The Pineapple Express is a stream of moisture in the atmosphere that delivers humid air from the tropical Pacific to the West Coast of North America. If there’s heavy rain in California, Oregon, Washington, or British Columbia, there’s a good chance the Pineapple Express is at play.
Not to be confused with the 2008 stoner comedy film, the Pineapple Express is arguably the world’s most famous example of an atmospheric river, a flowing band of water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere that has a major impact on levels of rain and snow.
It’s estimated that up to 50 percent of the rain and snow on the US West Coast is delivered by atmospheric rivers, including the Pineapple Express.
What are atmospheric rivers?
In terms of water content, atmospheric rivers are technically the largest freshwater “rivers” on Earth. Atmospheric rivers over the Pacific can transport more water than seven to 15 Mississippi Rivers combined.
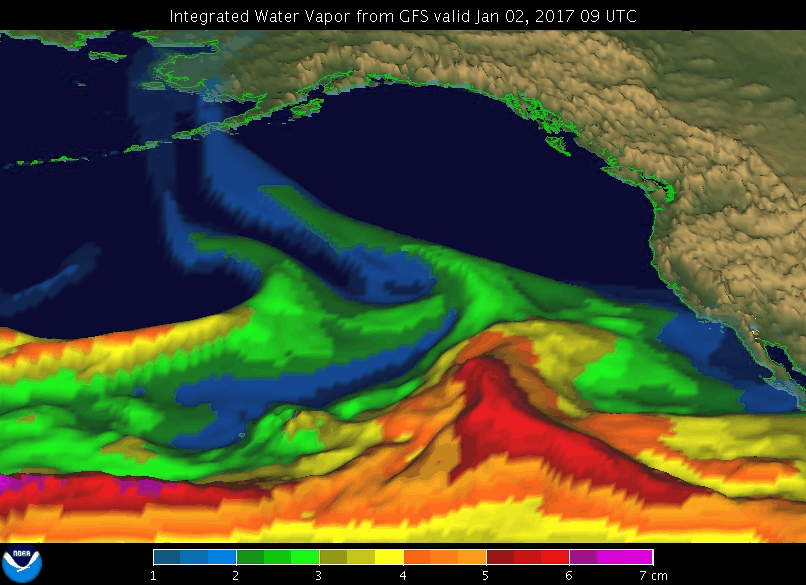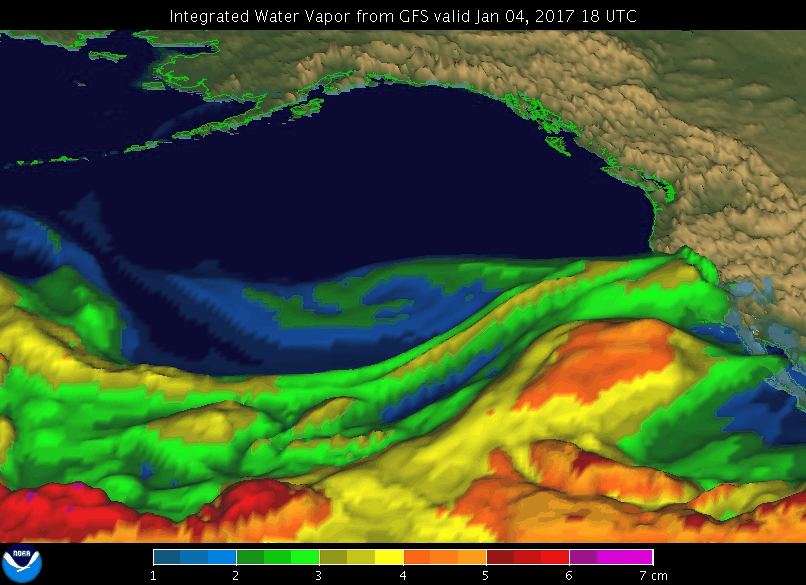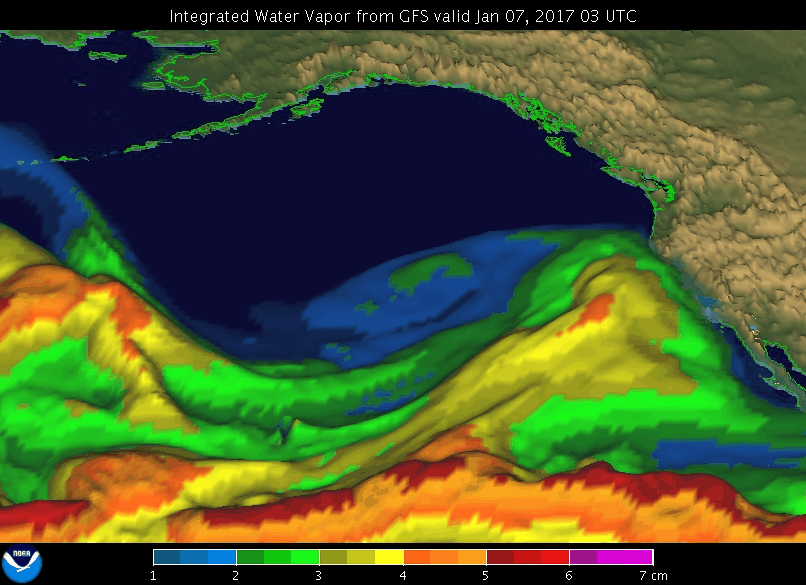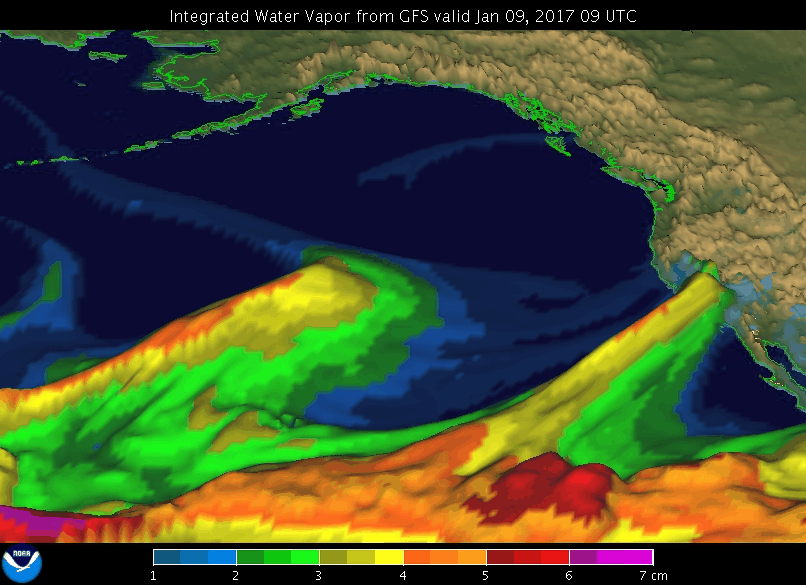
A GIF showing an atmospheric river event in January 2017 in the Pacific off the coast of North America.
Image credit: NOAA’s Earth System Research Laboratory
Where can you find atmospheric rivers?
They’re not just a North American phenomenon. Atmospheric rivers are estimated to deliver over half of the average annual runoff on the east and west coasts of North America, as well as France, northern Spain and Portugal, the UK, southeastern South America, southern Chile, Southeast Asia, and New Zealand.
