Beyond the glass cabinets of natural history museums lie thousands more rare specimens, but for many people – researchers and the public included – those specimens remained behind closed doors, accessible to only a select few. Now, thanks to the completion of a six-year-long project, we finally get to see some of them in impressive detail – without having to pay a penny.
Armed with CT scanners, the openVertebrate (oVert) project saw scientists from 18 institutions collaborate to produce 3D reconstructions of over 13,000 vertebrate specimens. The resulting collection covers more than half the genera of all amphibians, reptiles, fishes, and mammals.
Though the vast majority of the reconstructions are of skeletons, leading to some pretty spooky imagery, using special contrast-enhancing stains also allowed those working on the project to create colorful visualizations of creatures’ soft tissues (skin, muscle, and organs, that is – not a frog with a packet of Kleenex).
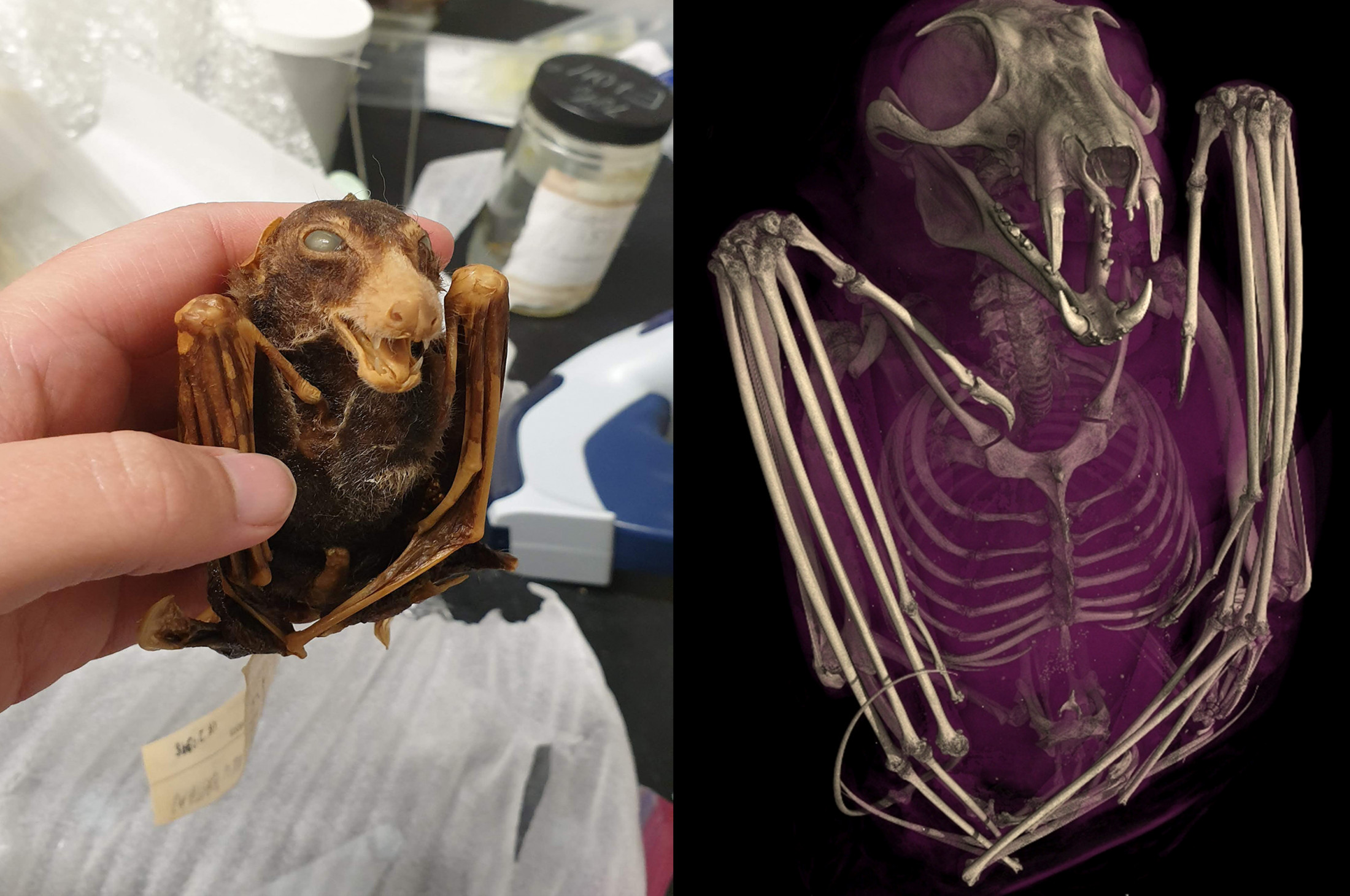
Halloween costume 2024?
