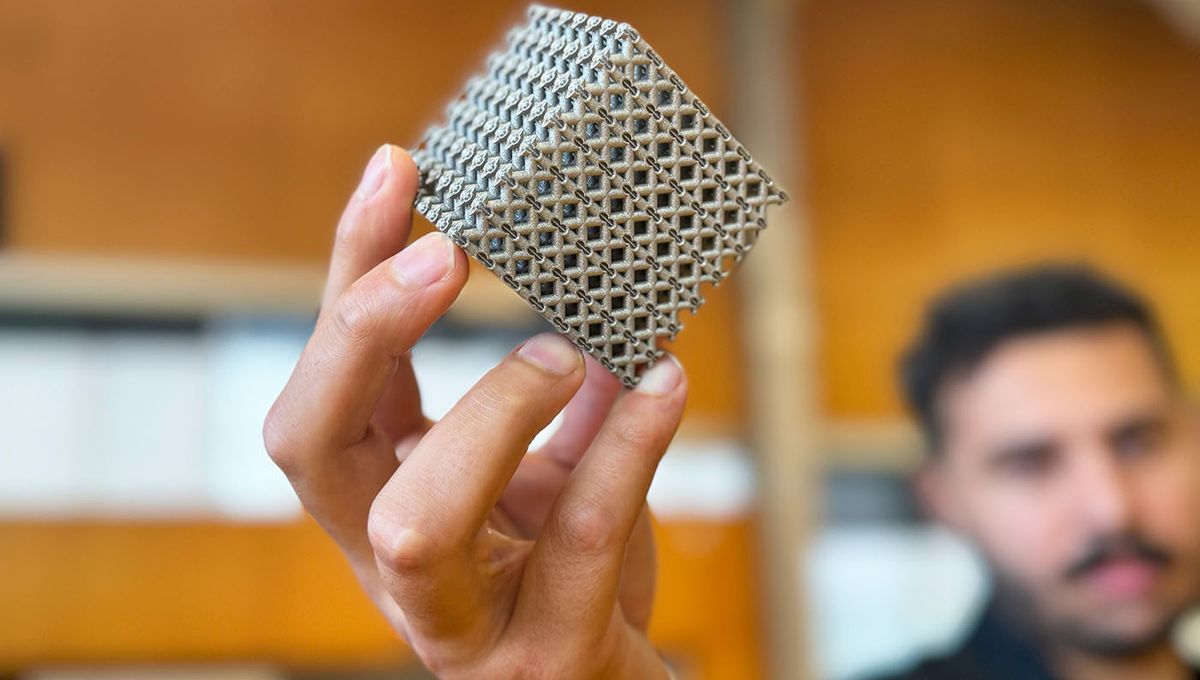
A new 3D printed “metamaterial” that apparently has levels of strength for weight that appear to supersede those in nature and most of the manufacturing world has been created by a team from RMIT University, Australia. This new material could have significant implications for everything, from medical implants to aircraft to rockets.
The new metamaterial – an artificially structured material exhibiting electromagnetic properties not seen in nature – is made from a common titanium alloy. But don’t let that fool you, there is nothing common about its ability.
What makes the difference here is its structure. The material has a unique lattice design that not only makes it unique, but also extremely strong. According to the team’s new study, the material is 50 percent stronger than the next strongest alloy of a similar density, which is used in aerospace applications.
But how did they come up with this design? As with many game-changing inventions, the inspiration for this new material came from observations of the natural world. In this case, strong hallow-stemmed plants such as Victoria water lilies and hardy corals such as organ-pipe coral (Tubipora musica) offered instruction on how to combine lightness with durability.
Yet observing a strong natural structure is one thing, replicating it in artificial materials is another. For decades, researchers have attempted to create their own hollow “cellular structures” similar to those seen in nature’s examples, but their efforts have been frustrated by issues of manufacturing and load stress, which has led to failures.
“Ideally, the stress in all complex cellular materials should be evenly spread,” Distinguished Professor Ma Qian explained in a statement. “However, for most topologies, it is common for less than half of the material to mainly bear the compressive load, while the larger volume of material is structurally insignificant.”
What has made the difference in this case, however, is the unprecedented innovative solutions offered by metal 3D printing.
“We designed a hollow tubular lattice structure that has a thin band running inside it. These two elements together show strength and lightness never before seen together in nature,” Qian added. “By effectively merging two complementary lattice structures to evenly distribute stress, we avoid the weak points where stress normally concentrates.”
Strength but with little cost
To create this new wonder material, Qian and colleagues 3D printed their design at RMIT’s Advanced Manufacturing Precinct using a technique called laser powder bed fusion. This approach melts layers of metal powder together using high-powered laser beams.
The outcome was a titanium lattice cube that is 50 percent stronger than cast magnesium alloy WE54, the strongest alloy with a similar density. This new structure effectively halved the amount of stress concentrated on the lattice’s weak points.
The structure, a double lattice design, also has the ability to deflect any cracks that may form so that they do not undermine its toughness.
The structure can be scaled as needed, from something as small as several millimeters to structures several meters in size, using different types of printers. Moreover, the structure’s printability, biocompatibility, and corrosion and heat resistance make it a potential game-changer for applications in various areas of manufacturing.
“Compared with the strongest available cast magnesium alloy currently used in commercial applications requiring high strength and light weight, our titanium metamaterial with a comparable density was shown to be much stronger or less susceptible to permanent shape change under compressive loading, not to mention more feasible to manufacture,” lead author Jordan Noronha explained.
The team now plans to refine their material and explore its application in higher-temperature environments. At the moment, the titanium cube can resist temperatures as high as 350°C (662°F), but they think they can make it withstand temperatures as high as 600°C (1,112°F). This would make it an excellent material for aerospace engineering and firefighter drones.
However, the technology needed to make the new material is not yet widely available, so its adoption may take time.
“Traditional manufacturing processes are not practical for the fabrication of these intricate metal metamaterials, and not everyone has a laser powder bed fusion machine in their warehouse,” Noronha said.
“However, as the technology develops, it will become more accessible and the printing process will become much faster, enabling a larger audience to implement our high-strength multi-topology metamaterials in their components. Importantly, metal 3D printing allows easy net shape fabrication for real applications.”
The paper is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Source Link: New Titanium “Metamaterial” Has Supernatural Strength