Scientists have created a rating scale for atmospheric rivers based on their physical characteristics and the level of destruction they cause, a bit like the hurricane rating system. The researchers note that some of the strongest ones, rated AR-5, often strike coastal cities along the North Pacific and Atlantic, Southeast Pacific, and Southeast Atlantic, such as San Francisco and Lisbon.
Originally named Tropospheric Rivers, they first appeared in the scientific literature in 1992. They are sometimes referred to as “a river in the sky,” but one made of water vapor, instead of liquid water. However, some scientists aren’t totally on board with this description because it’s not literally a river, it’s a region of enhanced water vapor transport.
Whatever you call them, this weather phenomenon has the potential to cause real havoc. With the help of wider El Niño conditions, the Pineapple Express contributed to fueling a string of storms that led to severe flooding in California in January 2024, just as it had done the previous winter.
How are atmospheric rivers changing?
Atmospheric rivers are being influenced by our rapidly changing world. A recent study found that atmospheric rivers in both hemispheres have moved approximately 6° to 10° closer to the poles over the past 40 years. In other words, areas affected by atmospheric rivers are farther north in the Northern Hemisphere and farther south in the Southern Hemisphere than they used to be.
The researchers explain that an underlying cause of the shift is cooling in the eastern tropical Pacific over the past four decades, although they note that the chain of events “remains to be fully explored.”
Source Link: Pineapple Express: An Atmospheric River That Feeds Rain To The US West Coast