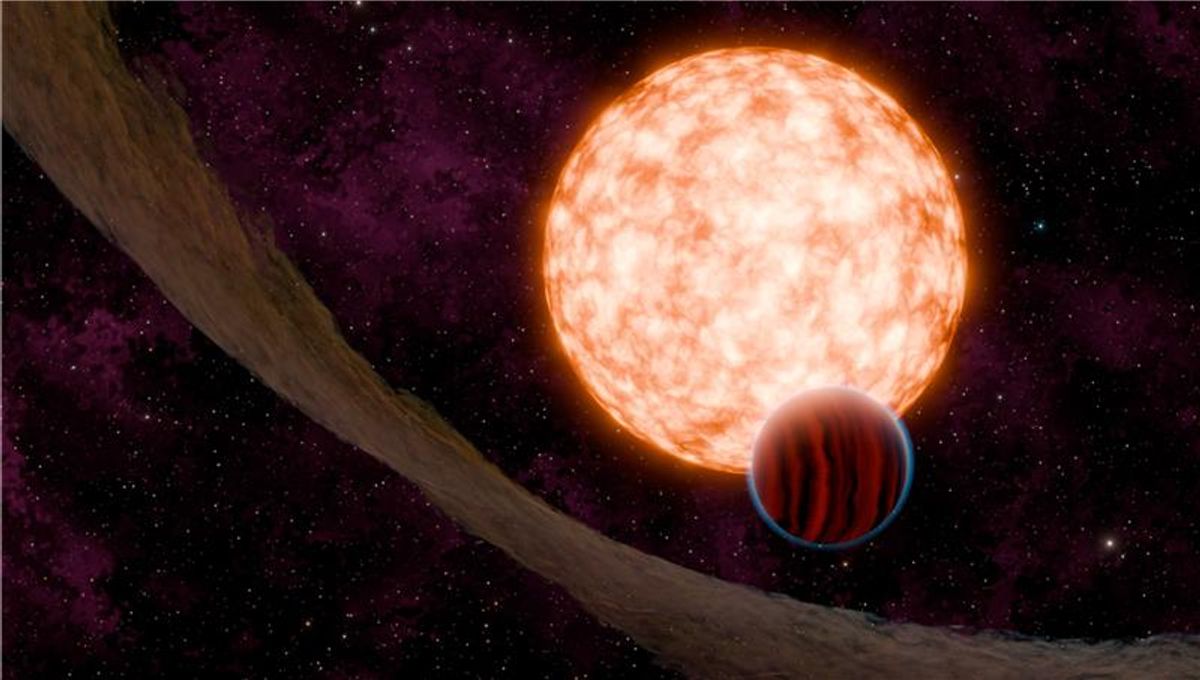
A planet has been found orbiting a three-million-year-old star. Better still, it transits across the star’s face from our perspective, offering opportunities to see the starlight passing through the planet’s atmosphere. The star is three times younger than any other previously observed to have a transiting planet – and since planets are thought to form after their star, the planet is almost certainly younger still.
Several methods have been used to find planets, but spotting them in transit is the most useful. From the start, we learn the planet’s size and orbital period, and this can be combined with other methods of detection that provide its mass, creating a fuller picture than is available for planets found in other ways. Moreover, when a planet transits, there is the potential to observe changes the parent star’s light undergoes as it passes through the planet’s atmosphere, revealing its composition. Although we’re only able to perform atmospheric analysis with a minority of transiting planets so far, and even then at great expense, opportunities are expected to grow.
The most popular reason to study the atmospheres of planets beyond the Solar System is to look for Earth counterparts that might support life. However, observing very young planets’ atmospheres – even those that are very un-Earth-like – could be a scientific bonanza, giving us insight into planetary formation unavailable in other ways.
In this context, the discovery of IRAS 04125+2902 b is a big step forward. IRAS 04125+2902 is a modestly-sized star, with a mass about 70 percent of the Sun’s but more significantly it is just 3.3 million years old, having formed out of the Taurus Molecular Cloud.
Previous young stars with transiting planets have been in the 10– to 40-million-year-old range, leading to questions about whether planets even form within the first 10 million years of a star’s life. That’s not necessarily the only reason very young planets have been absent from among the several thousand we have now found. Young stars are surrounded by protoplanetary disks, whose outer parts persist even after the first planets form. These usually get in the way of spotting transiting planets.
However, some disks get warped or broken, giving us a chance to spot new planets, and that has been seized for IRAS 04125+2902 b.
The planet has a radius 4 percent smaller than Jupiter’s, making it 10.7 times as wide as the Earth, leaving aside questions like whether it shares Jupiter’s polar flattening. Despite being almost as big as Jupiter, its density is much lower, and it has at most 30 percent of our local giant planet’s mass. Over time it is likely to contract and end up smaller than Saturn, and maybe even Neptune.
With a period of just 8.83 days, IRAS 04125+2902 b will already be receiving plenty of heat, despite orbiting a low-mass star, and that will increase as the star moves through its life. Then again, it is likely to be already very hot from the gravitational collapse that has been the main way we have spotted very young planets previously.
An intriguing aspect of the IRAS 04125+2902 system is that the outer disk is at a 30-degree angle to our line of sight, and therefore to the plane of IRAS 04125+2902 b’s orbit. This angling is what allows us to see IRAS 04125+2902 b’s silhouette as it passes in front of its star, but the reason for it is a mystery. Companion stars might be expected to cause outer disks and inner planets to not be in the same plane, but while IRAS 04125+2902 has a companion, it’s in the same plane as the planet (and IRAS 04125+2902’s equator) so the misalignment is mysterious.
All the planets of similar age we have found previously have been very different. These have been objects so massive they approach the boundary between planets and brown dwarfs. They have also been in very wide orbits around their stars, which combined with their remnant heat from formation, has allowed us to spot them directly. Some possible planets have been found around similarly aged stars using the radial velocity method, but not only do we have no chance to learn much about these, even their existence is still disputed.
The IRAS 04125+2902 system is about 521 light years away, so while hardly a near neighbor, it is still closer than most planets we have found and offers opportunities for further observations.
The study is published in the journal Nature.
Source Link: Newly Discovered Transiting Exoplanet Is The Youngest Ever Found At Under 3 Million Years Old