Down in the deep waters of the northeastern Australian coast, you might be lucky enough to come across a brand new species of shark. The painted hornshark (Heterodontus marshallae) is a newly described species that belongs to the order Heterodontiformes, characterized by their unusual human-like molars.
Heterodontiformes is an order with only one genus and nine different species within. However, genetic analysis performed on one of the species, thought to be Heterodontus zebra, shows it was actually genetically different, and therefore brings the species in this order to 10. How this species has gone unnoticed for so long might be because of the similarities in the patterns and markings on the shark’s skin that are slightly different between species. Heterodontus zebra has a dark bar behind the gills slits, which is absent in the new species.
“Both species are pale with 22 dark brown bands and saddles. But they have small differences in the markings on their snouts and below their gill slits. Their egg cases are also different,” Said Dr Will White research scientist at the Australian National Fish Collection (ANFC) in a statement.
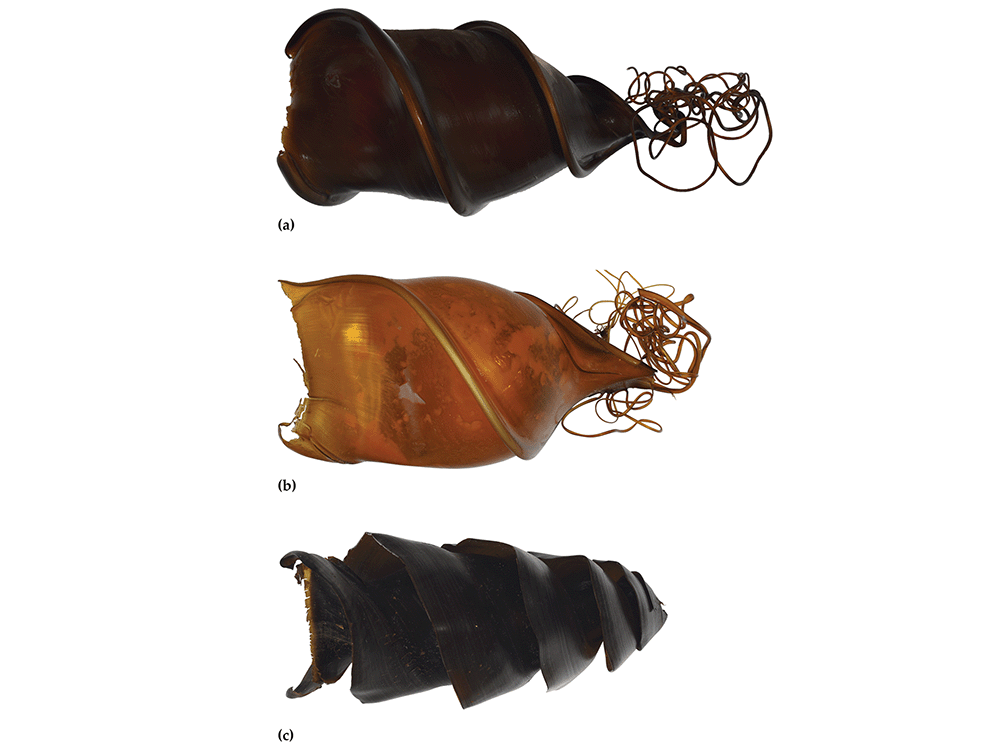
Egg case of: (a) Heterodontus marshallae, b) H. zebra, (c) H. portusjacksoni
The new species was described first by comparing museum specimens. By chance, a research vessel surveying seabed habitats with the ANFC in western Australia found a living specimen of the new species that was able to be the reference for the species’ scientific name.
“We have a female specimen in our collection, but the one we collected during the voyage is a male. We prefer to use males for shark holotypes because they have claspers, which are external reproductive organs that can vary between species and help us tell them apart.” said Helen O’Neill, fish biologist at ANFC.
The painted horn sharks live at depths of 125 to 229 meters (410 to 751 feet) and, while they have the typical shark teeth in rows at the front of their mouths, they have a more human-like morphology of molars behind the rows. This adaptation allows the sharks to crush prey like crustaceans and mollusks.
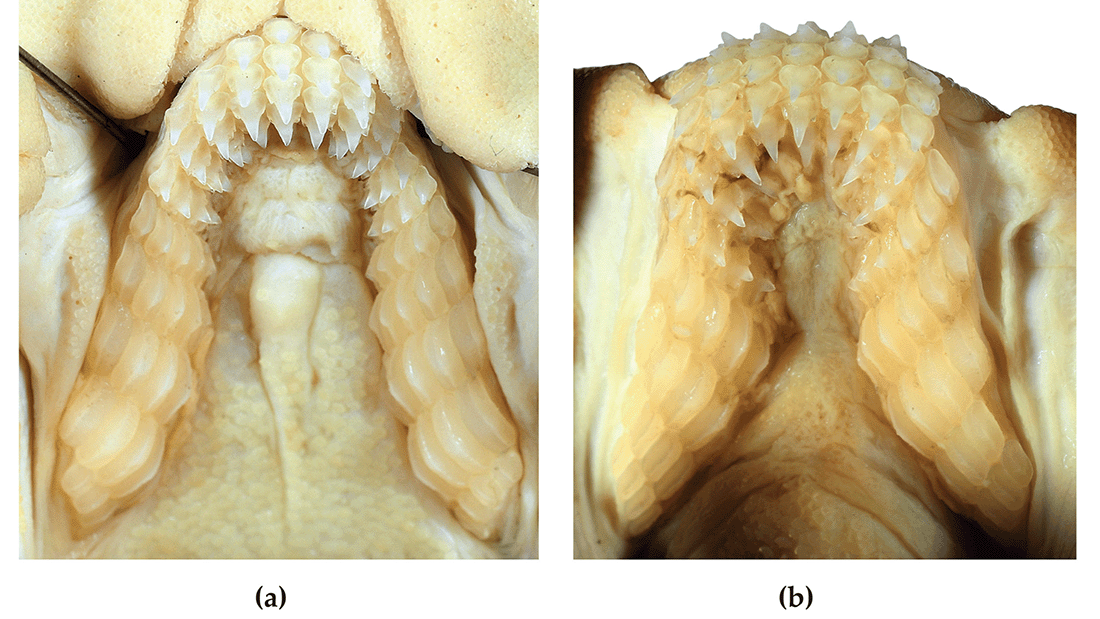
Open wide!
“They tend to sit on the sea floor and feed mainly on creatures like molluscs and crustaceans. They have a small mouth but crushing jaws that are huge relative to their skull size and powerful enough to crush cowrie shells.” said Helen.
The paper is published in the journal Diversity.
Source Link: New Shark Species With Human-Like Teeth Discovered In Australia