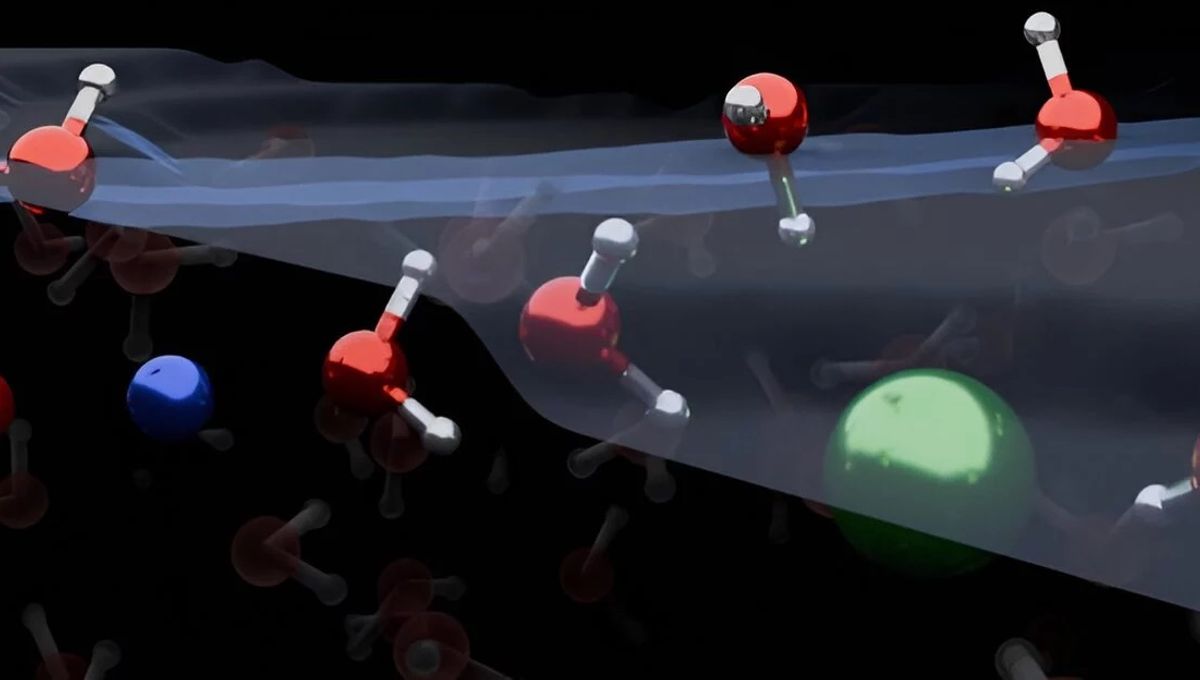
Charged molecules do not form a boundary layer between saltwater and air as previously thought, new research reveals. Indeed, they are depleted there relative to their abundance in the liquid as a whole. Instead, at a depth of a few molecule’s diameters an ion-enrichment layer lurks, like some mythical beast waiting to surprise. The discovery upends perceptions of these boundaries that were viewed with such confidence they were written into scientific textbooks.
Life is most abundant where land meets water and sea meets sky. Understanding what occurs at these contact points is critical. Yet when one moves to the world of the very small, studying the thinnest borders between these domains, our knowledge is scanty, leading scientists to make up stories based on what they expected to find. As technology has advanced our capacity to explore these borderlands, some of the tales have turned out to be wrong.
Salty water produces charged particles. If the salt is the familiar sodium chloride these will be primarily Na+ and Cl–, but other salts will produce different positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. Previous studies have reported larger ions are active at the surface. Ions that are easily polarized, such as bromine and iodine anions, were especially thought to accumulate at the surface. This has led to the conclusion they form a double boundary layer there, with the two sets of charges canceling out, and orientating the nearby water atoms in a particular direction.
“Our work demonstrates that the surface of simple electrolyte solutions has a different ion distribution than previously thought and that the ion-enriched subsurface determines how the interface is organized: going from air into the bulk salt solution, one first encounters a few layers of pure water, then comes a layer enriched in ions, before reaching the bulk,” Dr Yair Litman, of the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research and the University of Cambridge, said in a statement.
Besides having layers of water above them, Litman and colleagues found the ions defy expectations by orientating water molecules both towards and away from the surface, rather than pointing them all the same way.
The long-standing error occurred because studies of the molecules at the boundary were done using lasers to measure the surface molecules’ vibrations, a method known as vibrational sum-frequency generation (VSFG). This reveals changes in vibration intensity at specific wavelengths when salt is added to water, which was thought to indicate a build-up of ions there.
Although VSFG is effective at measuring the strength of vibrations, it can’t detect their orientation – specifically whether the hydrogen atoms in the water molecules point up or down.
Using a more advanced version, known as heterodyne detected-VSFG, the team examined the boundary layers in 11 types of electrolyte solutions at varying concentrations, and created computer models to make sense of what they saw.
The old models were not entirely wrong, however. Two common electrolytes, HCl and NaClO4, did indeed congregate at the surface.
Co-author Professor Mischa Bonn said, “These types of interfaces occur everywhere on the planet, so studying them not only helps our fundamental understanding but can also lead to better devices and technologies. We are applying these same methods to study solid/liquid interfaces, which could have potential applications in batteries and energy storage.”
The study is published open access in Nature Chemistry.
Source Link: New Evidence Reveals The Molecules In Saltwater Aren't Behaving Like Our Textbooks Told Us