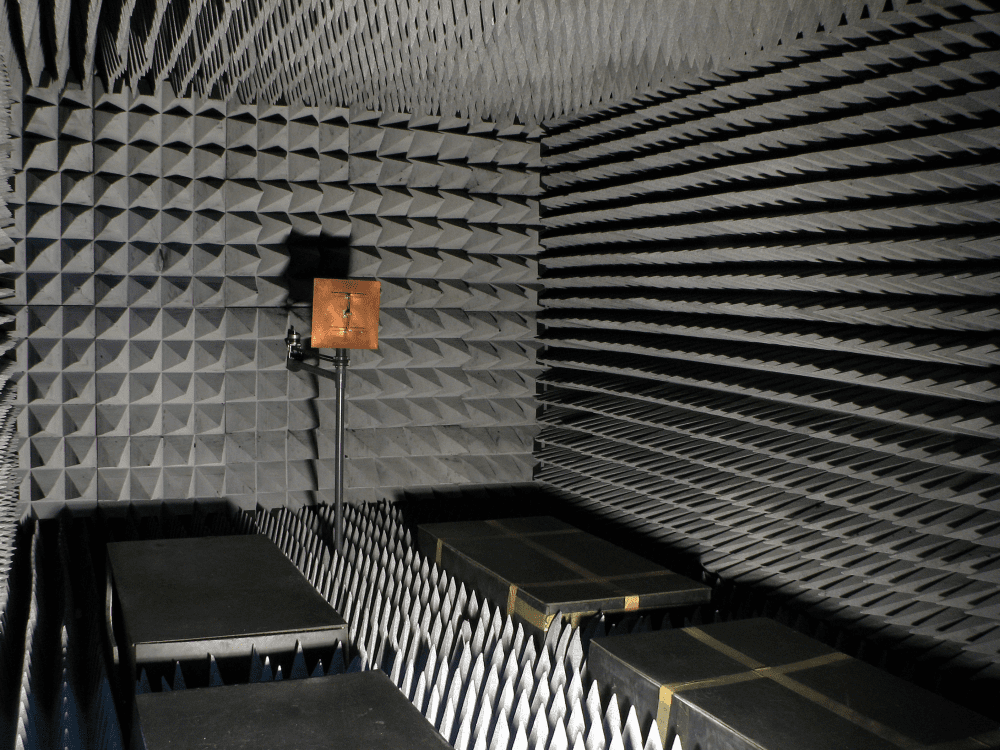
The study starred Daisy The Duck, who was first put into an anechoic chamber to hear what a duck’s quack sounds like when there is absolutely no echo. Echoes are the result of sound reflecting off a flat surface like a cliff face, but anechoic chambers are designed to absorb all reflection, often by having fuzzy, pointy edges.
They then popped Daisy into a reverberation chamber, a large room with hard, exposed surfaces ripe for bouncing the echo of a duck’s quack. “The sound produced is rather sinister… [but] it does indeed echo” said study lead Professor Trevor Cox, of the acoustics research center at the University of Salford, to Guardian.
Why did people think that duck quacks don’t echo?
The reasoning behind the myth is quite simple. Unable to take Daisy on the road in an effort to yield any results of scientific value, Cox turned to virtual simulations to see how quacks would respond in different environments. In the setting of a concert and by a cliff face, it became apparent that the quacks are sometimes too weak to be heard in real-world situations.
“A duck quacks rather quietly, so the sound coming back is at a low level and might not be heard,” Snopes reports Cox said.
“Also, a quack is a fading sound. It has a gradual decay, so it’s hard to tell the difference between the actual quack and the echo. That’s especially true if you haven’t previously heard what it sounds like with no reflections.”
Why did we need to know if ducks’ quacks echo?
In his book The Sound Book: The Science of the Sonic Wonders of the World, Cox delivers an anecdote about how he was contacted by the BBC to fact-check the myth that duck quacks don’t echo. Despite providing an explanation as to why they do, the “fact” was broadcast anyway and so Cox decided it was time to get concrete evidence on his side.
Cox is the first to admit some elements of the research were crude, especially his field experiments which essentially involved a spot of birdwatching near some promising echo hot spots. “In none of these places could I hear a clear, audible quack separate from the original call,” he wrote. “In the end, I came to the conclusion that the phrase should say, ‘A duck’s quack might echo, but it’s impossible to hear unless the bird quacks while flying under a bridge’.”
BRB, going to lurk under a bridge and wait for passing ducks.
Source Link: Myth Or Magic: Duck Quacks Don't Echo