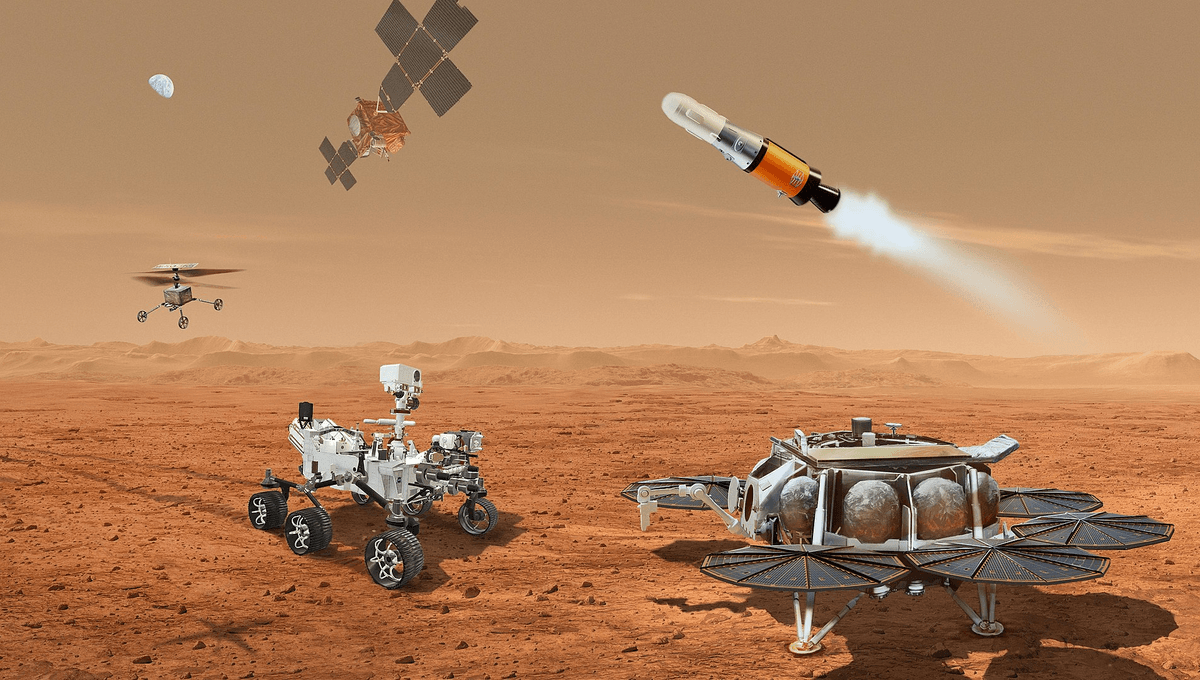
One of NASA’s most ambitious missions, bringing back samples from the surface of Mars for analysis on Earth, is in trouble. Cost estimates are blowing out, and some scientists are questioning the priority given to the project. However, in an announcement on the mission’s future, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson remained committed to the idea (with modifications) while seeking ways to improve. However, rather than settling anything, the announcement may have just kicked the real decision down the road.
Once estimated at $8-10 billion, Mars Sample Return’s budget is $11 billion, and there are doubts whether it can stick to it. With such a large portion of NASA’s exploration budget going into one project, other missions are under threat. Few question that the mission is more important than any one of those it might displace, given the possibility of finding life in those Martian rocks. On the other hand, if missions to several other planets need to be canceled or postponed, might the cumulative sacrifice be too great to make?
Nelson acknowledged the issues at a public announcement, saying; “Mars Sample Return will be one of the most complex missions NASA has ever undertaken. The bottom line is, an $11 billion budget is too expensive, and a 2040 return date is too far away,”
NASA thinks it has some of the answers. Nelson was speaking while releasing NASA’s response to the Independent Review Board report on the mission released last September.
That report pulled no punches stating; “There is currently no credible, congruent technical, nor properly margined schedule, cost, and technical baseline that can be accomplished with the likely available funding.”
The response outlines some changes to make the mission less complex and less likely to fail, but it’s clear NASA does not think it has all the answers yet. “Safely landing and collecting the samples, launching a rocket with the samples off another planet – which has never been done before – and safely transporting the samples more than 33 million miles back to Earth is no small task. We need to look outside the box to find a way ahead that is both affordable and returns samples in a reasonable timeframe,” Nelson said.
The announcement calls for NASA (and perhaps external) scientists to provide ideas on how to do the job cheaper and hopefully faster. Already, 70 experts have been interviewed and 20 changes to mission design have been evaluated. Most dramatically, the idea of using two Ingenuity-type helicopters to retrieve the samples if Perseverance is no longer operating has been dropped for weight reasons, although the replacement plan is not yet clear.
Instead of the budget being $11 billion, it is now in the $8 billion to $11 billion range, which may not ease the anxiety of planetary scientists focused further out, who fear their projects are on the chopping block. The anticipated return time for the samples Perseverance is already collecting has been moved to 2040, from the previous unofficial targets of 2029 and 2033 despite Nelson’s comments.
The key obstacle lies in the complexity Nelson referred to. Perseverance and Ingenuity have done their job superbly, collecting some samples scientists can’t wait to get their hands on. To get them back, however, requires flying two spacecraft to Mars. One of these, provided by the European Space Agency (ESA), will go into orbit. The other, the Martian Ascent Vehicle (MAV), will land on the surface, retrieve the samples and return them to the MAV. This will then become the first spacecraft in human history to take off from another planet, rendezvous with the orbiter, and return to Earth, where measures will be taken to prevent any possible lifeforms from killing us all.
Even if some outstanding novel thinking finds a way to slash the costs of one stage of the project, it could be eaten up in cost blowouts elsewhere. After all, these are the norm for missions seeking to do something really new.
Yet to cancel the mission would be a massive blow to NASA’s prestige, as well as to scientific research. For many people, Mars is the planet that matters – not just a place to search for life but our stepping stone to colonize the universe. The 2022 NASA strategic report mentions Mars 77 times, far more than all the other planets (Earth aside) and their moons combined.
The hype about sending humans to Mars emphasizes this. To anyone who has absorbed promises of a million people on Mars by the 2060s, the idea we can’t even bring a sample back ten years earlier is anathema.
Meanwhile, The Chinese Space Agency has expressed an intention to bring back a Martian sample by 2031. They may be equally unlikely to meet that goal, but it keeps the pressure on NASA.
So NASA is trapped between a red rock and a multitude of hard places. It might hope Congress will come up with more money, but under the current environment that seems a long shot.
Of course, it’s always possible a billionaire will decide they want this project to be their legacy and choose to fund it, or take it over wholesale – but barring that, delays might be NASA’s best option.
Source Link: NASA Seeks Ideas For Faster And Cheaper Mars Sample Return Amid Delays