It’s no secret that Earth is facing an ecological crisis. For example, global wildlife populations have plummeted by 69 percent since 1970. It’s a big problem faced by the global population – but it can be easy to feel powerless when it’s often the few creating emissions, run-off, and pollution that far outweighs that of the many. However, we can all play a part, big or small, in supporting biodiversity in our local area – especially if you have a garden.
A garden is a privilege that not everyone has access to, which is why if you’re fortunate enough to have one, or even a spit of outdoor space to play with, it’s imperative that you join the fight for biodiversity. Zoologist, author, and Prehistoric Planet lead consultant Dr Darren Naish recently shared some tips from his experience creating a wildlife-friendly garden on Twitter. As his success demonstrates, creating a garden that supports biodiversity is often the path of least resistance, letting it go wild in a way that’s aesthetically pleasing and rich in variety.
1 – “Give up on the idea that ‘weeds’ = bad.”
Some gardeners will tell you there’s no such thing as a weed. To quote Ralph Waldo Emerson, “What is a weed? A plant whose virtues have not yet been discovered.” However, we’re already pretty clued up on the many ways plants that are considered “weeds” can benefit biodiversity.
Many “weed” species are great for pollinators, and studies have shown that allowing them to grow can even increase fruit yield in agriculture. Often the hardiest of plants, if you’re lacking any natural weeds in your garden, Naish recommends growing them in pots to green up paved garden areas.
2 – Ponds are crucial
Even the most modest of ponds in urban areas can act like “stepping stones” to facilitate the movement of species across the land. While they may boast less biodiversity compared to rural ponds, they’ve been found to act as a vital lifeline for threatened species.
While bigger ponds generally are better for biodiversity, a diversity of pond sizes is also beneficial, so there’s no shame in having a small one. As they say, it’s quality, not quantity – and you can bump your pond up the charts with varied margins (slopes of different angles), “messy surrounds” for crucial frog cover, and shallow margins for an easy exit.
3 – Standing water can be a good alternative, depending on where you live
Many insect species need water to complete their lifecycle. While some need fresh flowing water, others will very happily get to work with standing water of any kind. Here, Naish recommends using anything from plastic boxes to glass tanks – but with the important caveat that the suitability of this tip depends on where you live. If waterborne pests and diseases are a problem where you live, standing water may invite unwanted mosquitos, so it’s important to research this before opening up an accidental disease-vector creche.
4 – Make a replica swamp
A swamp might not sound like the ideal garden aesthetic, but as Naish demonstrated, it doesn’t take much to create an artificial swamp habitat that could be invaluable for boosting insect numbers. Just a few rotting twigs and leaves in standing water can make a big difference, but again, it’s important to think about if mosquitoes could be an issue.
5 – Let hedges grow
Topiary really did nature in when it came to the way humans deal with hedges. While we can all delight in a giant box topiary snail, the fact is that bigger and bushier is better when it comes to gardening for wildlife.
“I’ve been in trouble with the council for letting hedges over-grow, but we MUST move away from the idea that hedges need to be cropped, squared… or, worse, removed,” writes Naish. “Let hedges grow if you can.”
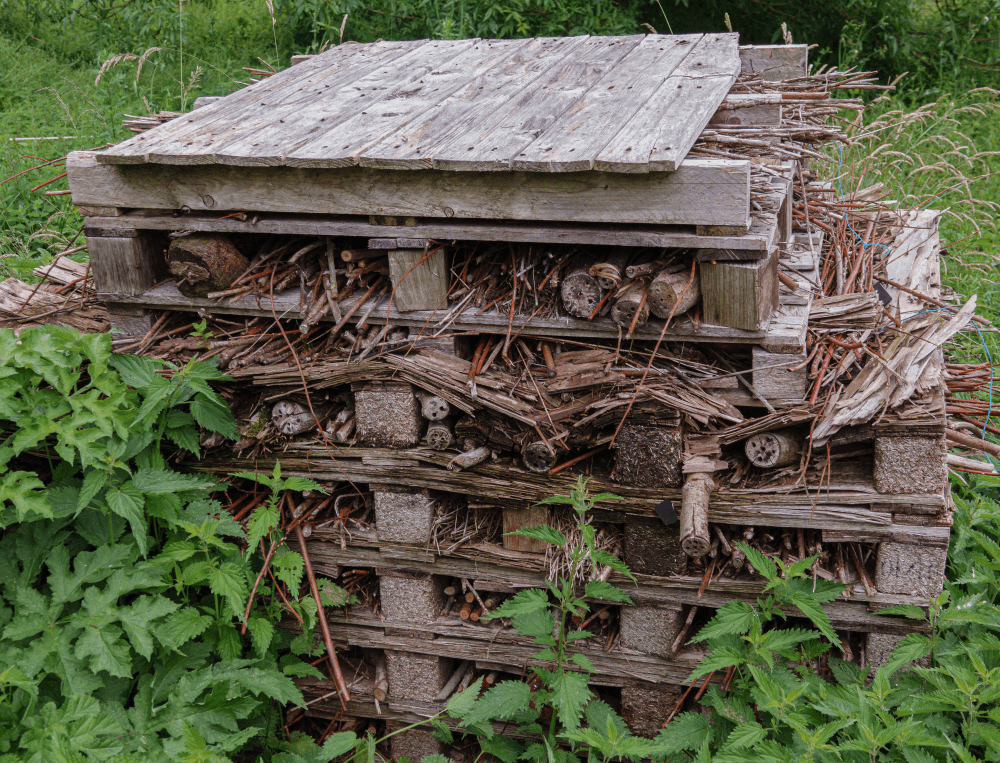
You don’t need a lavish bug hotel to attract a diverse range of insects.
Image credit: Martin Hibberd / Shutterstock.com
6 – Conserve water
Water is becoming a concern in parts of the globe where it was once taken for granted such as England where, despite being famous for its rain, wildfires have become increasingly common in recent years. Here, there was a fourfold increase in summer wildfires from 2021–2022.
You’ve got to get while the going is good, and by that, we mean when it’s raining. Water butts and buckets can be used to gather rainwater on drizzly days, meanwhile, domestic wastewater (sometimes called “grey water”) can also be used in the garden. According to the Royal Horticultural Society, “household soaps and detergents are harmless to plants, but water containing bleaches, disinfectants, dishwasher salt and stronger cleaning products should not be used.”
7 – Let “waste” areas go wild
Some people have a chip on their shoulder about tidiness, but when it comes to the garden there’s no harm in letting the unused corners, nooks, and crannies get a bit unkempt. Naish recommends moving away from putting green waste in landfill and instead using it to pile up sheltered areas in unused parts of the garden.
8 – Wildflowers: variety is the spice of life
A recent study found transforming a small lawn in King’s College, Cambridge, in England, into a wildflower meadow “supported approximately three times more plant species, three times more spider and bug species and individuals, and bats were recorded three times more often over the meadow than the remaining lawn.”
Rather than striving for the “picture-perfect” striped lawn, dedicate some patches to untamed bursts of color, texture, and variety. There are kits online that can effectively let off a grenade of pollinator potential, or you can find a guide to making your own here.
9 – Become a small part of a big change
Enough stepping stones can come together to form vital wildlife corridors that connect species threatened by habitat fragmentation and degradation. So if you have a little patch of ecosystem potential, see how many steps you can squeeze in to do your bit for biodiversity.
Source Link: Nine Easy Steps You Can Take To Support Biodiversity If You Have A Garden