Image credit: openVertebrate
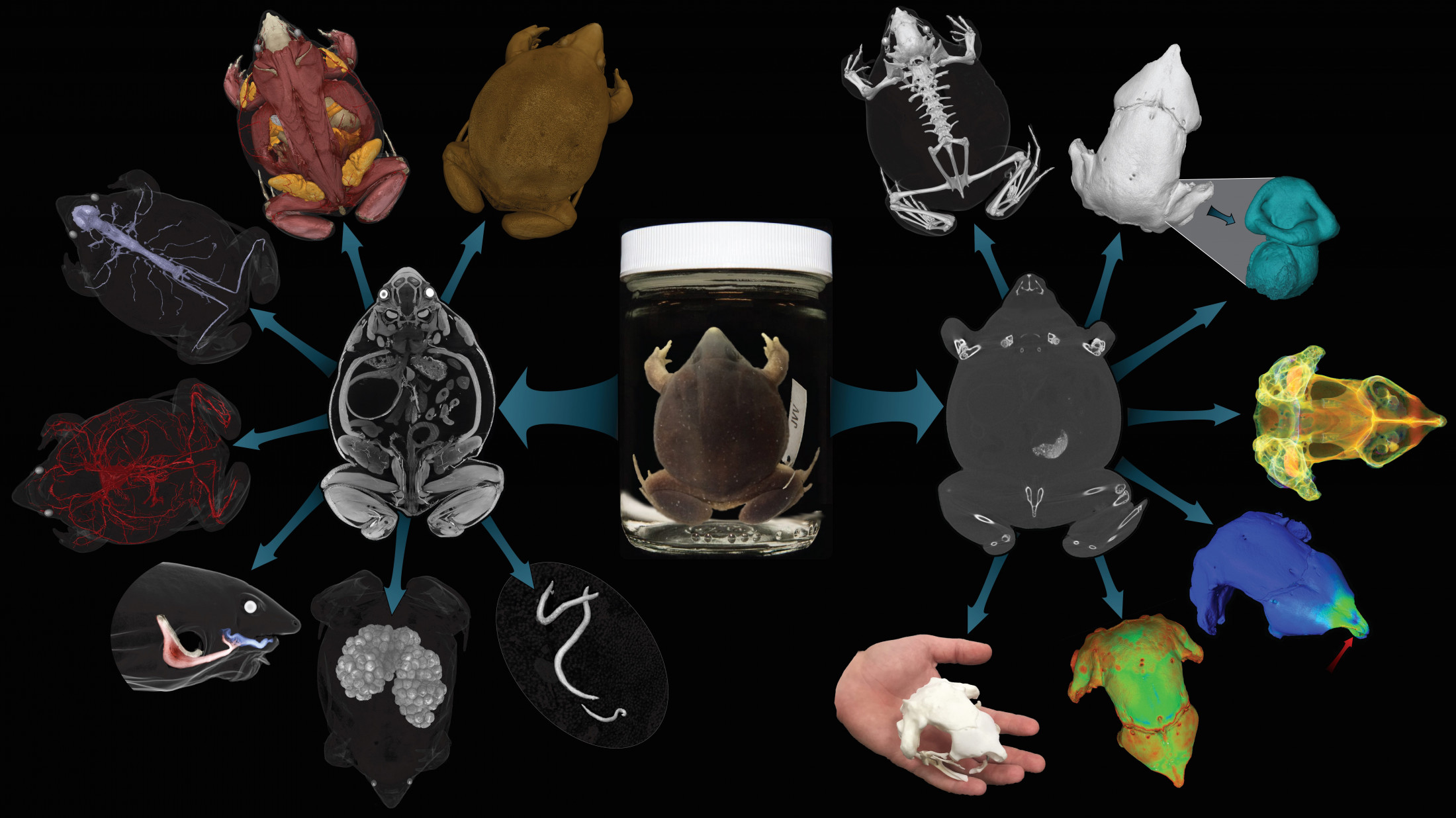
Who knew there were so many different ways to see a chonky frog?
