Microplastics are everywhere, which is why scientists have been dedicating a lot of time to trying to figure out a way to safely extract them. Now, it seems a super sponge-like foam that borrows the soaking skills of cotton and squid may be a promising candidate, as it was found to remove 98 to 99.9 percent of microplastics from water samples studied.
What’s more, the foam is sustainable and environmentally adaptable, without carrying the neuston-zone-destroying risks of some ocean-hoovering approaches. As well as targeting microplastics already in the environment, it could be used to treat water at factories before it gets released, working to both reduce the microplastics already in nature and those being leaked into it.
“Microplastics entering terrestrial and aquatic habitats are anticipated to continuously increase for thousands of years, due to the alarming volumes of plastic waste in the environment (~4.6 billion metric tons) and the difficulty of degradation under natural conditions,” wrote the study authors.
“The planet is under great threat from microplastics, and aquatic ecosystems are the first to suffer, as they provide convenient places for microplastics, which can combine with other contaminants and be ingested by multiple levels of organisms. The development of widely adapted approaches for microplastic remediation in the aqueous environment is urgently demanded.”
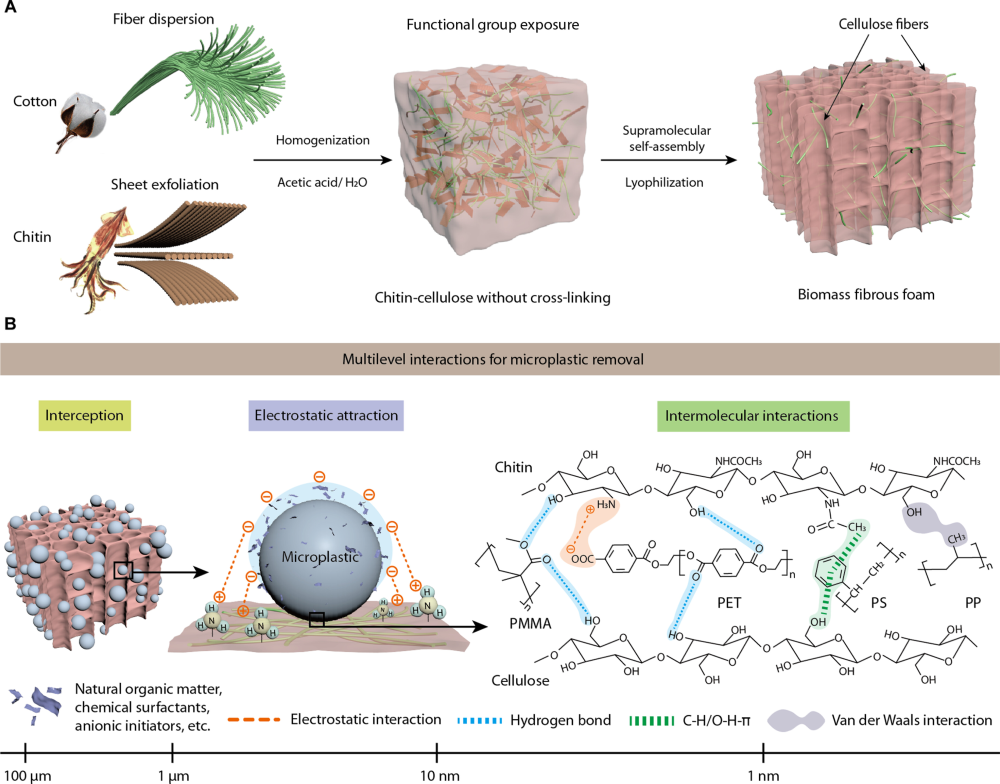
(A) The recipe for Ct-Cel biomass foam includes cellulose and β-chitin with some clever chemistry. (B) Microplastic removal by the foam occurs through physical interception, electrostatic attraction, and multiple intermolecular interactions thanks to the abundance of reactive functional groups.
To address that demand, they created a sponge-like substance called Ct-Cel biomass foam that combines two substances found in nature: cellulose from cotton, and chitin from squid bone. Squid are famously squishy, but inside their soft tissues sits a small pen-shaped skeleton made of chitin.
The two substances stuck together nicely when the team broke their original hydrogen bonds and induced intermolecular interactions of cellulose and chitin, creating a stable framework with loads of activated hydrogen boding sites for microplastic adsorption. By running adsorption tests as well as computational studies, they observed that it could capture microplastics in several ways: physical interception, electrostatic attraction, as well as multiple intermolecular interactions.
They then took the Ct-Cel sponge for a spin with four water types: agriculture irrigation, lake water, still water, and coastal water, and after an impressive five cycles it was still showing high removal efficiency of more than 95 percent. That it can be reused means that it could well be scalable, and the researchers hope that, with a bit more testing, it could be rolled out to start tackling the ongoing microplastics crisis.
“The Ct-Cel foam has great potential to be used in the extraction of microplastic from complex water bodies,” concluded the authors. “Thus, our design principles would facilitate the future development of practical and sustainable strategies based on biomass foams to address microplastic pollution.”
Ever wondered what microplastics are doing to our health? Sign up to our newsletter to receive the February issue of CURIOUS that will tackle the question in our Deep Dive feature.
The study is published in the journal Science Advances.
Source Link: New Sponge-Like Biomass Foam Found To Soak Up 99.9 Percent Of Microplastics