There have been a number of ancient fossil dolphins discovered over the years that are famous mostly for their big teeth, though one species lost theirs to slurp up squid. Most believe the teeth of these ancient dolphin species were used for thrusting forwards towards large prey; however, a newly described dolphin called Aureia rerehua has teeth that it is thought to have used like a cage instead.
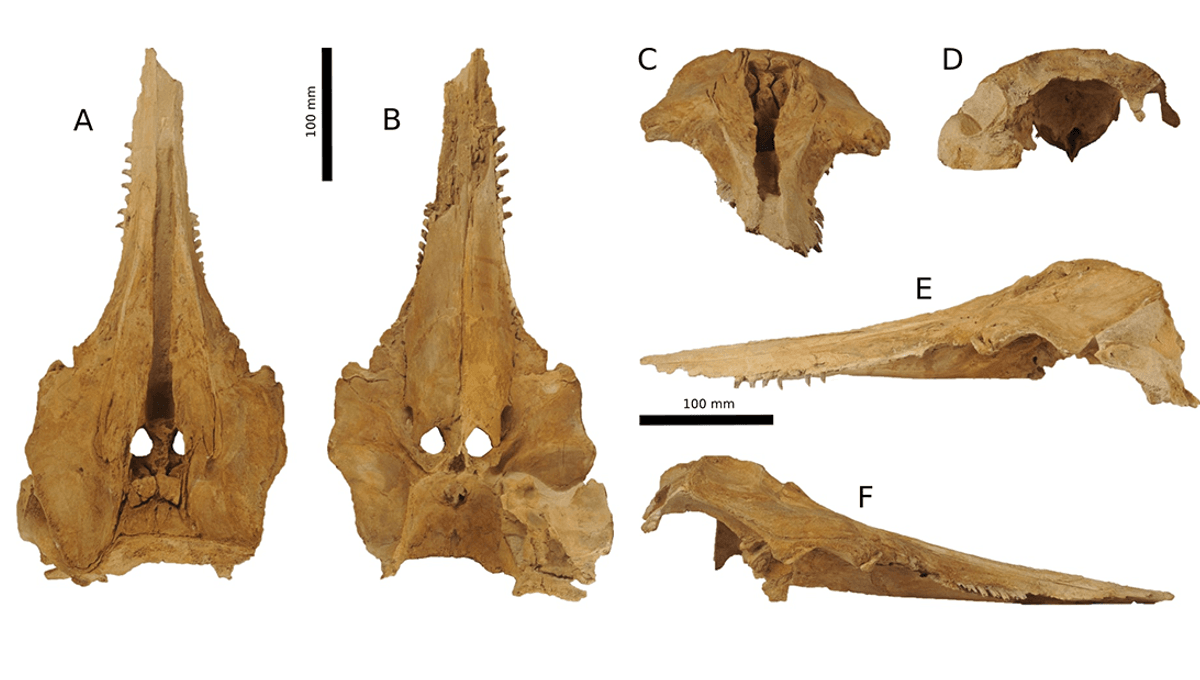
The specimen, named OU22553, includes a skull, teeth, vertebrae and ribs, as well as ear and jaw bones. A. rerehua was collected from a limestone quarry in Hakataramea Valley, South Canterbury, New Zealand, with researchers estimating the specimen to be around 22-23 million years old. The skull in particular is extremely well-preserved and shows off interesting features, including a weak, flexible neck and unique sideways-facing teeth.
The team think that this means A. rerehua would have scanned shallow waters hoping to capture small fish in a basket of teeth. The name Aureia comes from the Māori word aurei, “cloak pin”, in reference to the shape of the dolphin’s teeth, while rerehua means “beautiful”, owing to the excellent preservation of the skull and face.
A. rerehua is quite similar to other known fossils of dolphins from a similar period called Otekaikea and Waipatia, and shares features including protruding teeth, and shallow depressions known as fossae for the attachment of muscles.
From the size of the skull, the team think this ancient dolphin species would have measured just under 2 meters long (6.5 feet). Inside the skull, the team found 24 teeth still within the mandible and 45 other teeth that were loose in the surrounding substrate.
The team also performed a phylogenetic analysis to find out where A. rerehua would have fit within the other known ancient dolphin species. They identified three groups. The first are the “Waipatia-type” dolphins, with cheek teeth and teeth with multiple denticles. The second group, the “Nihohae-type” dolphins, have flat skulls and shark-like dental crowns. The final group, the “Otekaikea-types”, include the new species and have triangular temporal fossae and dental crowns of many different types.
The researchers think these different tooth morphologies between the groups meant that they tackled different prey or even had different strategies across the groups for prey capture. The new dolphin might have hunted by quickly snapping its jaws together, the researchers suggest. Its teeth were thin and delicate, rather than serrated like other known species.
The team concluded that the dolphin most likely would have foraged for prey in shallow waters, where it trapped fish species within its caged jaws after using echolocation. Its relatively small size and skull shape would have allowed it speed and maneuverability through this ancient habitat.
The study is published in the Journal Of The Royal Society of New Zealand.
Source Link: New Species Of 23-Million-Year-Old Dolphin Thought To Snap Up Fish In The Shallows