Image credit: openVertebrate
This means that, as well as being great to look at, the 3D reconstructions and images have a particularly valuable purpose. Previously, researchers would have to use destructive methods like dissection to get a peek at the inside of a specimen; these scans help to keep the samples intact instead.
As a result, the project has allowed researchers to make all kinds of new discoveries. Specimens from oVert revealed that frogs have an on-off relationship with teeth, with scientists estimating that they’ve lost and regained them more than 20 times during their evolution. They also added further fuel to the fiery debate over whether or not giant dino Spinosaurus was actually aquatic.
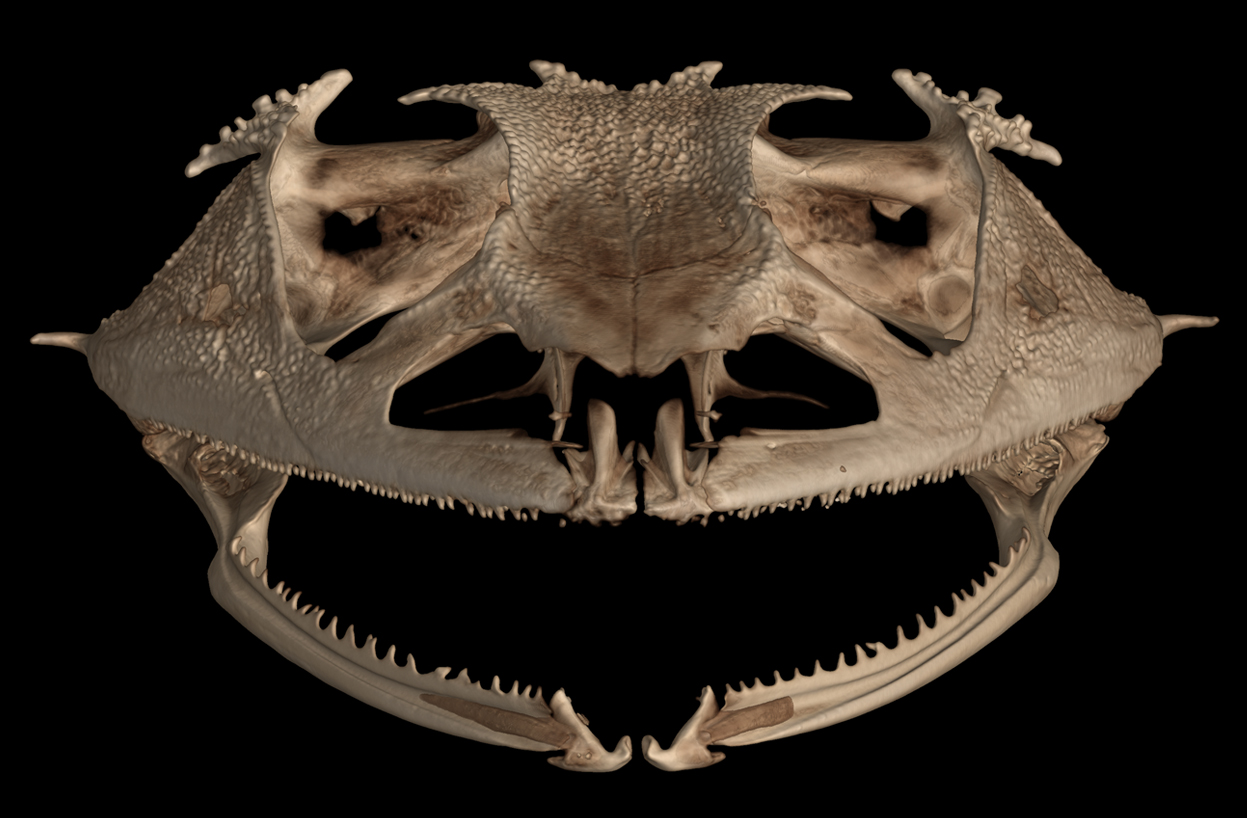
Say “ahhhhhh”.
