Besides having an orbit that could cause it to hit Earth far in the future, asteroid 3200 Phaethon is primarily known for having that most unasteroid-like thing, a tail. Astronomers initially thought the tail was dust blasted off the surface by the extreme heat Phaethon experiences, but experimental evidence now supports an alternative hypothesis, that sodium gas leaks out from deep inside.
Comets have tails, asteroids don’t, or so we thought. However, nature has a way of subverting binaries. We now know even Mercury – certainly no comet – has a tail, and so does 3200 Phaethon, which has a rocky composition nothing like an icy comet.
The accepted explanation for Phaethon’s tail is that its close approaches to the Sun heat the surface to such high temperatures that dust is burned off. However, a new paper reveals the tail is made of sodium gas instead.
“Our analysis shows that Pheathon’s comet-like activity cannot be explained by any kind of dust,” said California Institute of Technology graduate student Qicheng Zhang in a statement. This means we need another explanation for Phaethon’s third curious feature: its status as the only asteroid known to be responsible for a meteor shower.
Comets are “dirty snowballs” composed of a mix of ice, rock, and dust. On approach to the Sun, the ice turns to gas, which the solar wind pushes away from the Sun, carrying some of the dust with it.
Main belt asteroids such as Ceres can have ice, but don’t get close enough to the Sun for it to melt. Those on closer orbits either never had any ice, or lost it long ago, leaving nothing to make tails. When NASA’s Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) spotted something pointing away from the Sun as Phaethon passed its perihelion (closest approach to Sun) in 2009 it created a mystery. Observations are hindered by a perihelion around 40 percent of Mercury’s average distance from the Sun, so the expectation this was dust went untested.
Zhang decided to test a theoretical suggestion of sodium as the cause of Phaethon’s tail. “Comets often glow brilliantly by sodium emission when very near the Sun, so we suspected sodium could likewise serve a key role in Phaethon’s brightening,” Zhang said.
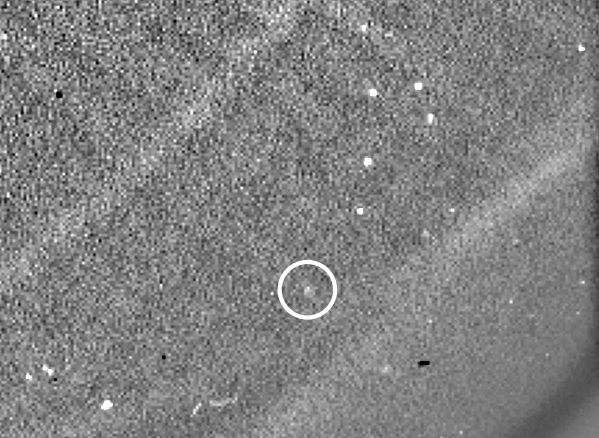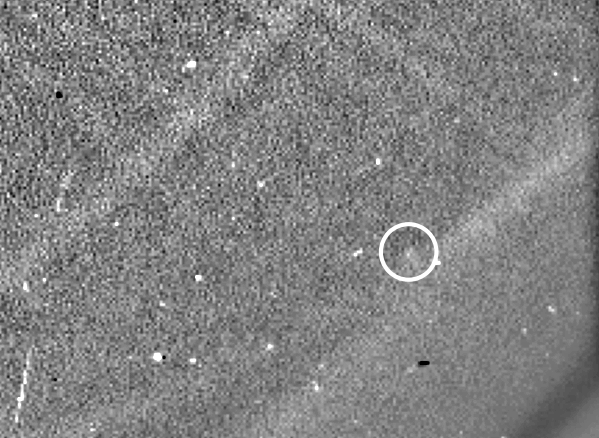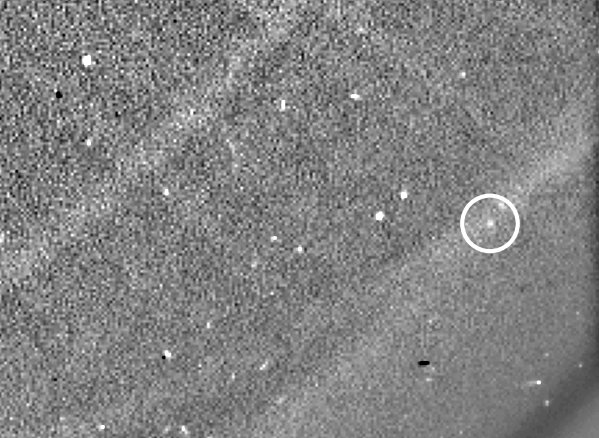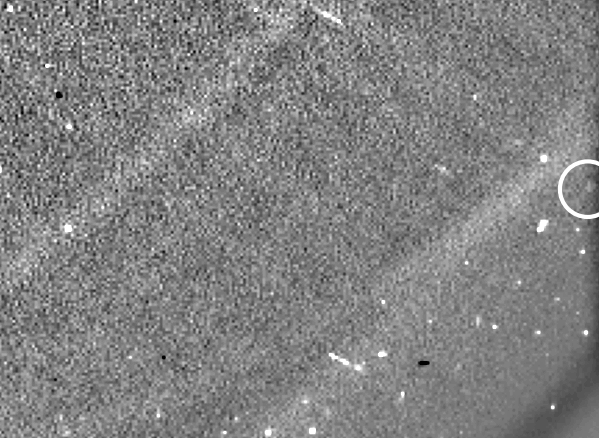
Two hours of Phaethon’s movements near its closest approach to the Sun. Look closely and you can see the tailImage Credit: ESA/NASA/USNRL/Karl Battams
Taking the NASA/ESA Solar and Heliosphere Observatory (SOHO) away from its normal solar observations, Zhang and co-authors used filters to observe Phaethon near perihelion at different wavelengths. The tail is bright in the wavelengths associated with sodium, and invisible in those used to detect dust. Its curve under pressure from the solar wind also indicates gaseous, not dusty composition.
