Our world is becoming increasingly salty and according to a new study, it’s all down to human activity. As a result of this saline shift, the chemistry of our rivers is being radically altered, impacting the quality of our water and affecting human health.
The planet has a natural “salt cycle” in which geologic and hydrologic processes, such as the weathering of rocks and minerals, bring salts to Earth’s surface over long periods of time.
However, in recent decades, humans have massively accelerated this cycle through mining and land development, unearthing salt and bringing it to the surface way faster than natural processes.
In turn, the concentration of salt ions has substantially increased in streams and rivers over the last 50 years, while human-caused salinization has impacted approximately 1 billion hectares (2.5 billion acres) of soil around the world.
“Twenty years ago, all we had were case studies. We could say surface waters were salty here in New York or in Baltimore’s drinking water supply. We now show that it’s a cycle—from the deep Earth to the atmosphere—that’s been significantly perturbed by human activities,” Gene Likens, study co-author and an ecologist at the University of Connecticut and the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies, said in a statement.
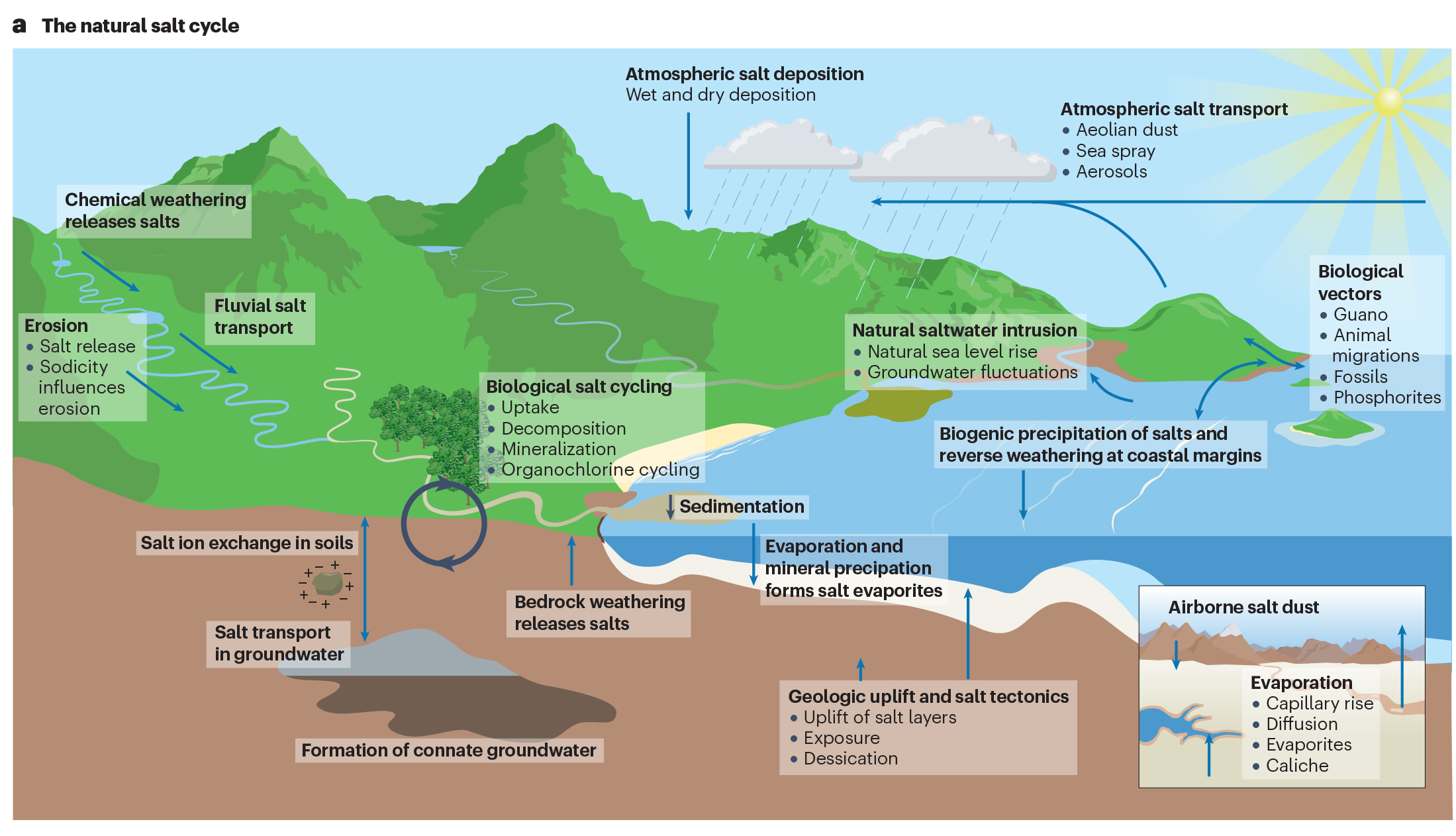
The natural salt cycle.
Image credit: S S Kaushal et al/Nature Reviews Earth & Environment 2023
When scientists talk about salt, they’re not just describing sodium chloride, the white stuff sprinkled on food. In the terminology of chemists and geologists, a salt is any chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
“When people think of salt, they tend to think of sodium chloride, but our work over the years has shown that we’ve disturbed other types of salts, including ones related to limestone, gypsum, and calcium sulfate,” added Professor Sujay Kaushal, lead author of the study.