Image credit: openVertebrate
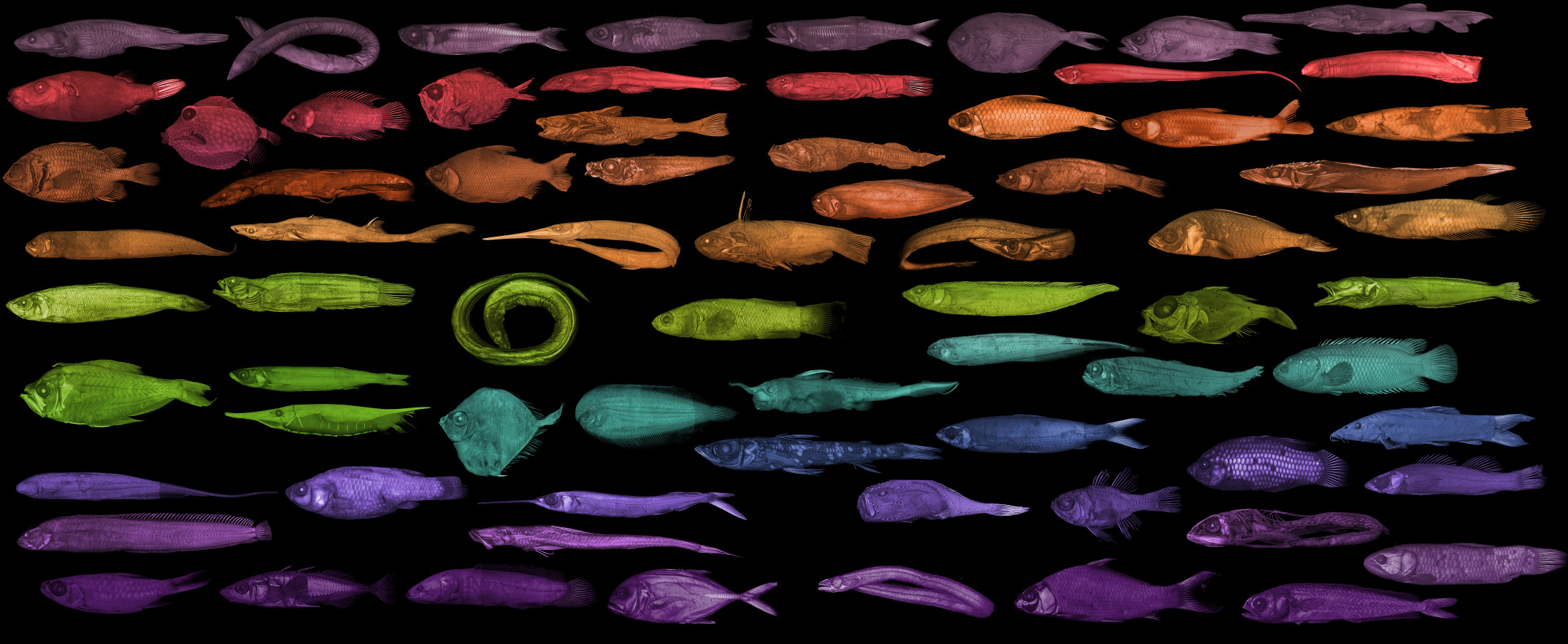
Just keep swimming… oh wait.
Image credit: openVertebrate
But it wasn’t always easy and scientists had to come up with some pretty creative ways to produce the scans and images – like using a swim ring to balance Galápagos giant tortoise specimens.
Putting pool inflatables on the expenses form was arguably worth the questionable looks from Accounts, given the wealth of ways in which the data from oVert can be used. As well as the scientific discoveries made, it’s been used for paleoart, expanding museum exhibits, and even in the classroom.
We think they make great desktop backgrounds too.
A summary of the project is published in BioScience. A selection of interactive 3D models can be found on Sketchfab, whilst the full data repository can be accessed on MorphoSource.
Source Link: Natural History Lover? Check Out Thousands Of Amazing Specimen Scans For Free