A new plastic has been created, and its makers say it combines durability with complete recyclability while also breaking down in seawater and soil, in case it is not disposed of properly. Given the scale of plastic buildup in the oceans and the widespread presence of microplastics in the environment, any solution is welcome, but hopes have been raised before.
It’s hard to keep up with the scale of the plastic garbage patches growing in each ocean. Meanwhile, microplastics produced by the breakdown of larger plastic items are appearing in many disturbing places. Although how much harm microplastics do is still uncertain, there are signs that even when they are not harmful themselves, they can offer a ride to other undesirables.
With plenty of people apparently resistant to all pleas to dispose of plastic items responsibly, and recycling programs tackling a tiny portion of the problem, a technological solution is in great demand. Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science say they have the answer.
Many plastics advertise themselves as biodegradable – but while some really will decompose in your compost bin, or even in landfill, they won’t do the same in salty water. To address this, the RIKEN team combined two monomers with salt bridges between them. Each monomer can easily be consumed by bacteria, and indeed one of them – sodium hexametaphosphate – is a common food additive found to be harmless to animals in extensive testing.
The bonds between the monomers are based on reversible interactions, so the team hoped they would come apart when needed, allowing each to be safely absorbed into the environment.
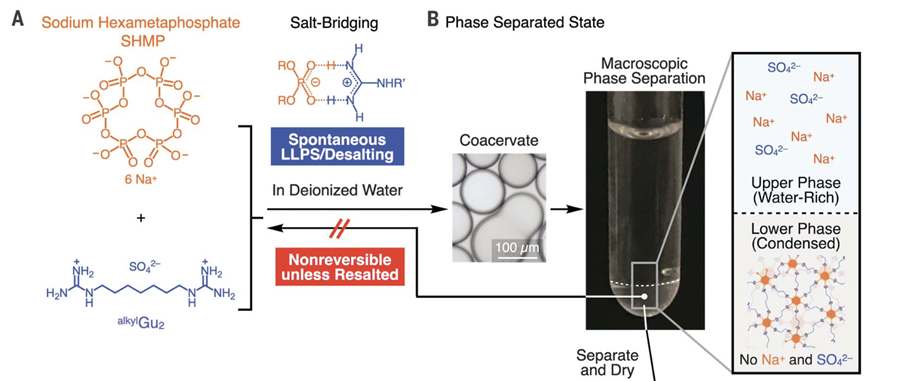
(A) Molecular structures of SHMP (orange) and a guanidinium sulfate (Gu)–based monomer. (B) Spontaneous liquid-liquid separation after mixing aqueous solutions of the monomers. The lower liquid dries to a degradable plastic.
Image Credit: RIKEN
“While the reversable nature of the bonds in supramolecular plastics have been thought to make them weak and unstable, our new materials are just the opposite,” said Professor Takuzo Aida of the University of Tokyo in a statement.
Mixing the ingredients produced two liquids that would not blend, and expelled sodium sulfate. Once the salt was removed, and the thicker liquid dried, it became a plastic the team called alkyl SP2. The bridges holding the monomers together are stable unless exposed to the sorts of salts common in seawater, in which case alkyl SP2 products break down entirely within hours.
Like other thermoplastics, alkyl SP2 can be reshaped at temperatures above 120°C (248°F) to fit the form required, and is also non-toxic, the makers report. The hardness can be changed to meet requirements by choosing between a range of candidates for the second monomer. A small trial recovered more than 80 percent of the ingredients in recycling by using a combination of alcohol and salt water.
Tests show alkyl SP2 sheets biodegrade in soil in 10 days, in case plastic items don’t reach the ocean, and even provide fertilizer in the form of nitrogen and phosphorus when they do. Moreover, the raw ingredients are not obtained from crude oil, like most current plastics.
“With this new material, we have created a new family of plastics that are strong, stable, recyclable, can serve multiple functions, and importantly, do not generate microplastics,” Aida said.
The fact the breakdown rates have been published in a prestigious journal gives the work more credibility than past such claims, but there is still a long way to go before we can declare this problem solved.
One issue to be settled is cost, and whether plastic made this way will be competitive for those not willing to pay extra.
Potentially a bigger problem, however, is that the largest source of ocean plastic is not water bottles or shopping bags, as important as those are, but fishing equipment. A plastic that breaks down in salt water may be a hard sell to fishing trawlers, so we might not have this problem beaten just yet.
The work is published in the journal Science.
Source Link: New Biodegradable Plastic Leaves No Microplastic Waste In Seawater