A small, implantable device that detects a drop in respiration that can signal an opioid overdose and automatically administers the lifesaving drug naloxone – aka Narcan – has been tested successfully in animals. It even has the ability to alert the emergency services, and the researchers say the same kind of technology could be applied to lots of other medical conditions.
The World Health Organization estimates that globally, in 2019, around 80 percent of deaths attributable to drug use involved opioids. The opioid crisis is particularly acute in North America, where both illegal opioids like heroin, and prescription medications like oxycodone and fentanyl, have contributed to around 600,000 deaths since the turn of the Millennium.
There is an effective antidote to an opioid overdose that, if delivered in time, can reverse the respiratory depression caused by the drugs and keep the person breathing. It’s called naloxone, and it can be purchased over the counter in US pharmacies as an injectable or a nasal spray. Knowledgeable bystanders who can recognize the signs of an overdose and happen to be carrying naloxone can and do save lives.
“But during an overdose, people are often alone and unable to realize they are overdosing,” said Dr Robert W. Gereau, director of the WashU Medicine Pain Center and co-author of the new study, in a statement. “If someone else is present, they need access to naloxone – also known as Narcan – and need to know how to use it within minutes.”
Recent research shows that this use of naloxone by good Samaritans is on the increase, but still not enough to tackle the problem of overdoses. That’s one reason why the new implant idea is so exciting.
“We identified an opportunity to save more lives by developing a device that quickly administers naloxone to at-risk individuals without human intervention,” said Dr Gereau.
In collaboration with a team of engineers and materials scientists led by Dr John A. Rogers at Northwestern University, the scientists developed a device they’ve called the Naloximeter. Inserted just below the skin, it detects a drop in oxygen levels that could signal an overdose. The user’s cellphone will then receive a notification, giving 30 seconds to respond and confirm they’re okay.
If they don’t respond, the device releases its stored dose of naloxone and can also be programmed to send an alert to emergency first responders.
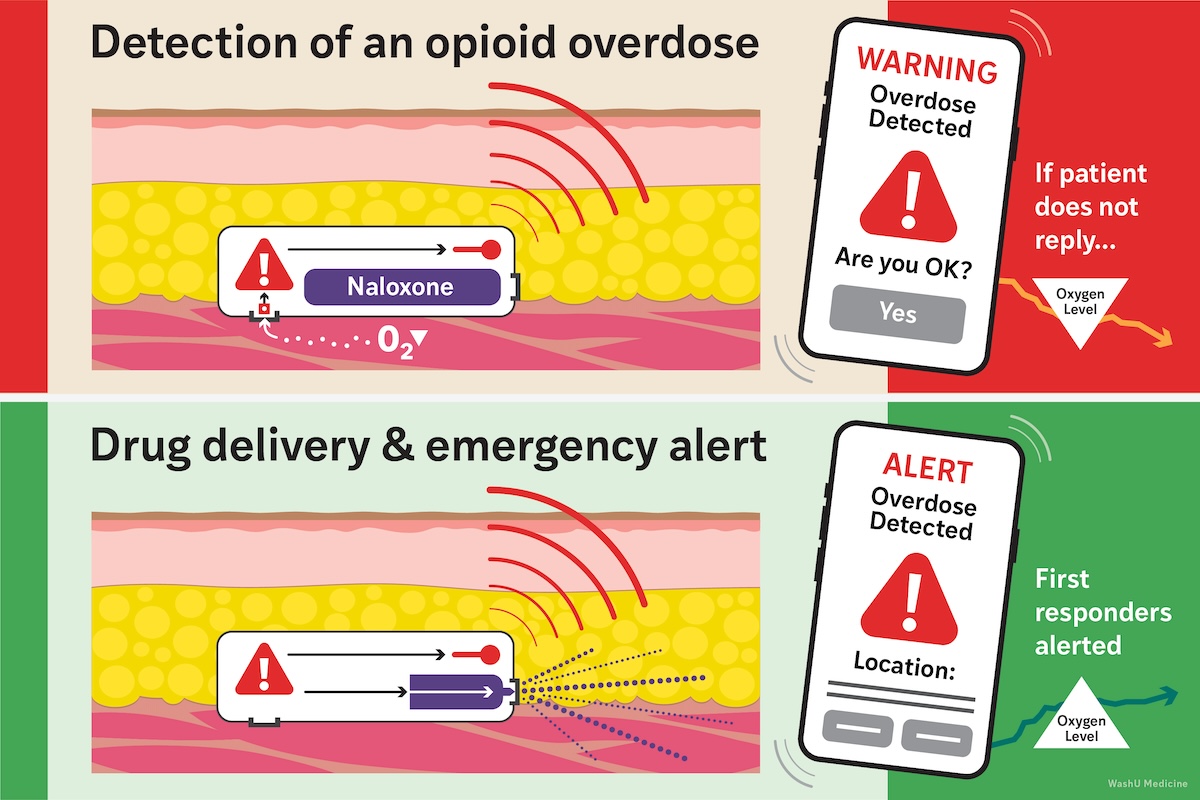
How the Naloximeter works.
Image credit: Eric Young
This last step is important as naloxone is not a permanent fix – it temporarily prevents opioid drugs from binding to their receptors in the brain, but once it is cleared from the body the symptoms of the overdose can come back, so more medical intervention is needed.
“An additional benefit of calling first responders is that it helps people re-engage with health-care providers. We want to save people from dying from an overdose and also reduce harm from opioids by helping people access the resources and treatments to prevent future overdoses from occurring,” explained co-author Dr Jose Moron-Concepcion.
Testing modified versions of the Naloximeter in both rats and pigs, the team found that the device kicked in as intended when it detected a drop in oxygen levels, and all the animals fully recovered within five minutes of the naloxone being released.
With further development, it’s hoped the device could be put to use in humans, and that similar implants could help with conditions like epilepsy and anaphylaxis.
“Our study lays important groundwork for future clinical translation,” said graduate student Joanna Ciatti. “We hope others in the field can build off of these findings to help make autonomous rescue devices a reality.”
The study is published in Science Advances.
Source Link: New Implant Detects Opioid Overdose, Gives Lifesaving Drug, And Even Calls For Help