The evolution of proteins isn’t just something that happens out in the wild. It can happen in the lab, too, and brings with it the possibility of developing new and improved proteins that can be used in all sorts of useful ways. Trouble is, that’s also a massive slog – until now.
The rest of this article is behind a paywall. Please sign in or subscribe to access the full content.
A team from the Department of Chemistry and Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology at the Scripps Research Institute have developed a so-called “evolution engine”, which can continuously introduce mutations into living bacterial cells at a rate 100,000 times higher than it would naturally acquire them.
“This is like giving evolution a fast-forward button,” said co-senior author Pete Schultz, the President and CEO of Scripps Research, in a statement. “You can now evolve proteins continuously and precisely inside cells without damaging the cell’s genome or requiring labor-intensive steps.”
The “engine” is called T7-ORACLE and works by introducing an artificial DNA replication system into E. coli. Yep, you read that right; not all E. coli gives you an iffy belly – it’s also widely used to produce proteins, as it grows easily and rapidly.
This second, separate replication system doesn’t target E. coli’s main, chromosomal DNA, leaving the host cell unaffected. Instead, it targets small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmids, which are often introduced into bacteria for the purpose of producing large amounts of proteins.
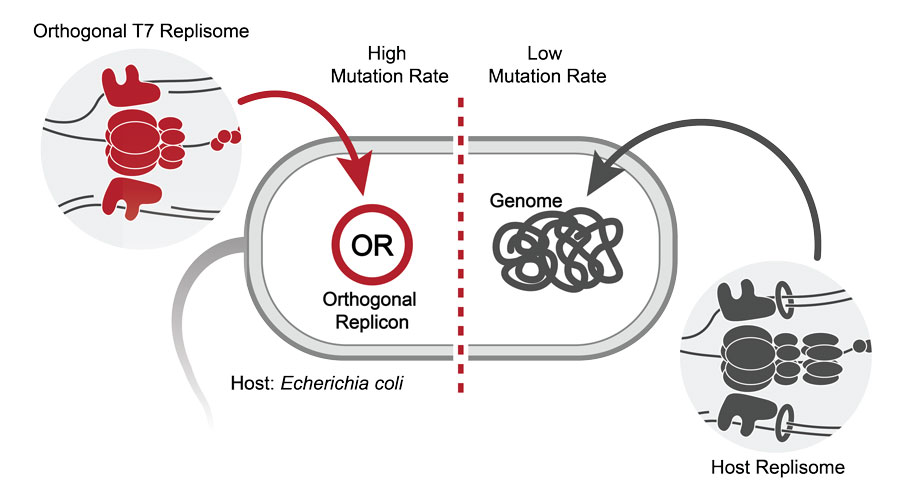
The T7-ORACLE system.
Image credit: Scripps Research
According to the researchers, it’s a simple system to set up. “The main thing that sets this apart is how easy it is to implement,” said co-senior author Christian Diercks, an assistant professor of chemistry at Scripps Research. “There’s no specialized equipment or expertise required. If you already work with E. coli, you can probably use this system with minimal adjustments.”
The team tested the system out with a gene encoding a protein that gives bacteria antibiotic resistance, and gradually exposed E. coli cells to increasingly high doses of antibiotics. The results were impressively rapid; it took less than a week for a protein to evolve that could handle a dose up to 5,000 times higher than the first.
“This system represents a major advance in continuous evolution,” said Diercks. “Instead of one round of evolution per week, you get a round each time the cell divides – so it really accelerates the process.”
It’s hoped that the T7-ORACLE system could be at its most useful in medicine, helping to speed up the process of finding new and improved therapeutic proteins for all kinds of conditions, including cancers and neurodegenerative diseases.
“What’s exciting is that it’s not limited to one disease or one kind of protein,” Diercks explained. “Because the system is customizable, you can drop in any gene and evolve it toward whatever function you need.”
“[W]e can now evolve virtually any protein, like cancer drug targets and therapeutic enzymes, in days instead of months.”
The study is published in Science.
Source Link: New “Evolution Engine” Can Mutate Target Genes 100,000 Times Faster Than Normal