An unusually tall, wide-hipped man who died 1,000 years ago in Portugal was the oldest known carrier of Klinefelter syndrome, a rare genetic condition in which males are born with an extra copy of the X chromosome. Describing the case in The Lancet, researchers say that this discovery could shed light on the prevalence of genetic disorders throughout human history.
Most humans carry 23 pairs of chromosomes, one of which encompasses the sex chromosomes, known as X and Y. Biological females are born with two X chromosomes while biological males have one X and one Y, resulting in a total of 46 chromosomes.
However, people with Klinefelter syndrome are born with what’s known as the 47,XXY karyotype, meaning they have two X chromosomes and one Y. Thought to affect around 0.1 percent of genetic males, the condition is associated with a number of physical characteristics, such as above-average height, wide hips, small testes, and gynaecomastia – otherwise known as “man boobs”.
People with Klinefelter syndrome also often have misaligned or protruding jaws as well as an increased risk of osteoporosis.
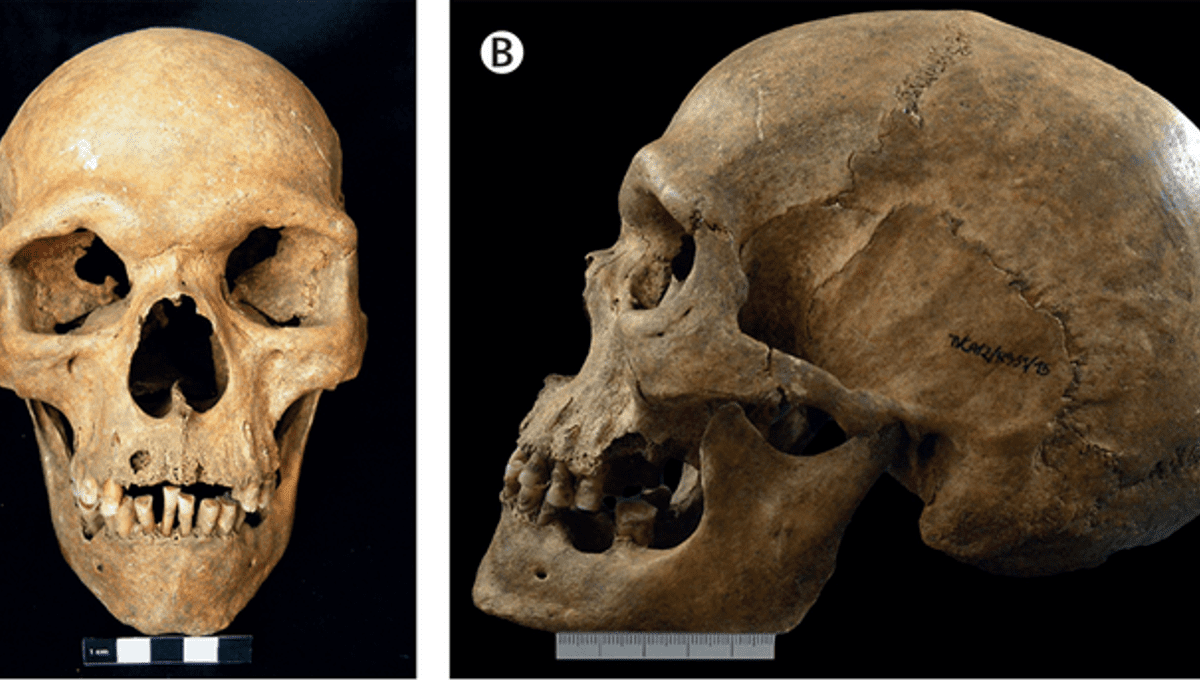
The study authors describe their specimen as “an outstandingly well preserved skeleton of an adult who was likely to have been more than 25 years old at the time of death.” A morphological analysis of the pelvis indicated that the deceased individual was male, while radiocarbon dating revealed that the bones had been buried in the 11th century.
Approximately 1.8 meters (5.9 feet) in height, the skeleton was the tallest of six examined by the researchers. The width of the man’s hips was measured at 289 millimeters (11.4 inches), which is considerably more than the average waistline of ancient Portuguese men.
Finally, the researchers note that the man’s teeth were asymmetrically worn, indicating that the jaw was probably misaligned, while the upper jawbone was protruding.
The study authors’ suspicions were then confirmed by a genetic analysis, which identified the 47,XXY karyotype.
“Considering the morphological findings – specifically the height, the bi-iliac width, the possible jaw malocclusion, and the maxillary prognathism – the genetic findings – indicating a karyotype of 47,XXY – we concluded that the studied individual had Klinefelter’s syndrome,” write the researchers.
Highlighting the significance of this finding, study author Dr João Teixeira explained in a statement that the research “shows the immense potential of combining different lines of evidence to study the human past, and the frequency of different health conditions through time.”
However, he insists that “while the study offers compelling evidence for the genetic history of Klinefelter Syndrome, no sociological implications can be drawn from this diagnostic.”
Source Link: Oldest Case Of Rare Genetic Condition That Sees Males With Extra X Chromosome Discovered