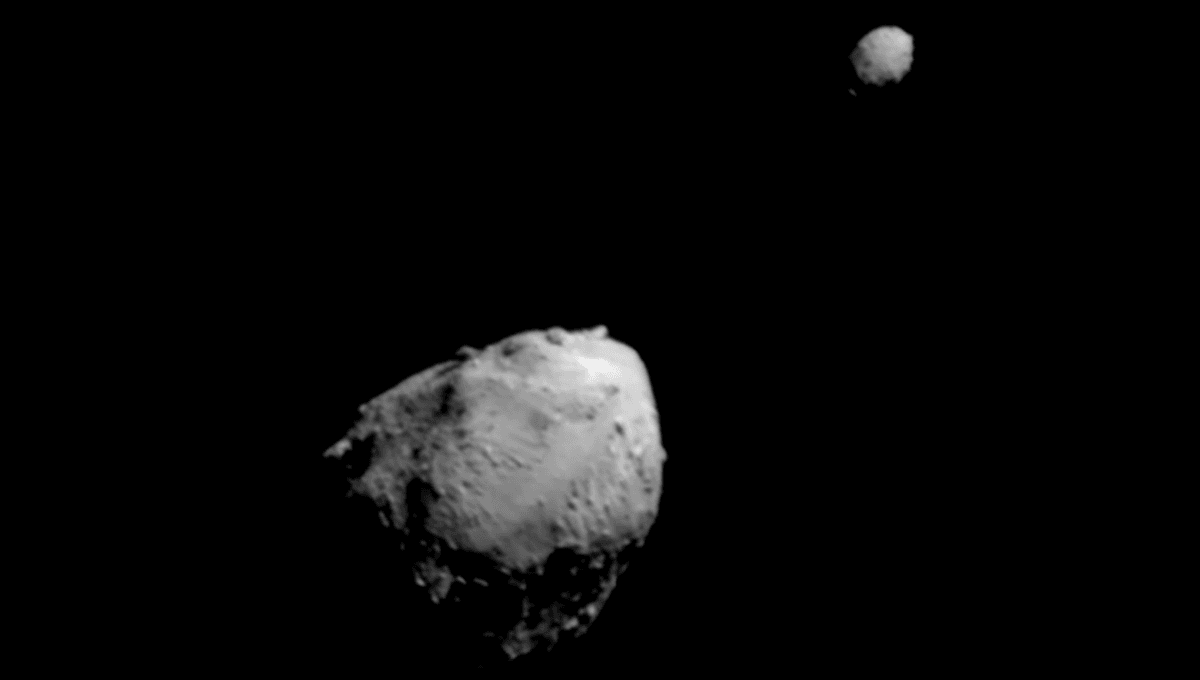
In September 2022, NASA performed the first serious test of planetary protection in space. The DART mission was sent to smash into asteroid Dimorphos, the small moon of asteroid Didymos. It was the first time humanity moved a celestial body. DART stands for Double Asteroid Redirection Test, and as tests go it did very well. Maybe too well. Dimorphos might have experienced global deformation from the event.
On September 26, 2022, DART fired its engines and plummeted into Dimorphos. The momentum that was delivered in such an impact was significant. DART was expected to shorten the period of the asteroid around Didymos by seven minutes. It actually shortened the period by over 33 minutes, and the asteroid also shed boulders that were seen flying off by several telescopes.
The beyond-expectations results are great, but it is important to understand how it was possible to change the motion of this body this much. Researchers were able to produce a series of simulations about the properties of Dimorphos, and quite a dramatic picture is being painted.
The bulk density of Dimorphos, and the number of boulders estimated to be on its surface and subsurface were estimated from the data collected by DART before the collision. Combined with the other data related to the collision, researchers estimate Dimorphos to be a rubble-pile object similar to asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, both of which were visited by sample retrieval missions.
Didymos is a stony S-type asteroid, and it’s thought that Dimorphos is the accumulation of material shed by Didymos as it spins. And for that reason, Dimorphos behaved in a very unusual way following the impact. Basically, the impact changed Dimorphos for good, but without leaving a crater behind.
Dimorphos is about 160 meters (520 feet) across compared to 780 meters (2,560 feet) for Didymos. The collision with DART at the high speed of 6.6 kilometers (4 miles) per second imparted enough energy to make the major changes discussed above. But the material that makes Dimorphos is so loose that the impact led to the whole asteroid getting rearranged. No crater was left because the whole asteroid changed around the impact site.
This is extreme, but not unheard-of. When OSIRIS-REx touched Bennu to collect its sample, it sunk into the loosely held material that makes up the asteroid. It’s a space ball-pit in terms of consistency.
The European Space Agency is expected to launch a follow-up mission called Hera that will go and study the new configuration of the system – the researchers are certain that Hera will find a reshaped asteroid rather than a crater. The name Dimorphos means “having two forms” in Greek, and it was chosen to represent the past and present orbit of the object. Now it has an even more apt meaning.
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
Source Link: NASA Hit An Asteroid So Hard It Completely Changed Its Shape