Co-author Dr Karl Battams of the Naval Research Laboratory celebrated the fact “We did this using two heliophysics spacecraft – SOHO and STEREO – that were not at all intended to study phenomena like this.”
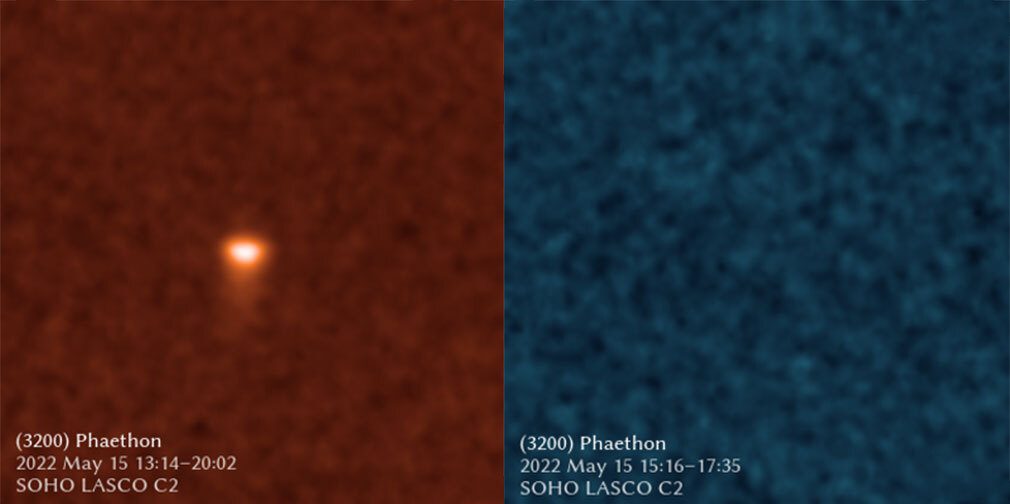

Phaethon studied with two filters, one for sodium light and another for dust.Image Credit: ESA/NASA/Qicheng Zhang
The sodium hypothesis proposed that sodium boils deep inside Phaethon as the asteroid heats up, eventually escaping through deep cracks. The authors now wonder if Phaethon is unique, or if some other objects, designated as comets, are really showing the same behavior. The sungrazing comet C/2012 S1 brightened dramatically during a close approach and almost all the brightness was at sodium wavelengths.
Most meteor showers are the result of dust and slightly larger debris left behind by comets. The Earth plows into these on specific dates each year. Showers are matched to comets through their shared orbits, and the Geminids’ orbit is too much like Phaethon’s to be a coincidence.
Nevertheless, it is very strange that an asteroid is responsible not just for a meteor shower, but for one of the most active showers of the year. The mystery deepened in 2018 when the Parker Solar Probe demonstrated Phaethon’s solar approaches couldn’t account for the more than 10 million tonnes per orbit of material required to explain the Geminids.
The authors propose the Geminids must result from something catastrophic – a chunk of Phaethon breaking away and then breaking up, perhaps after a collision with a smaller object. If so, they think this must have happened in the last 10,000 years, and might have been visible from Earth.
The work does not, however, explain Phaethon’s recent changes in spin, nor the extreme polarization of the light it reflects. Perhaps we will have to wait for the DESTINY+ mission to visit Phaethon in 2028.
The study is open access in The Planetary Science Journal
Source Link: "Potentially Hazardous" Asteroid Phaethon's Curious Tail Isn’t What We Thought