The proliferation of salt is likely to have an array of detrimental impacts on the environment and human health. One of the chief concerns is water quality. Salt ions can bind to contaminants in soils and sediments, forming “chemical cocktails” that circulate in the environment and can end up in water supplies.
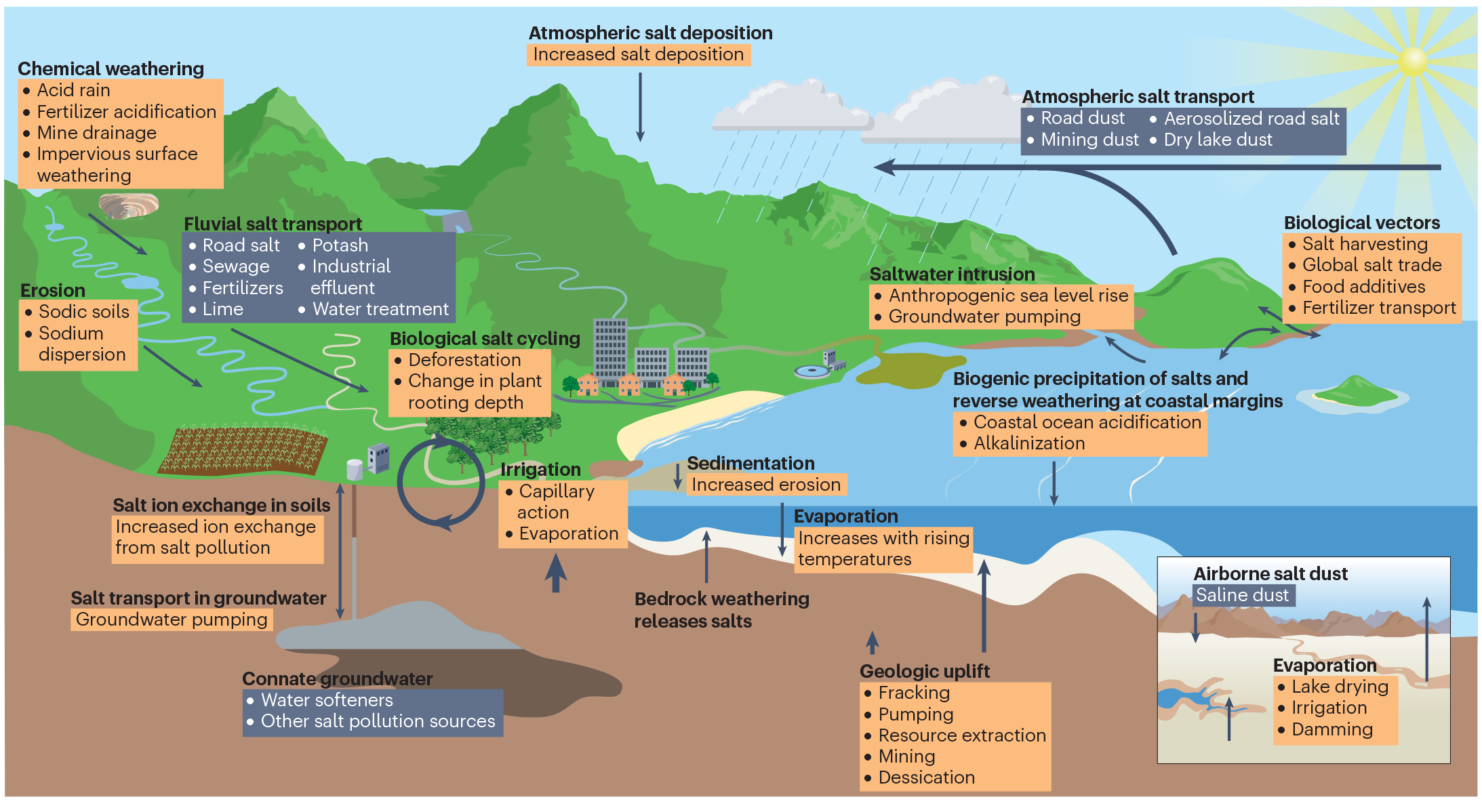
The anthropogenic salt cycle.
Image credit: S S Kaushal et al/Nature Reviews Earth & Environment 2023
Even the air isn’t safe from rapid salinization. When lakes dry up – an increasingly common reality due to climate change – it can kick up plumes of salty dust into the atmosphere. The researchers explain that this too is likely to have a negative impact on human health.
A major source of the problem is salt sprayed on icy roads during the cold months. In the US, this represents 44 percent of salt consumption and accounts for almost 14 percent of the dissolved solids that enter the country’s rivers.
Part of the solution might be to cut back on the amount of salt put on roads during the winter. However, as the researchers acknowledge, this runs the risk of increasing the number of road traffic accidents.
“There’s the short-term risk of injury, which is serious and something we certainly need to think about, but there’s also the long-term risk of health issues associated with too much salt in our water. It’s about finding the right balance,” Kaushal said.
“This is a very complex issue because salt is not considered a primary drinking water contaminant in the US, so to regulate it would be a big undertaking,” Kaushal added.
“But do I think it’s a substance that is increasing in the environment to harmful levels? Yes.”
The study is published in the journal Nature Reviews Earth & Environment.
Source Link: Our Planet Is Getting Saltier And That's Very Bad News